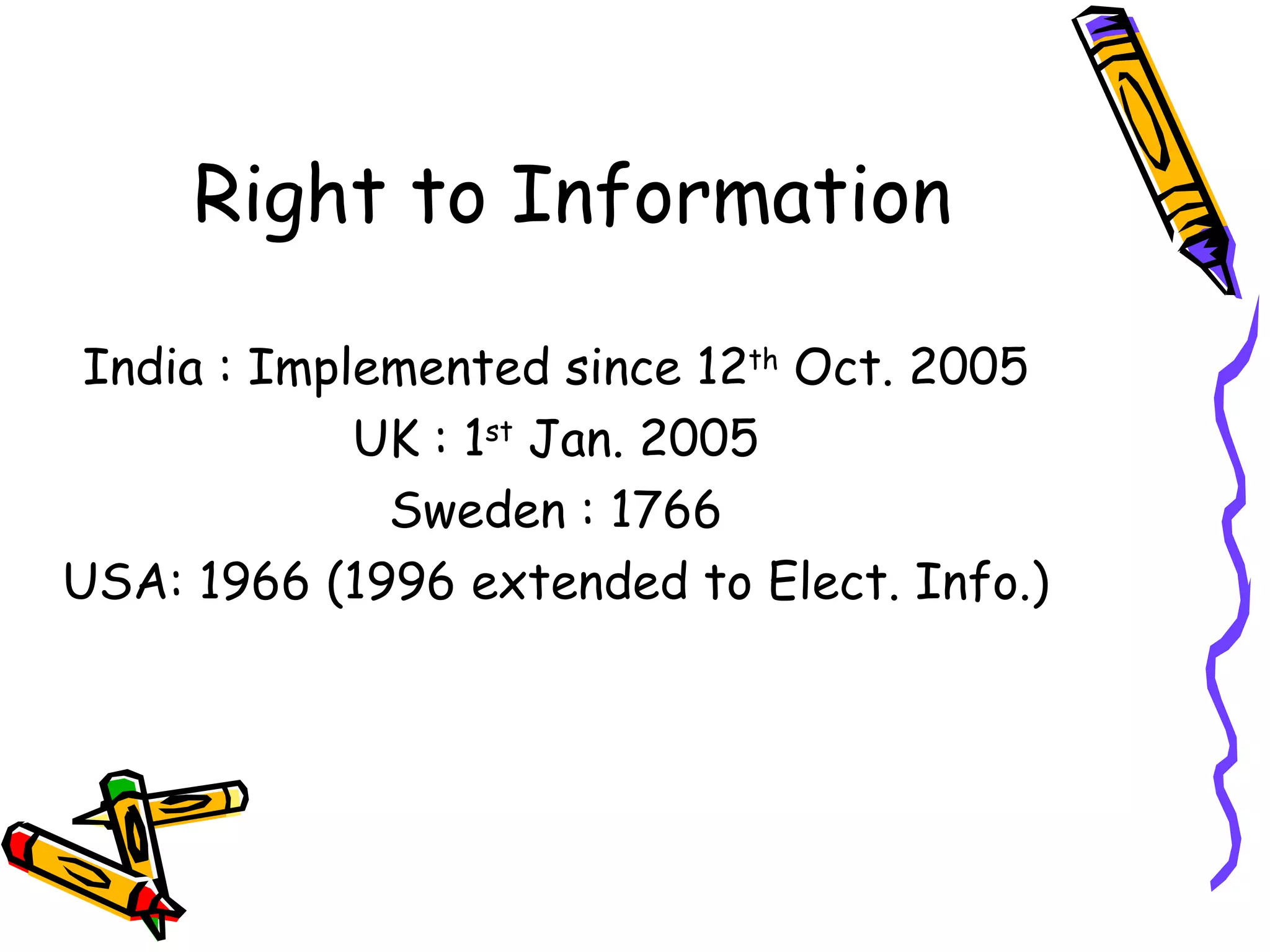
The document summarizes the Right to Information Act passed by the Government of India in 2005. Some key points:
- The Act empowers citizens to seek and obtain information from public authorities and introduces mechanisms of transparency and accountability in government.
