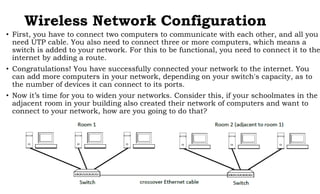
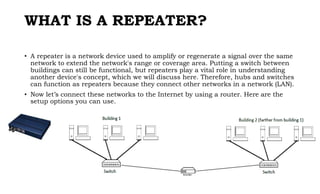
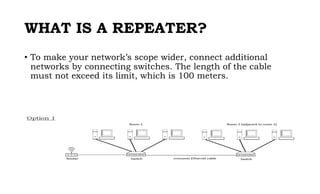
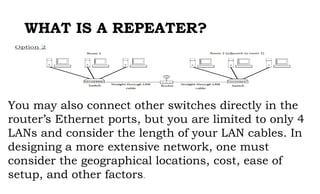
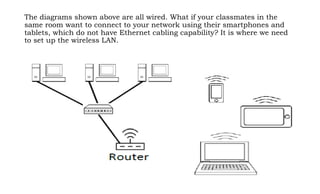
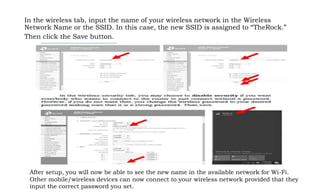
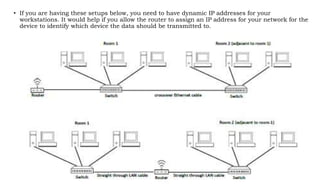
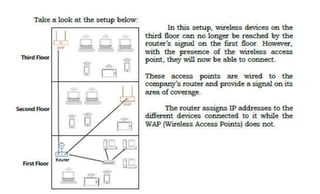
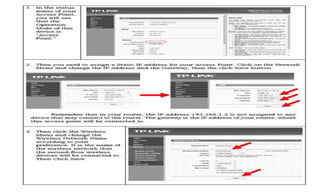
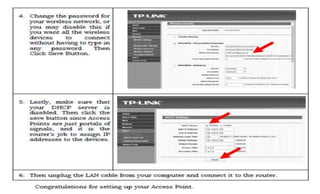
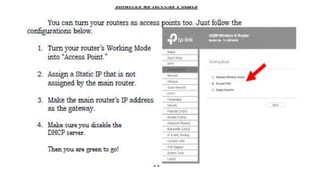
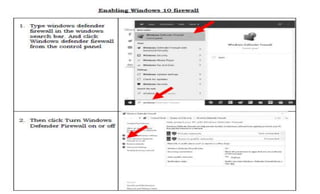
This document provides instruction on setting up and configuring a wireless network. It begins by reviewing concepts covered in previous lessons, such as connecting computers via Ethernet cables and switches, and connecting a network to the internet via a router. It then discusses more advanced scenarios that require additional devices, such as connecting to nearby networks using switches or repeaters, and extending the wireless network range using wireless access points. The document provides detailed steps for configuring routers, switches, repeaters and wireless access points, including assigning IP addresses via DHCP. It also defines key terms like DHCP, firewall and wireless network configuration.