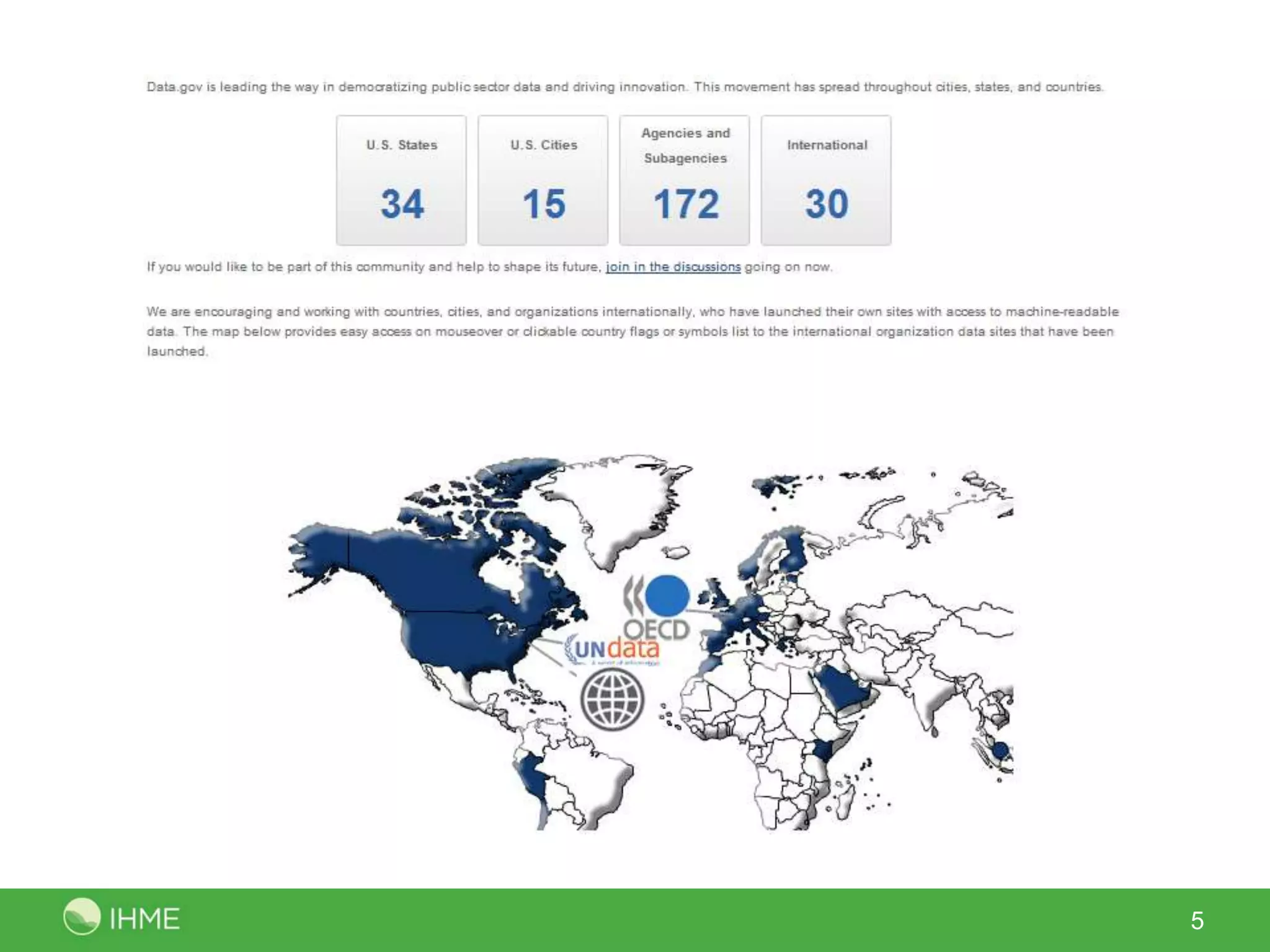
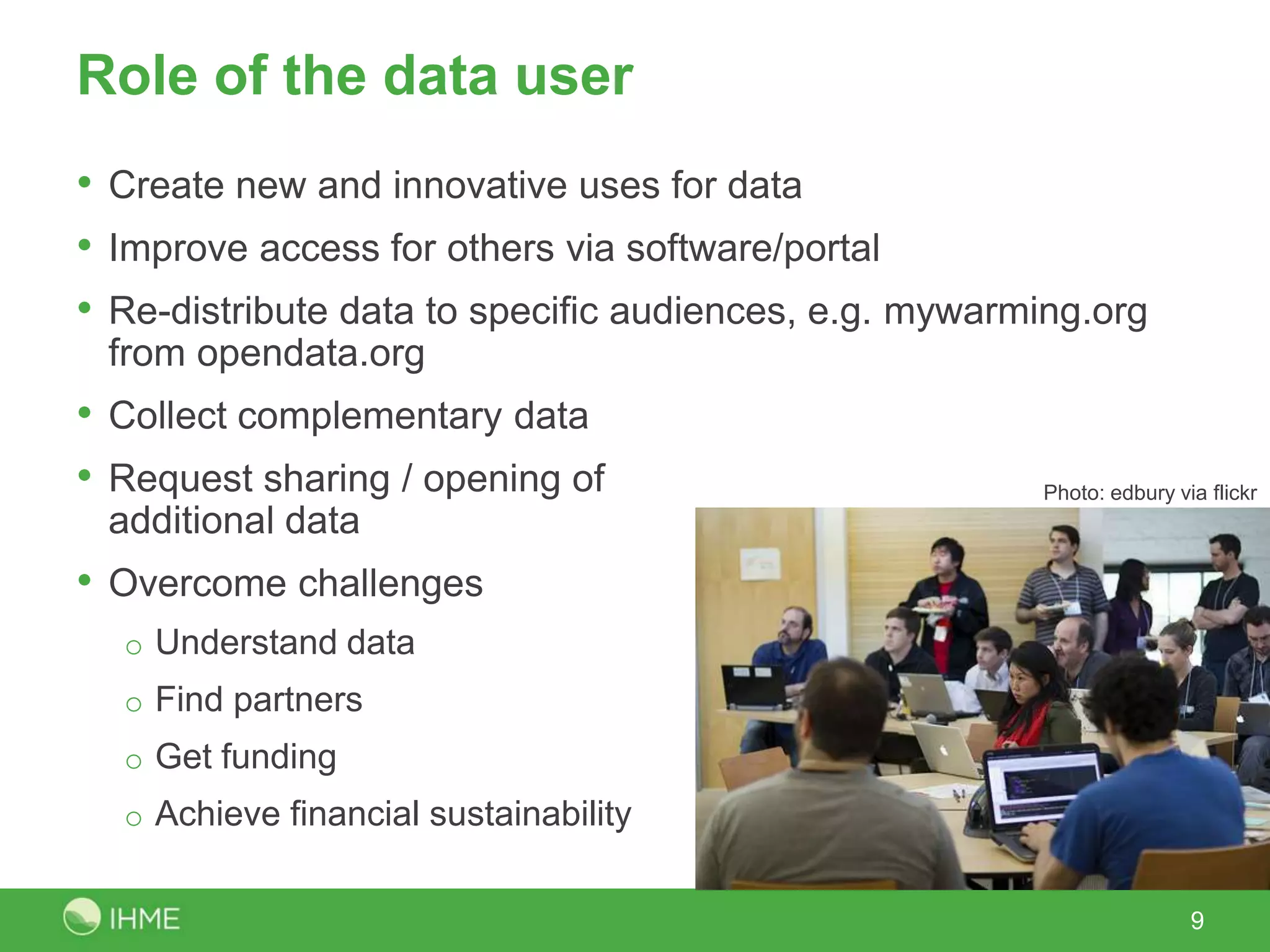
The International Open Government Data Conference in 2012 gathered 400 participants from 50 countries to discuss the potential and challenges of open government data. The event emphasized the importance of creating an ecosystem around data availability, focusing on improved public service, accountability, and economic opportunities. Key takeaways included the need for broader involvement of stakeholders and a shift from just publishing data to encouraging its innovative use.