This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence and machine learning concepts. It discusses different types of machine learning including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. It also describes various machine learning algorithms like decision trees, Bayesian classifiers, artificial neural networks, and how they can be applied to problems like spam filtering, product recommendations, and price prediction. Finally, it lists several resources for learning more about AI/ML including books, online courses, code libraries, and datasets.







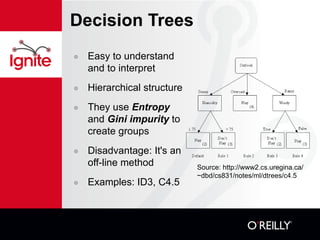
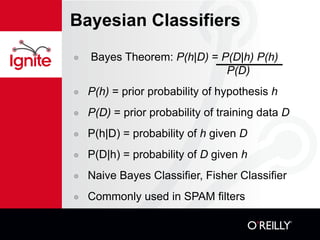
![Decision Trees, example Create .names and .data files with training data Generate tree and rules (c4.5 -f <file> and c4.5rules -f <file>) Outlook Temperature Humidity Windy Play or Don't Play Sunny 80 90 true Don't Play Overcast 83 78 false Play Rain 70 96 false Play Categorize new data (consult,consultr). Use GPS/Geocoding, Google Maps and Yahoo Weather APIs to enhance aservin@turin:~/Projects/C45: consult -f golf C4.5 [release 8] decision tree interpreter Sat Jan 17 00:05:16 2009 ------------------------------------------ outlook: sunny humidity: 80 Decision: Don't Play CF = 1.00 [ 0.63 - 1.00 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-practicalai-111019130223-phpapp02/85/Practical-Artificial-Intelligence-Machine-Learning-Arturo-Servin-11-320.jpg)