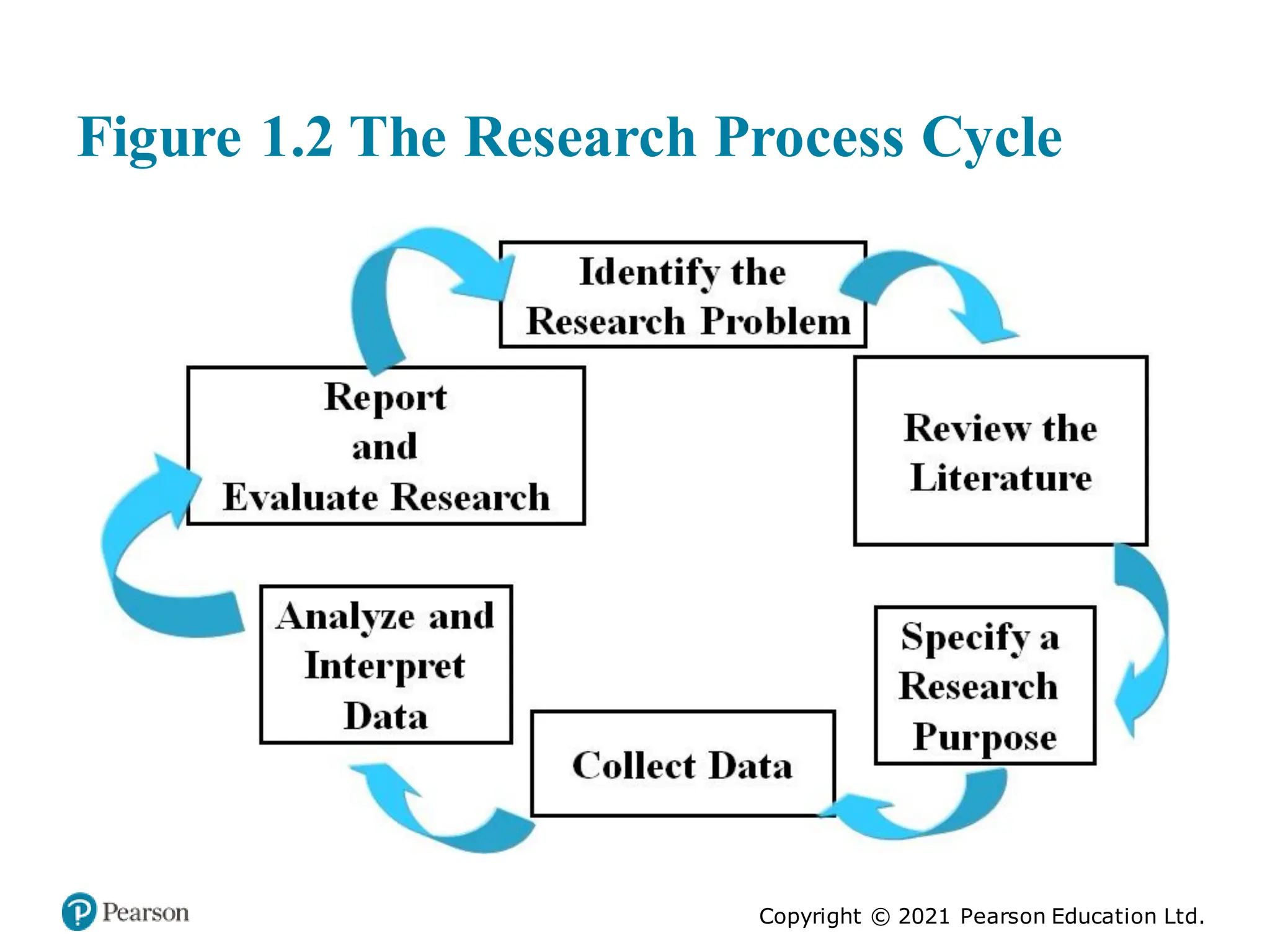
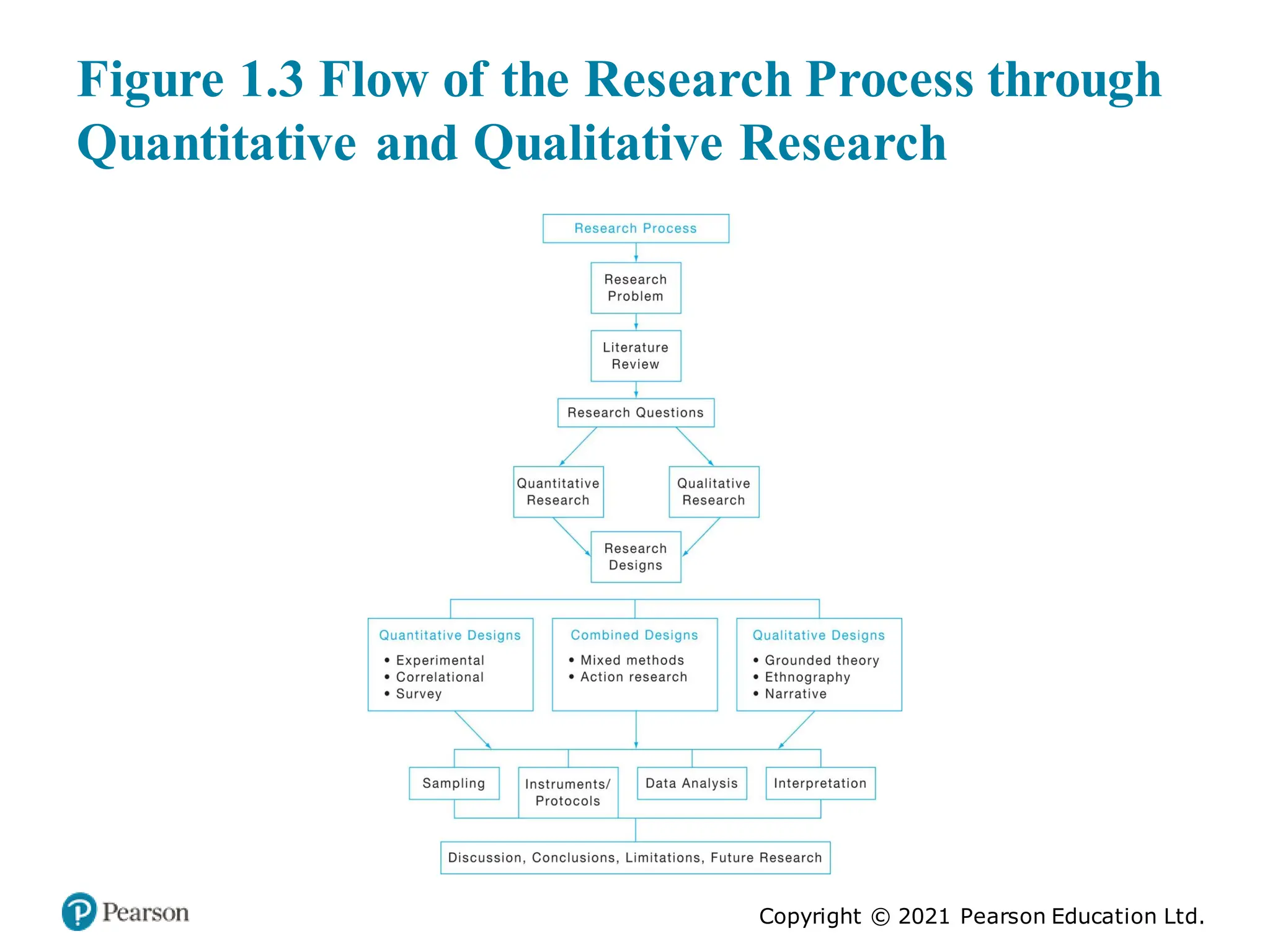
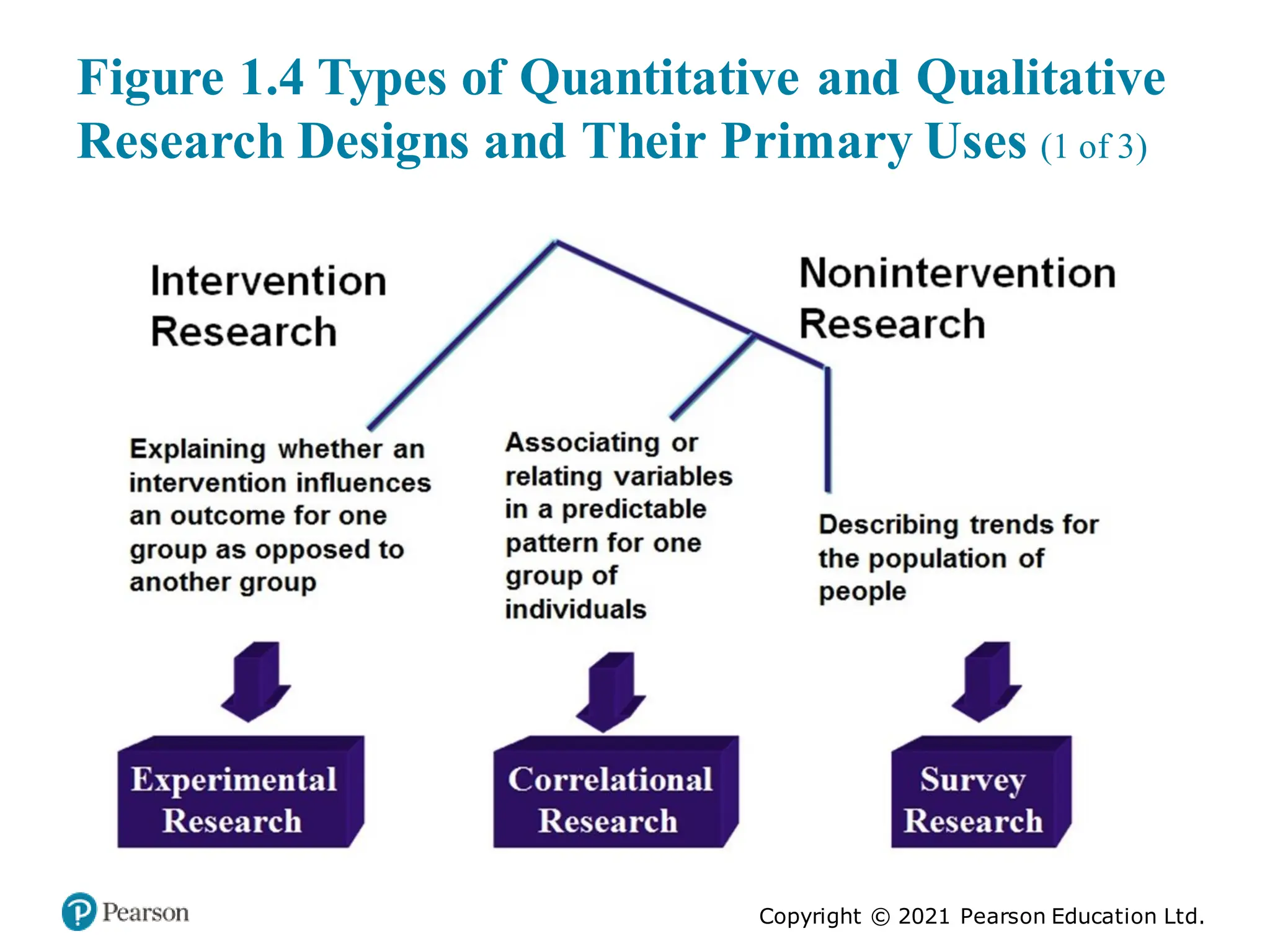
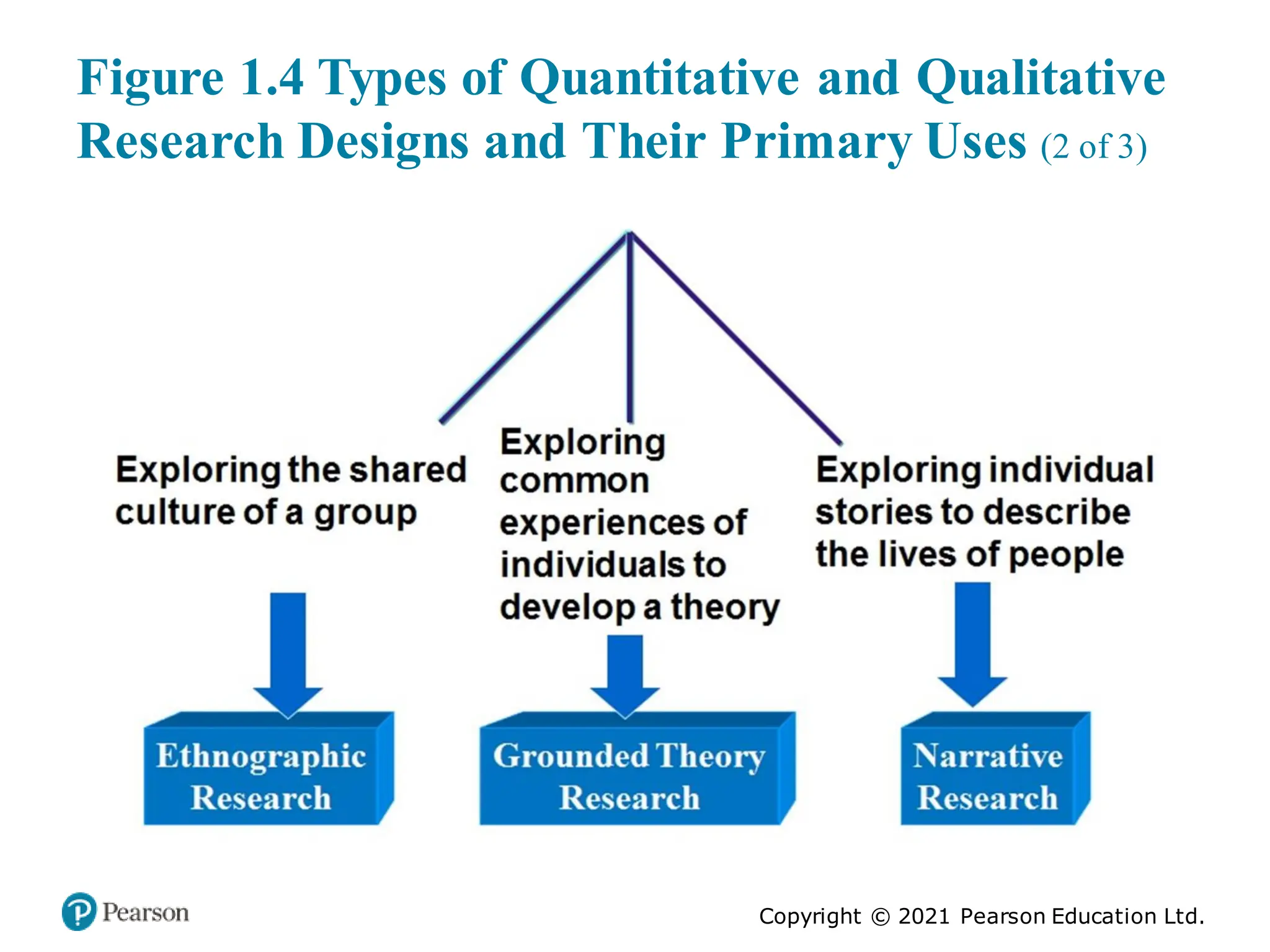
