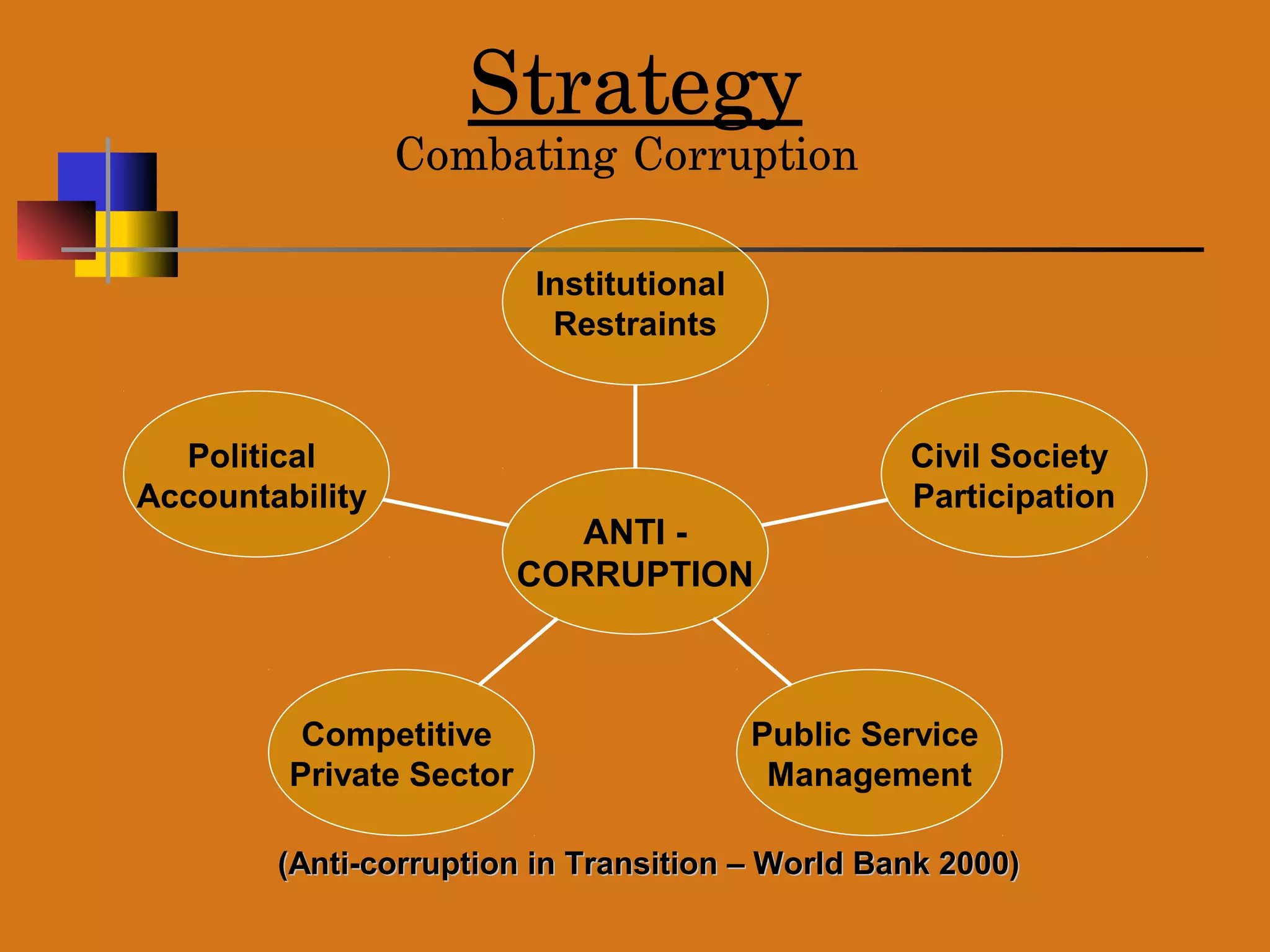
This document outlines India's strategy to combat corruption in public services. It discusses that corruption is a major impediment to good governance. The strategy involves establishing institutional restraints like an independent judiciary, increasing political accountability through transparency laws, encouraging civil society participation through right to information acts, promoting a competitive private sector through economic reforms, and improving public service management. It details India's legal and institutional frameworks against corruption and its action plan to prevent, detect, and punish corruption through methods like citizens' charters, empowering civil servants, and the right to information act.