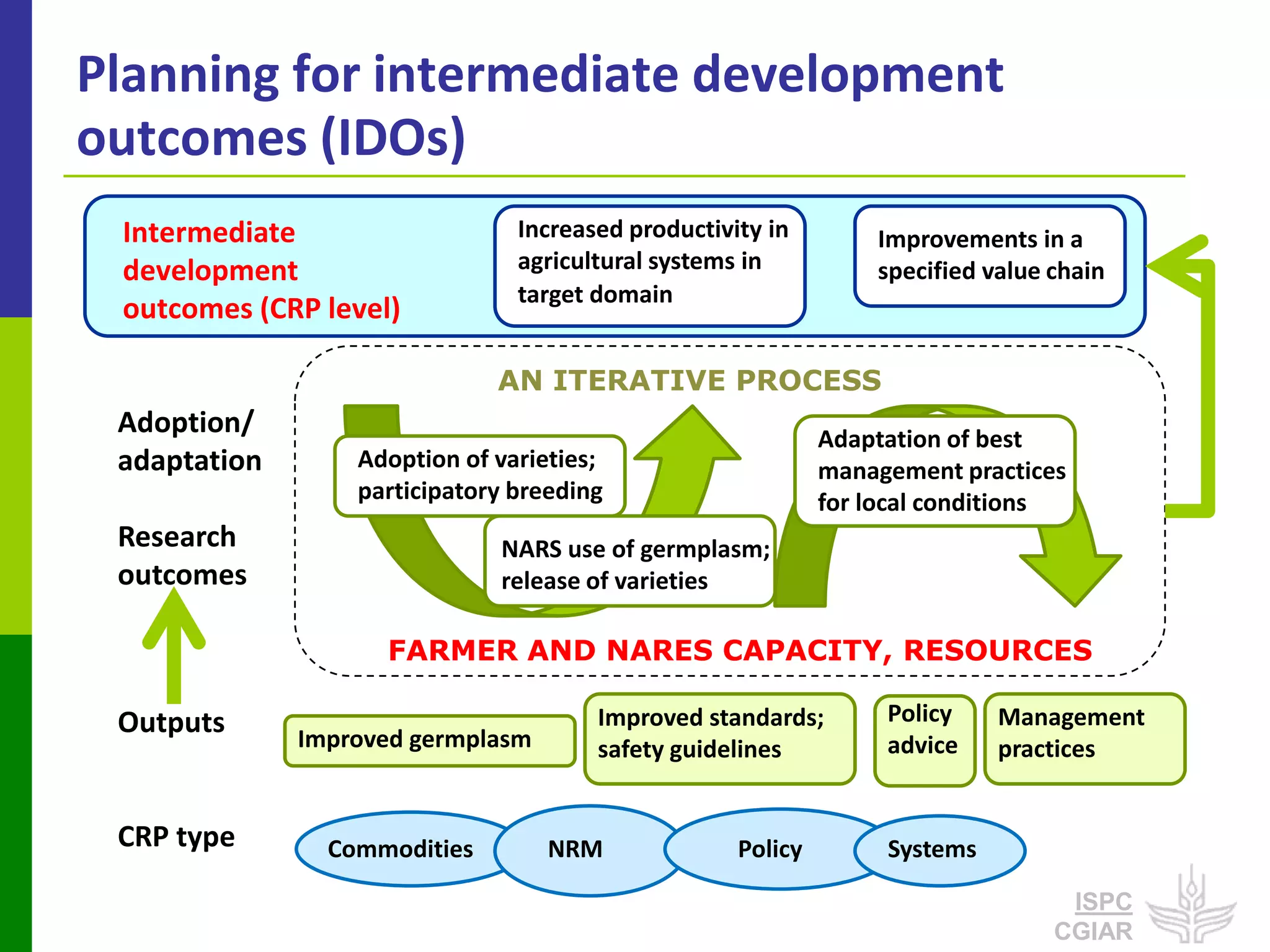
