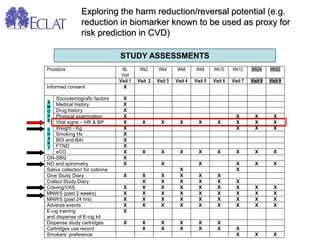
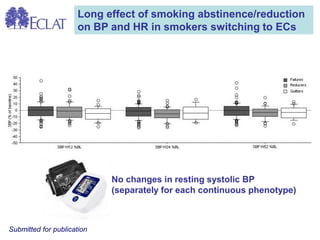
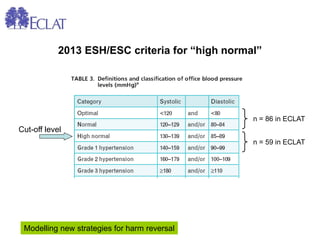
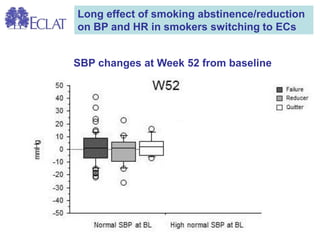
- Professor Riccardo Polosa is the director of the Institute of Internal Medicine and Clinical Immunology at the University of Catania. He has conducted research on e-cigarettes and has received funding from pharmaceutical companies and the e-cigarette industry.
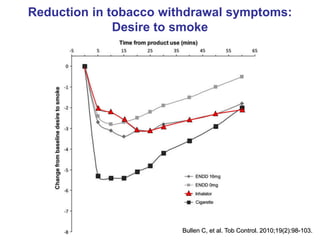
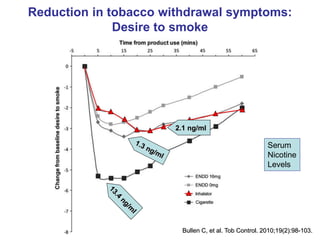
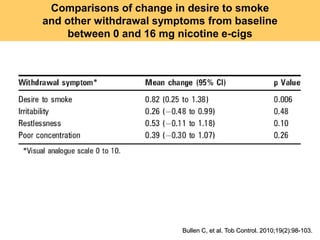
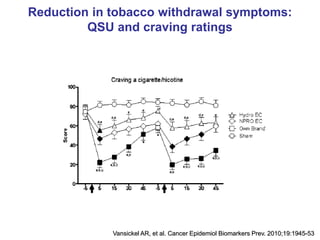
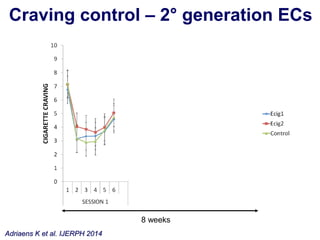
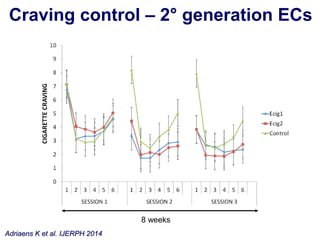
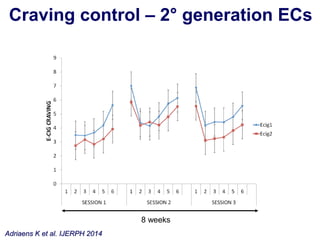
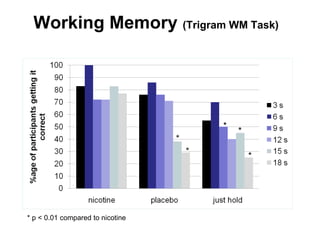
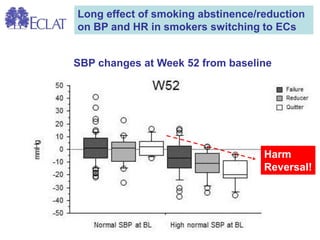
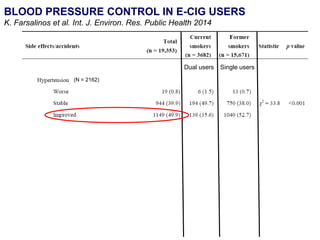
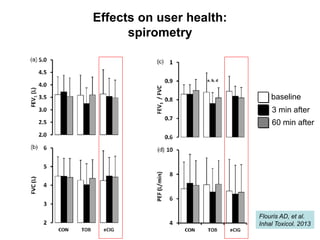
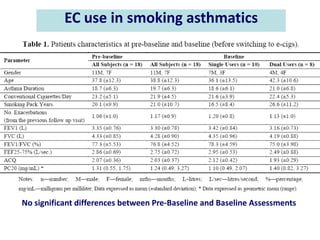
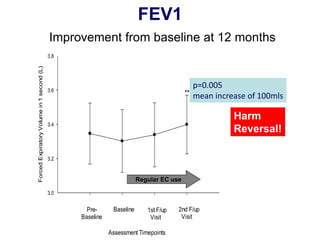
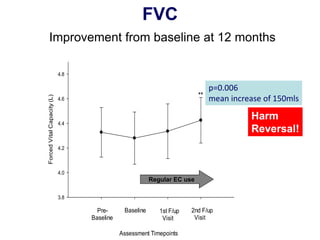
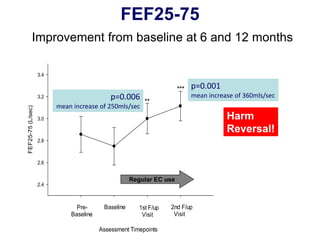
