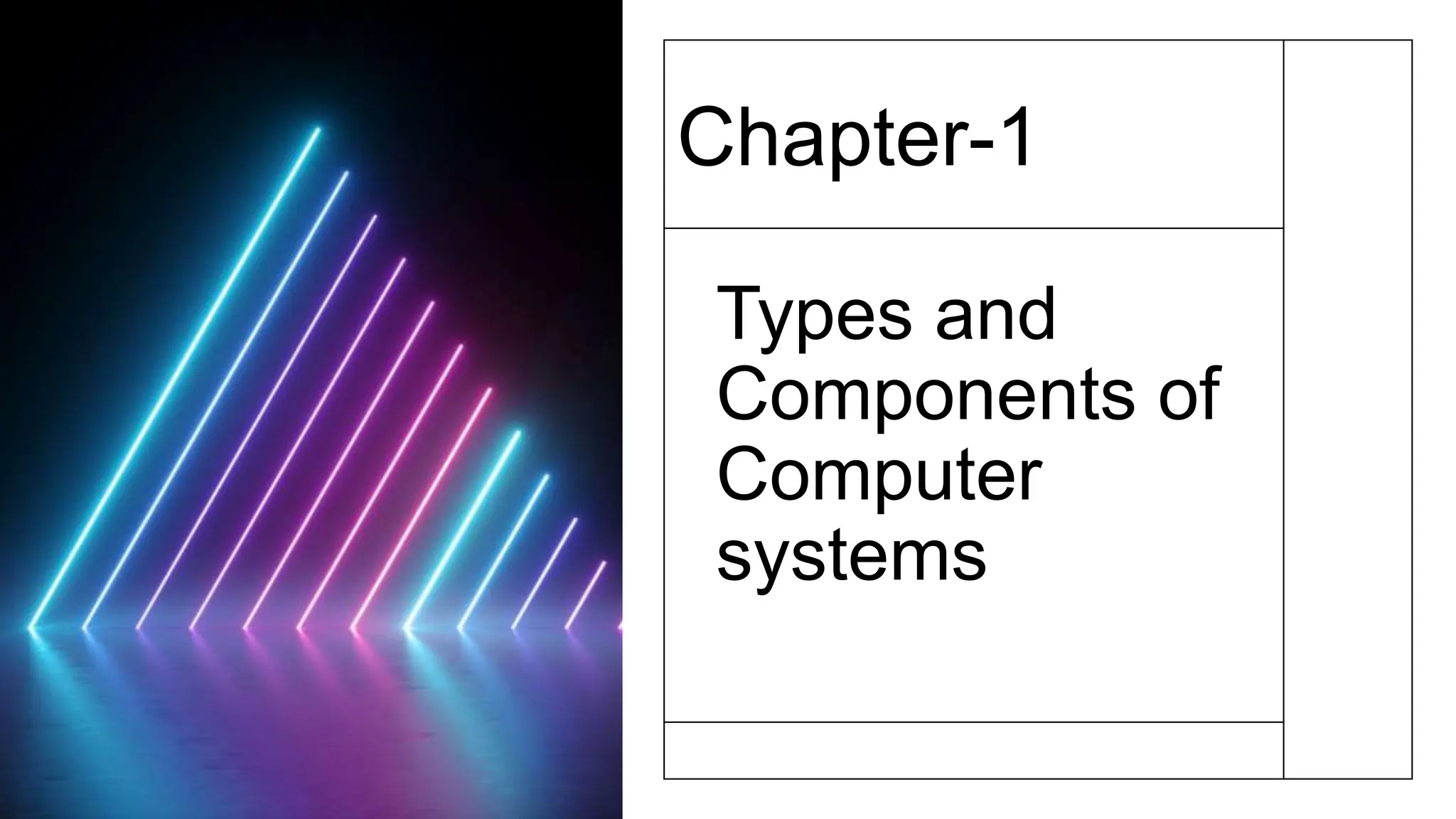
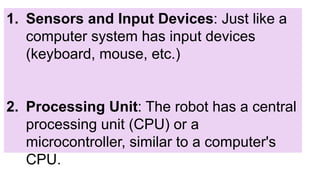
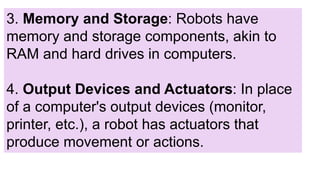
The document discusses the components of computer systems and parallels in robot design, highlighting similarities in input devices, processing units, memory, output devices, and software. It also outlines the advantages of using robots in the workplace, such as increased productivity, consistency, cost efficiency, and enhanced safety, while addressing potential disadvantages like high initial costs, job displacement, and ethical concerns. The content emphasizes the significant impact robots are having on labor and industrial processes.