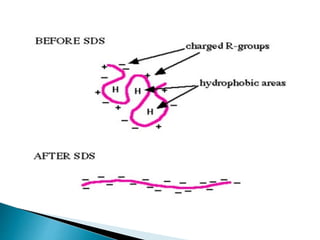
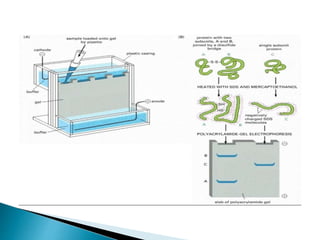
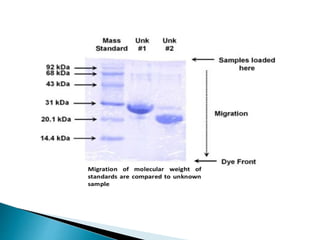
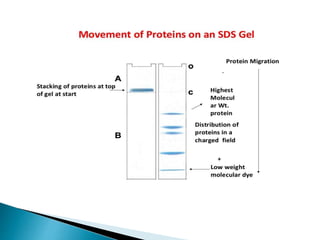
The document describes SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis), a technique used to separate proteins based on their molecular weight. SDS denatures proteins and gives them a uniform negative charge, allowing separation based primarily on size in the polyacrylamide gel. The document provides details on preparing the resolving and stacking gels, running the electrophoresis, and using SDS-PAGE to separate and analyze proteins.