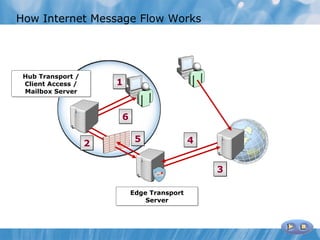
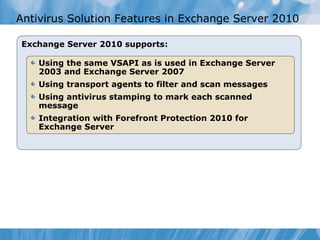
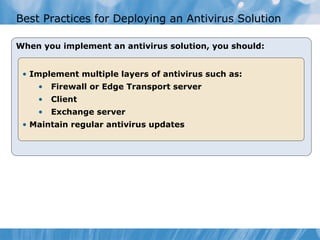
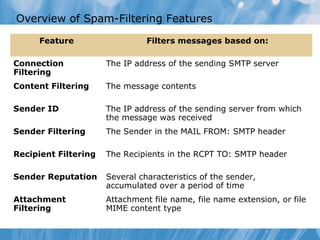
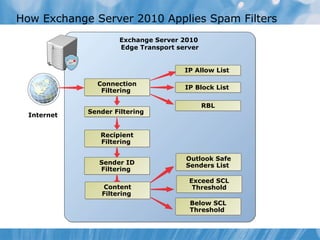
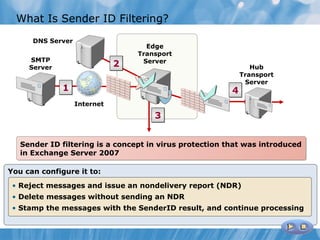
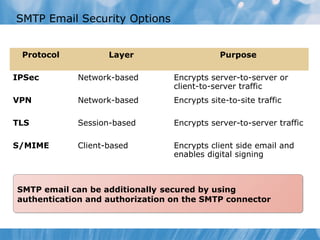
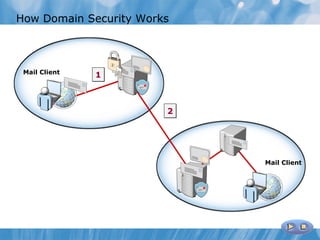
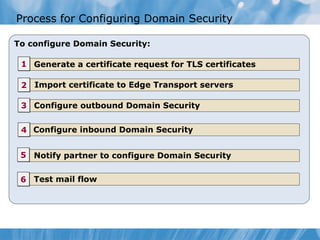
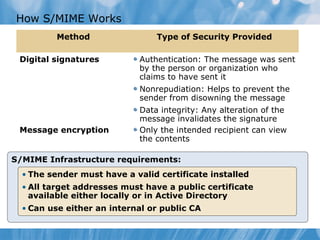
The document provides an overview of implementing messaging security in Exchange Server 2010. It discusses deploying Edge Transport servers and configuring them for secure SMTP messaging. It also covers deploying an antivirus solution like Forefront Protection 2010 and configuring anti-spam options. The lessons include demonstrations of configuring Edge Transport servers, Forefront Protection 2010, and anti-spam options to filter spam messages.