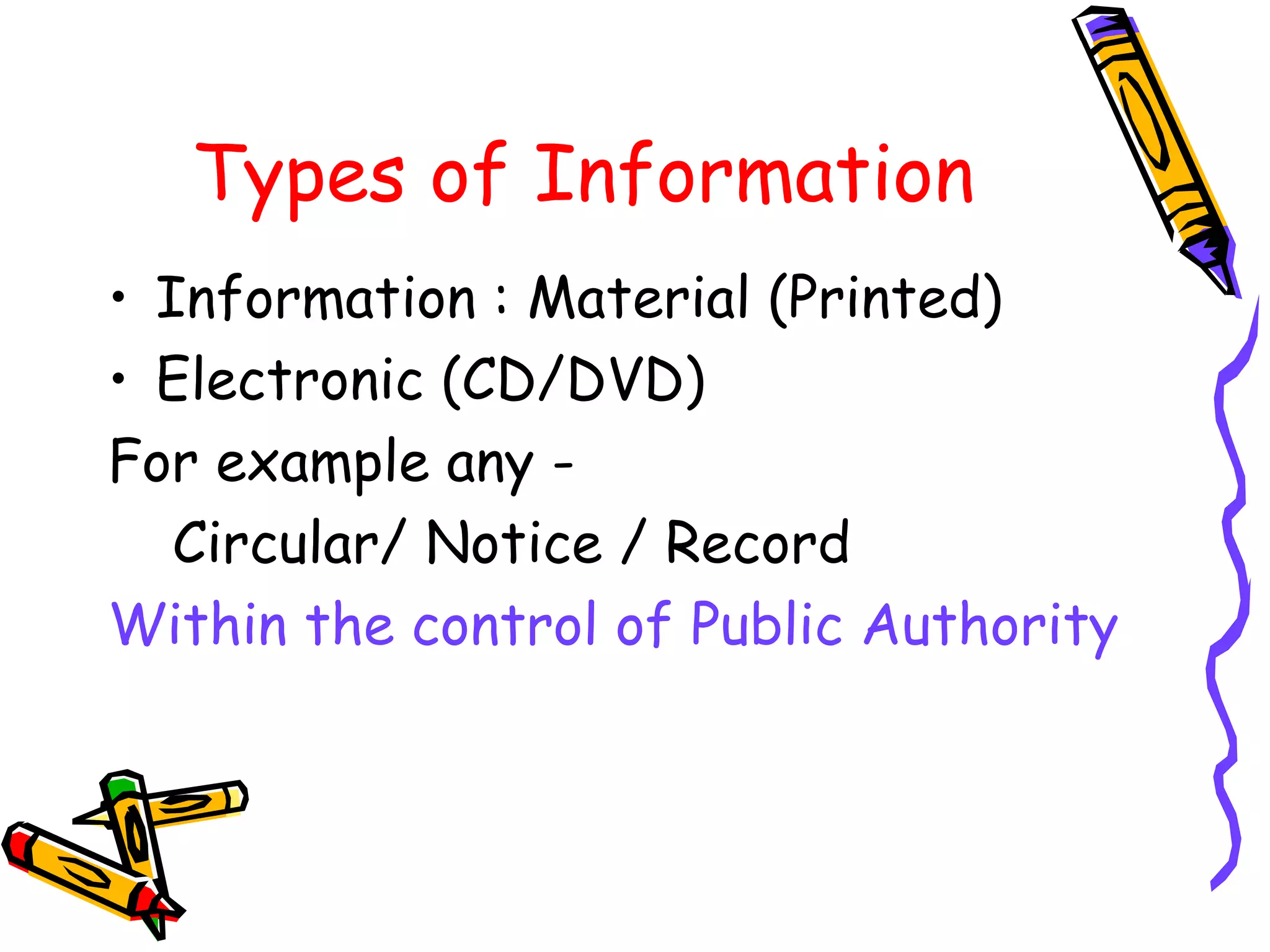
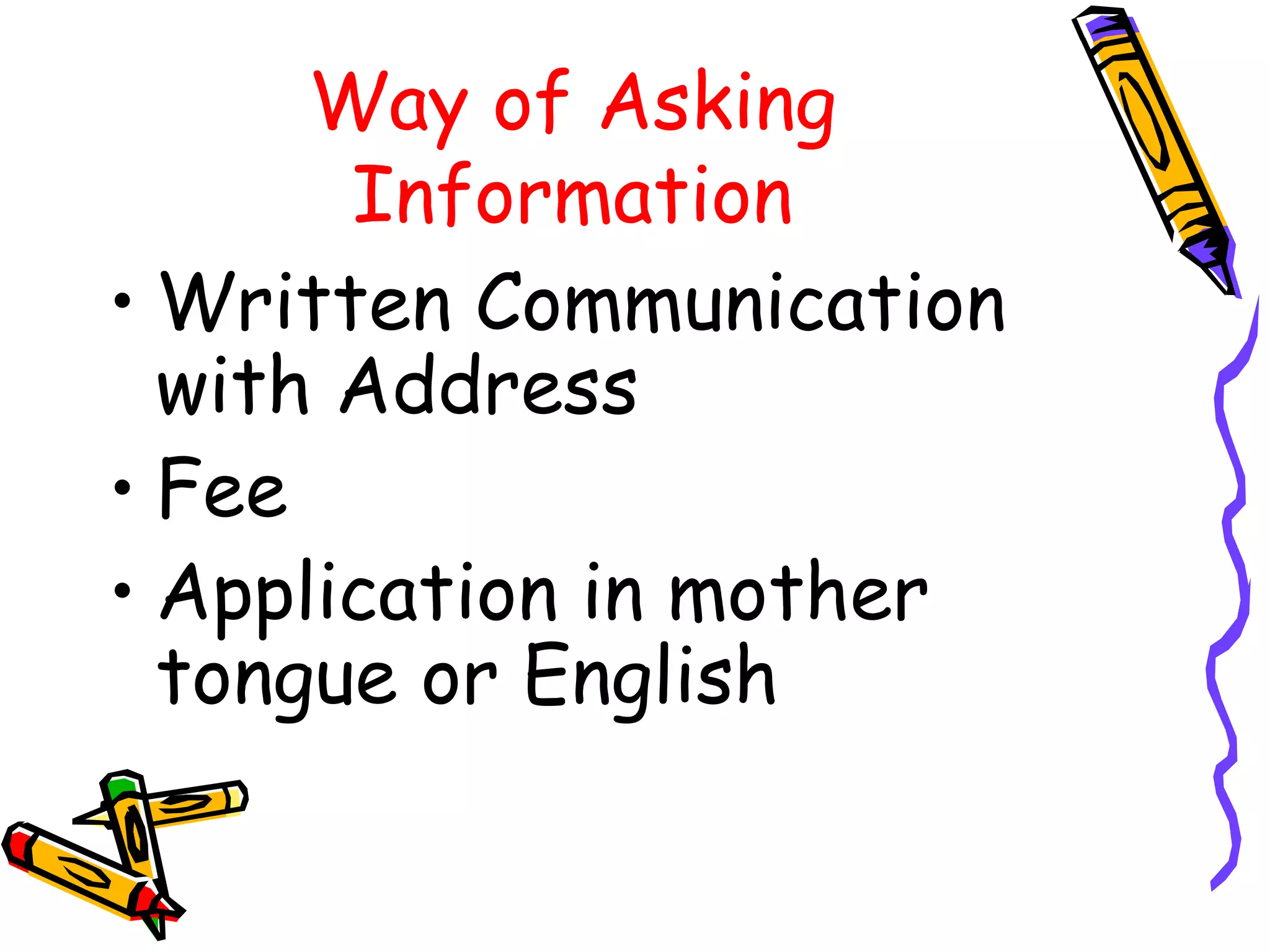
- Under the Act, citizens can request information from public authorities in writing or verbally in their local language within defined time periods. Authorities must provide information in the requested format within 30-48 days.
- There are provisions for fees for applications and penalties for non-compliance by authorities. Certain information related to sovereignty, security, and individual privacy is exempt.
- The Act aims to promote transparency and prevent corruption through a practical regime for citizens to access information






![Freedom of expression encompasses the freedom of speech and the corollary right to receive information. [Indian Constitution, article19,(1)a] Libraries and Librarians protect and promote these rights by selecting, producing, providing access to, identifying, organizing, providing instruction in the use of, and preserving recorded expression regardless of the format or technology.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/righttoinformationactbyvivekanandjain-111024004059-phpapp02/75/Right-to-information-act-by-vivekanand-jain-8-2048.jpg)














![For more information - Vivekanand Jain Deputy Librarian Central Library Banaras Hindu University Varanasi – 221005 India Email : [email_address] Ph. 0542-2367133/ 94505 38093](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/righttoinformationactbyvivekanandjain-111024004059-phpapp02/75/Right-to-information-act-by-vivekanand-jain-25-2048.jpg)