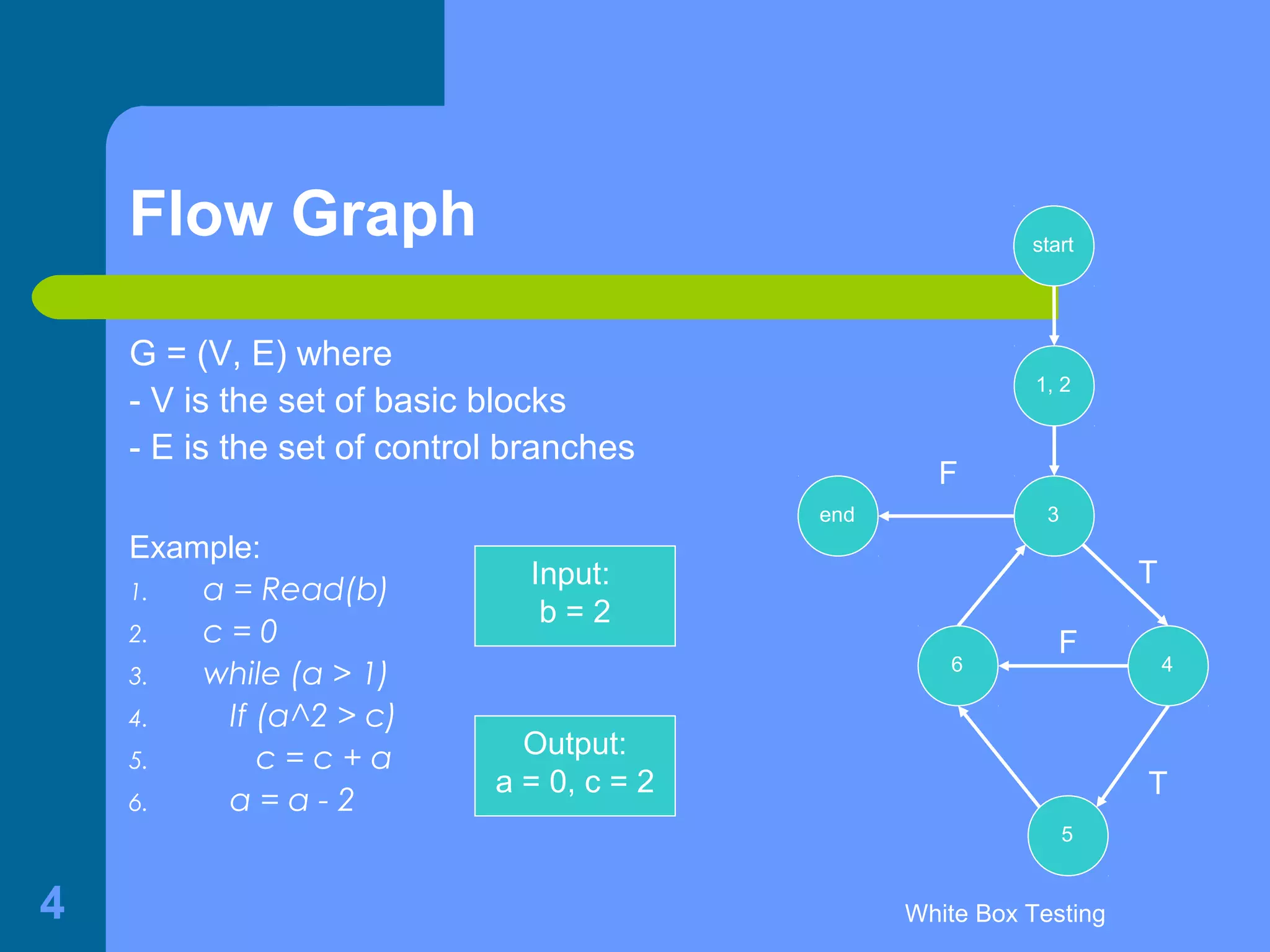
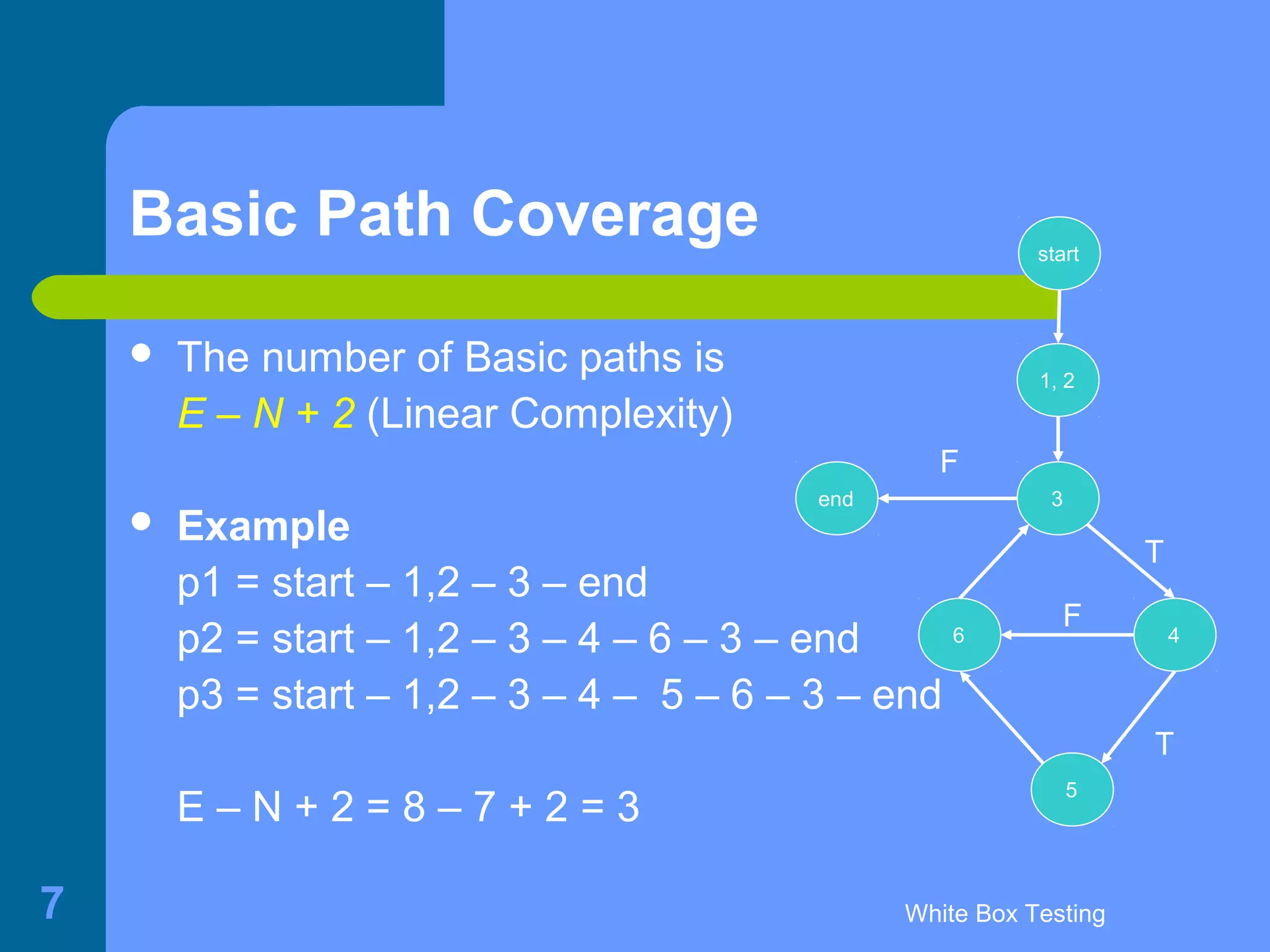
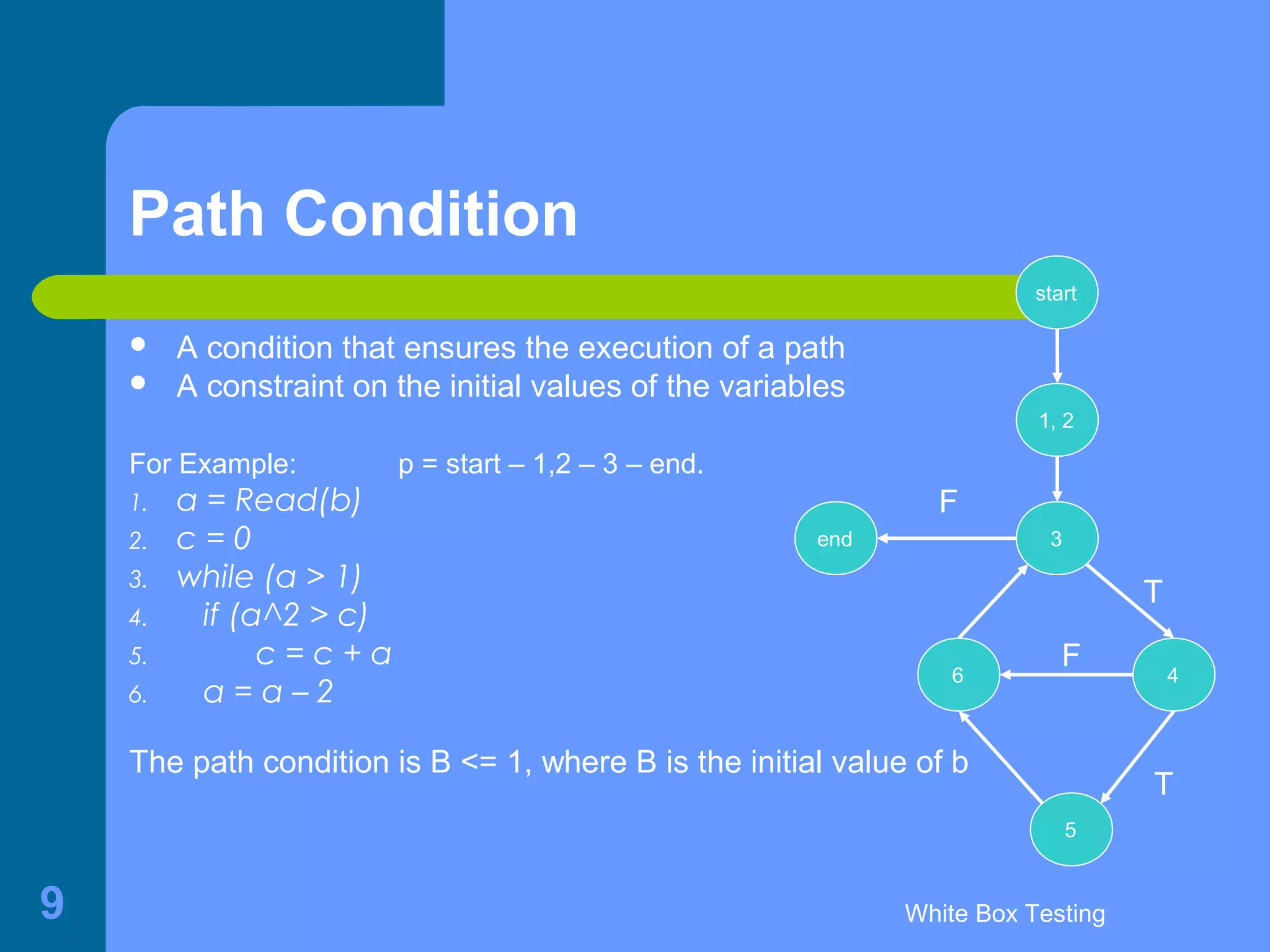
