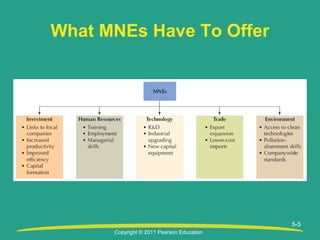
This document is from a chapter about globalization and its impact on society. The chapter objectives are to evaluate the economic effects of multinational enterprises on home and host countries, discuss responsible corporate behavior, and examine issues around the social impacts of globalized business. It discusses topics like the impact of foreign direct investment, ethics and bribery, environmental sustainability, labor conditions, and developing corporate codes of ethics.