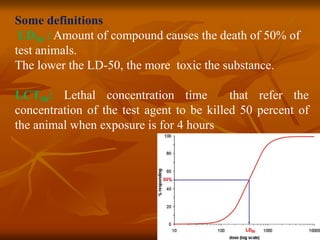
The document describes procedures for acute toxicity tests to determine the lethal dose of a compound. Acute toxicity tests involve administering a single dose of a compound to test animals and observing symptoms and lethality. The LD50 is the dose that causes death in 50% of animals. Tests are done by injection or oral routes in rats or mice. Animals are observed for symptoms and mortality rates over a period of time to determine the LD50 and establish a dose-response curve for lethality. The tests provide information on the lethal concentration and time of exposure, as well as the order of toxicity and symptoms caused by a compound.