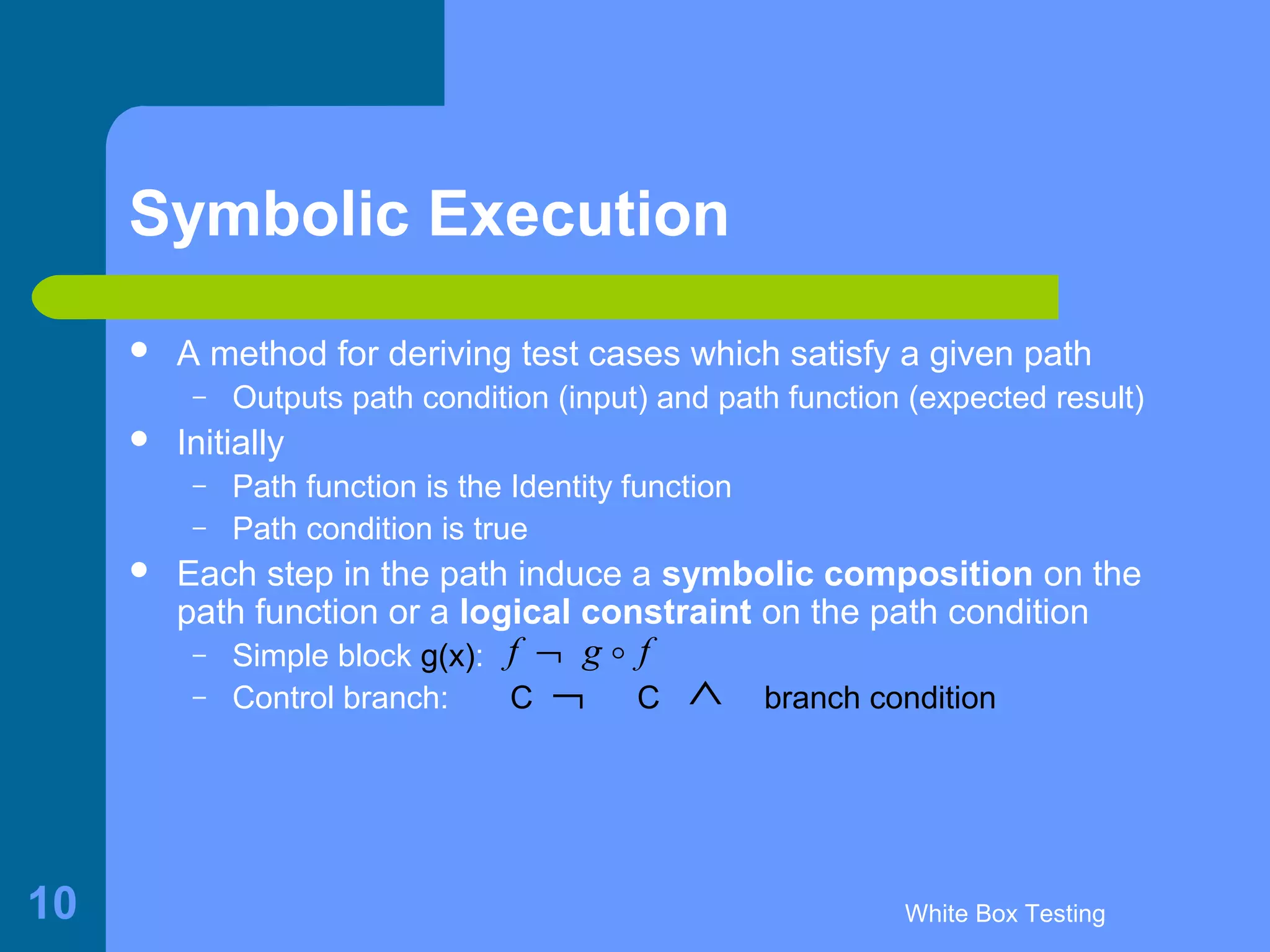
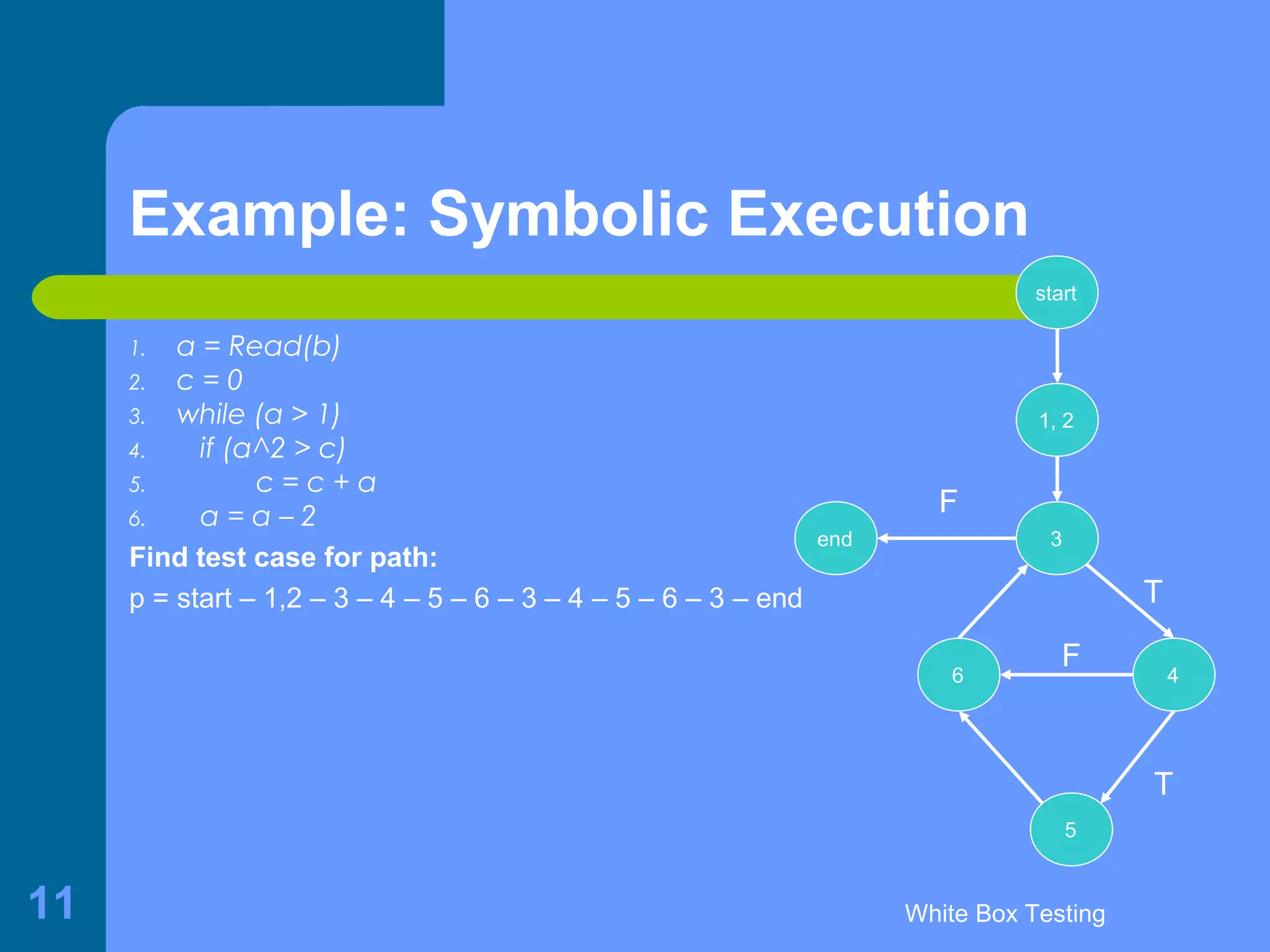