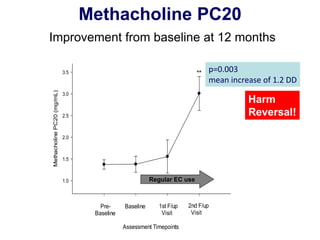
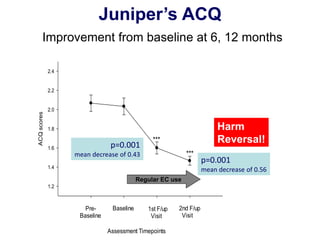
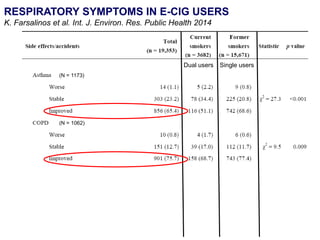
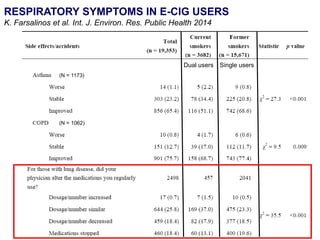
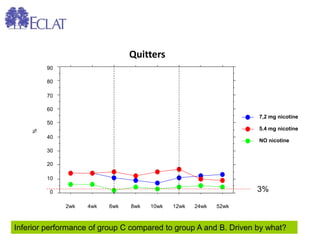
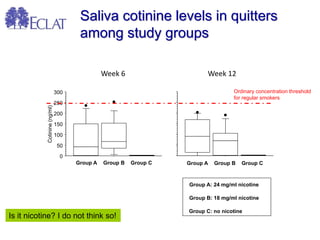
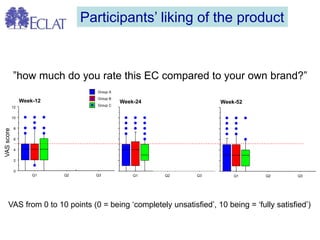
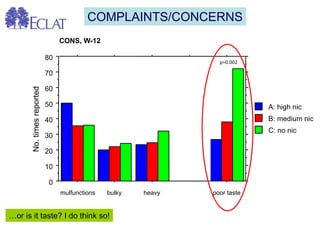
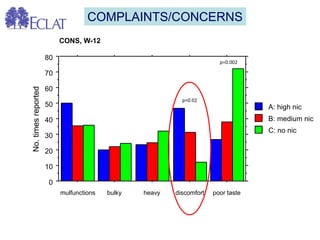
- He presented on clinical studies that have evaluated the effects of e-cigarettes on withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Studies have found that e-cigarettes can reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings, though the effect on cravings depends more on the ritual than nicotine.
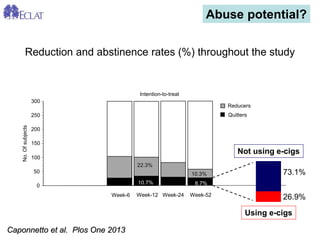
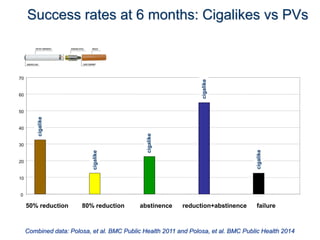
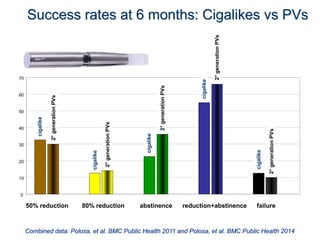
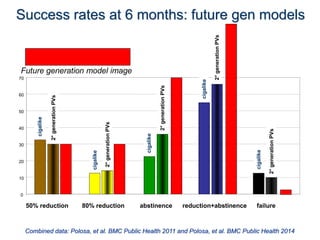
- Larger randomized controlled trials have also found that e-cigarettes help smokers reduce or quit smoking compared to other nicotine replacement therapies or no aid. Success rates were