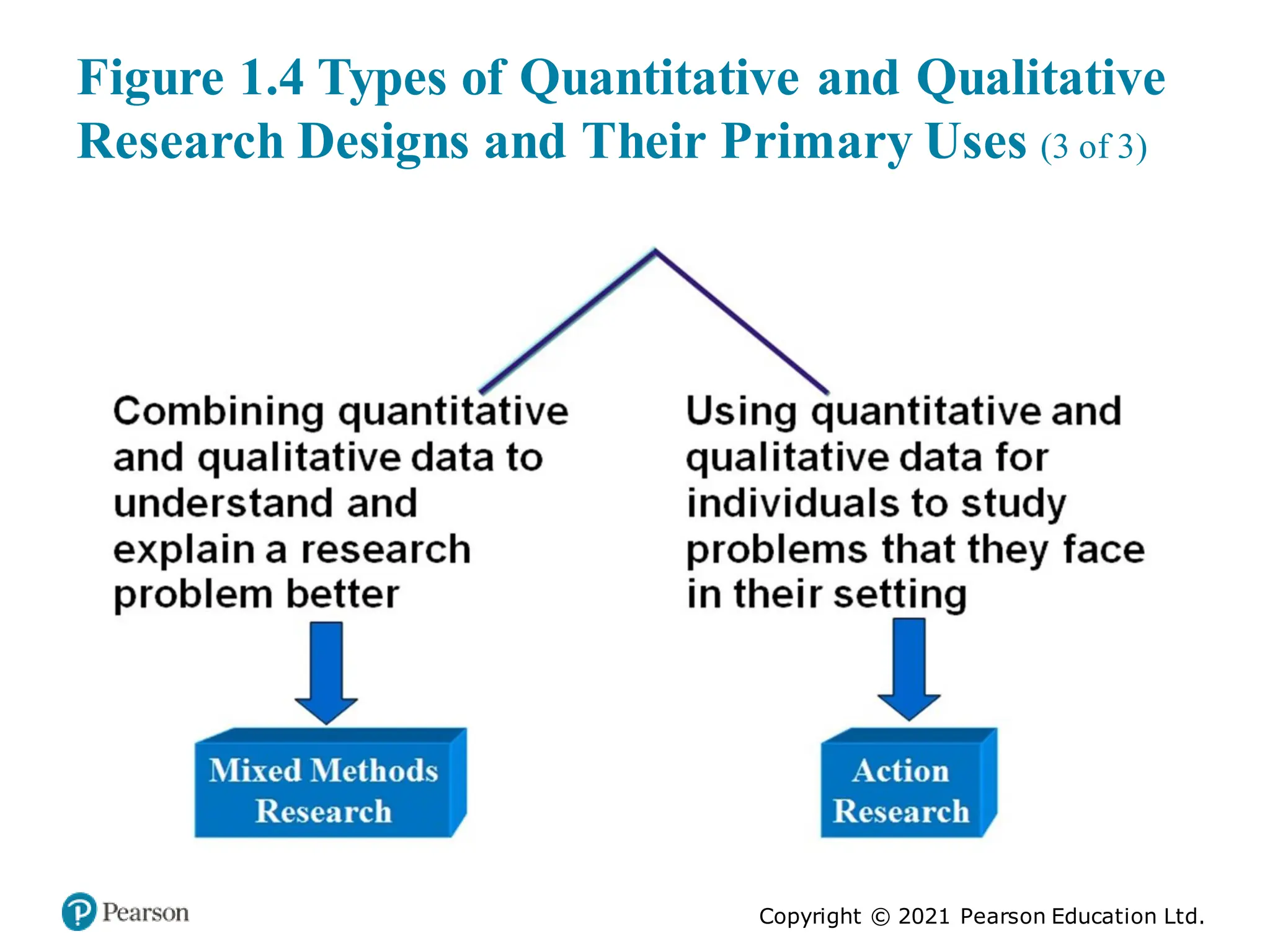
The document outlines the process of conducting educational research, emphasizing the importance of both quantitative and qualitative approaches through six key steps: identifying the research problem, reviewing literature, specifying research purposes, collecting data, analyzing data, and reporting research. It discusses the significance of research in enhancing knowledge, improving educational practices, and informing policy debates, while also addressing challenges such as contradictory findings and ethical considerations. Finally, it contrasts quantitative and qualitative research characteristics, highlighting their similarities and differences, and emphasizes the skills necessary for effective research.