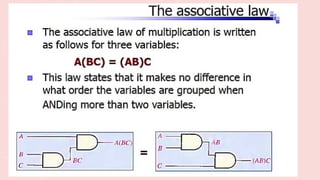
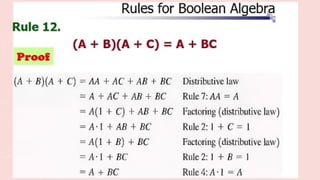
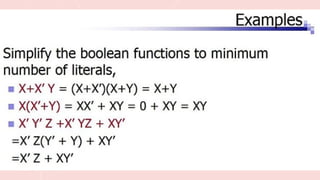
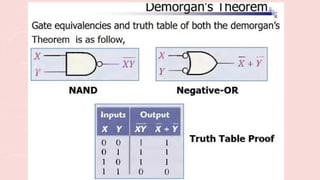
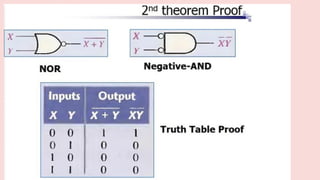
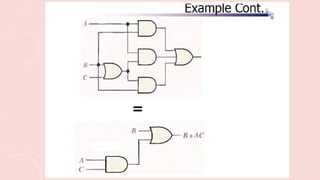
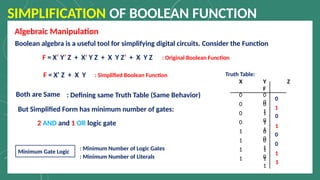
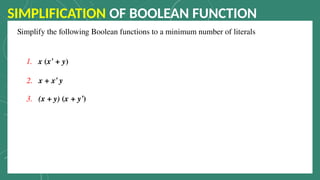
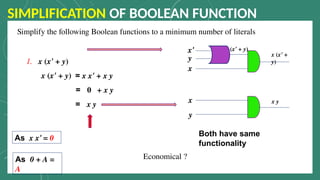
The document outlines the basic identities and principles of Boolean algebra, including commutative, associative, and distributive properties. It emphasizes the duality principle and provides simplification techniques for Boolean functions using identities. The text also illustrates how to effectively reduce the number of logic gates in digital circuits through algebraic manipulation.