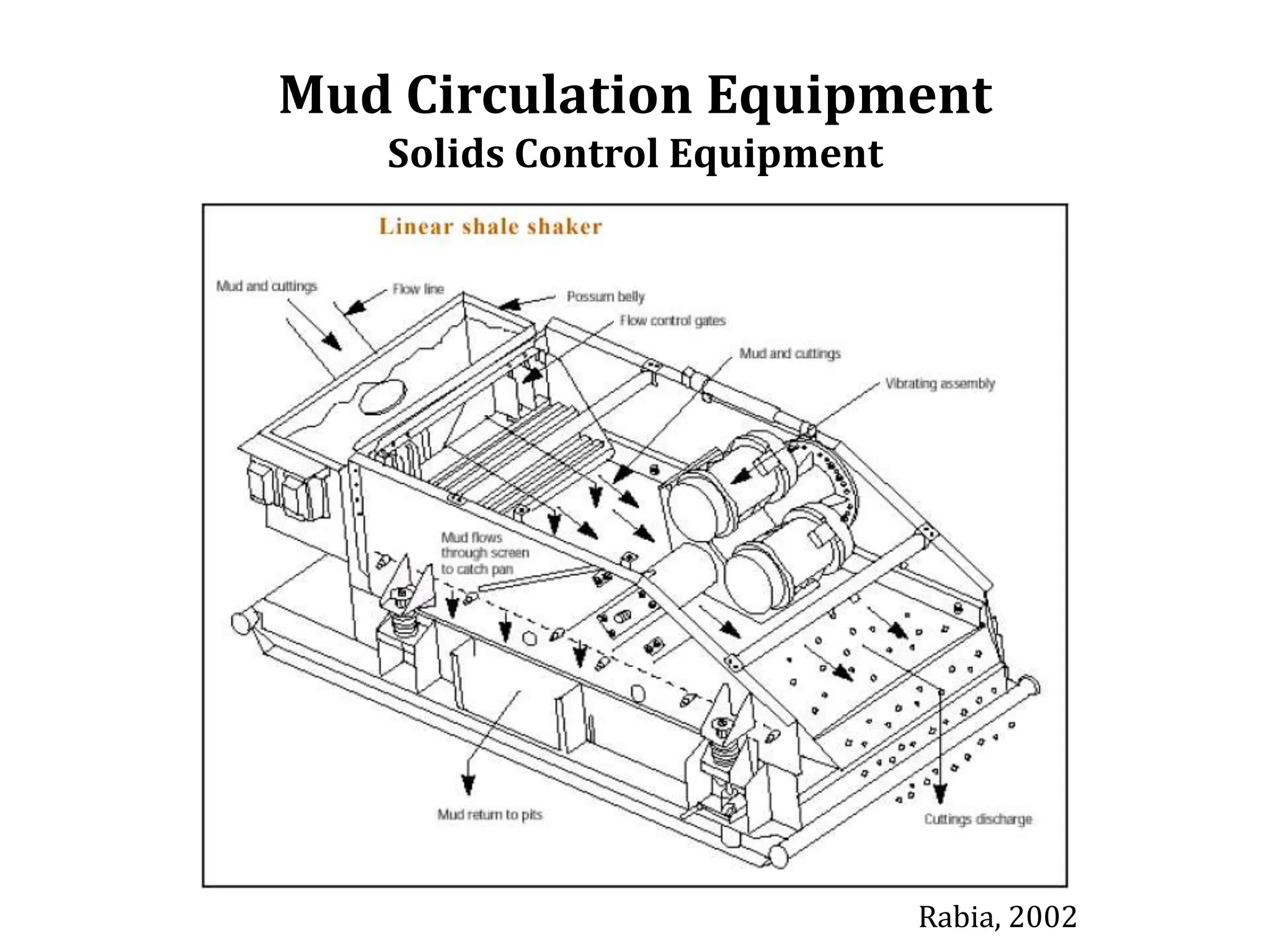
Mud circulation systems aim to retain desirable mud components by separating out solids and contaminants. There are four stages to remove solids from mud: 1) Screen separation using shale shakers and screens to remove up to 80% of solids, 2) Settling separation in non-stirred pits where heavy solids settle out, 3) Removing gas using vacuum degassers, 4) Forced settling using centrifugal devices like desanders and desilters that separate solids from mud using centrifugal forces. Proper solids control equipment and operation are needed to maintain an efficient mud system.