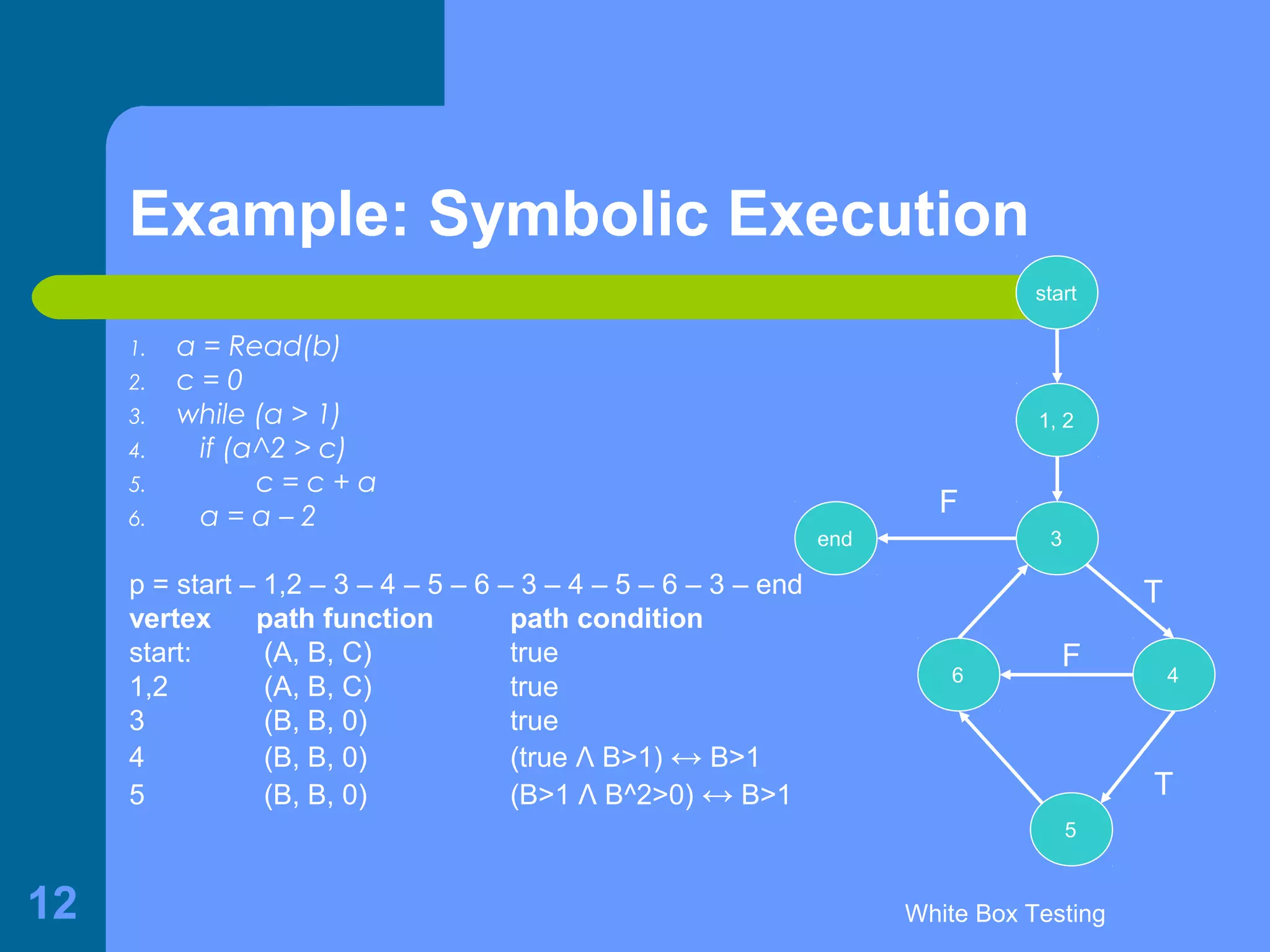
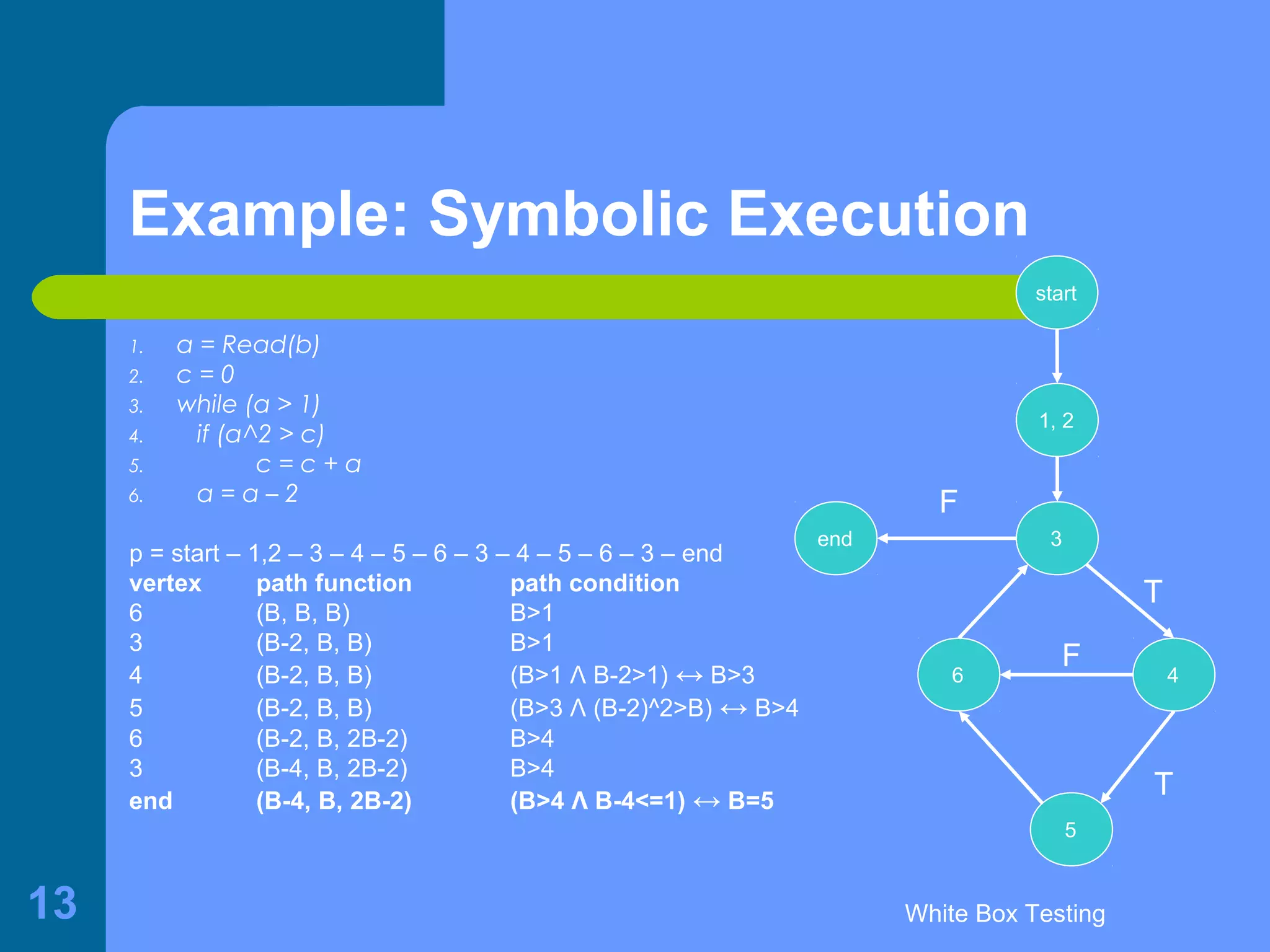
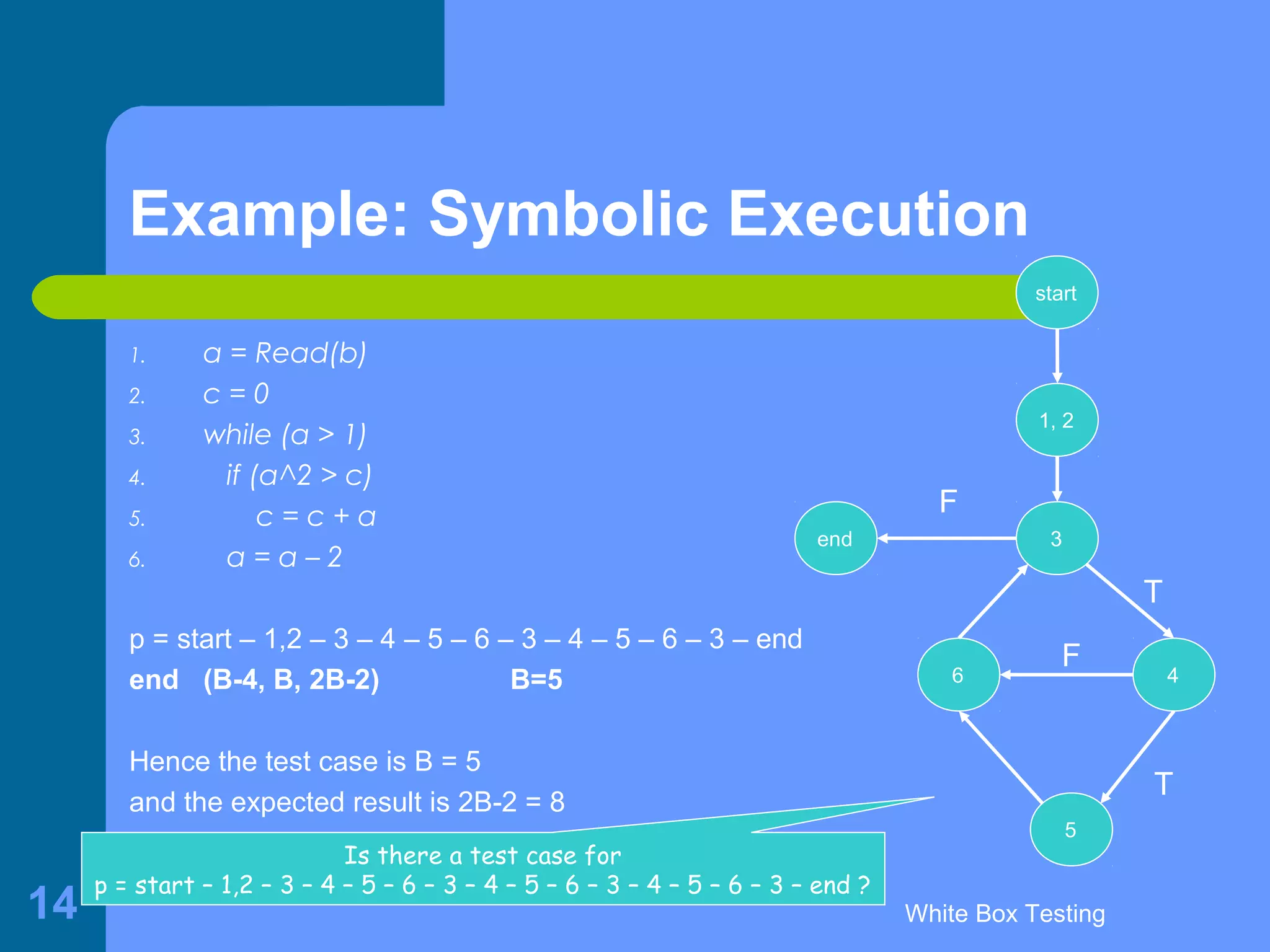
This document discusses white-box testing techniques. It defines white-box testing as execution-based testing that uses the program's inner structure and logical properties. It describes using a flow graph to model the program and discusses different types of coverage like statement coverage and branch coverage. It then explains symbolic execution, where path conditions and path functions are derived to generate test cases that satisfy a given path through the program. An example is provided to demonstrate symbolic execution.