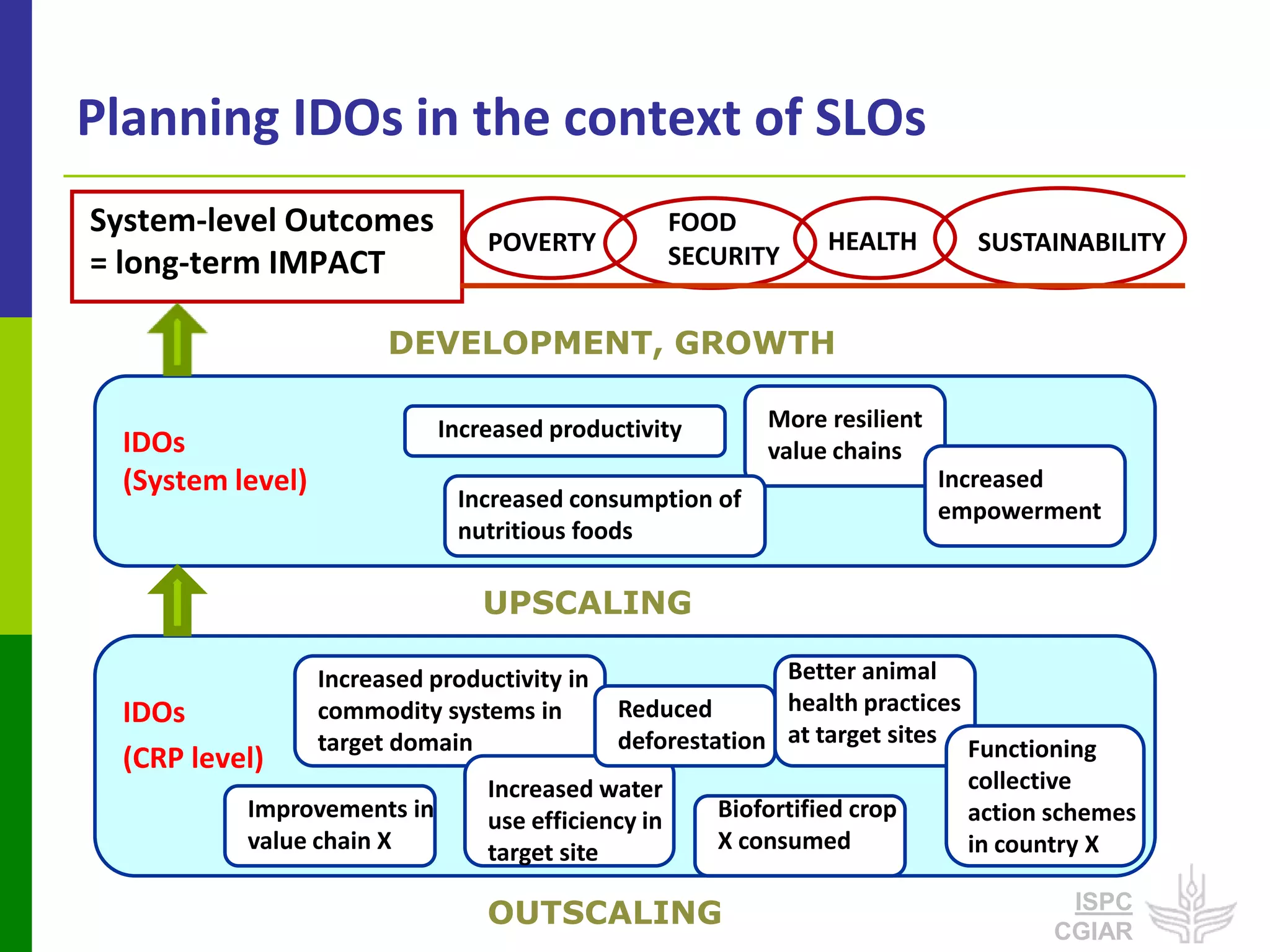
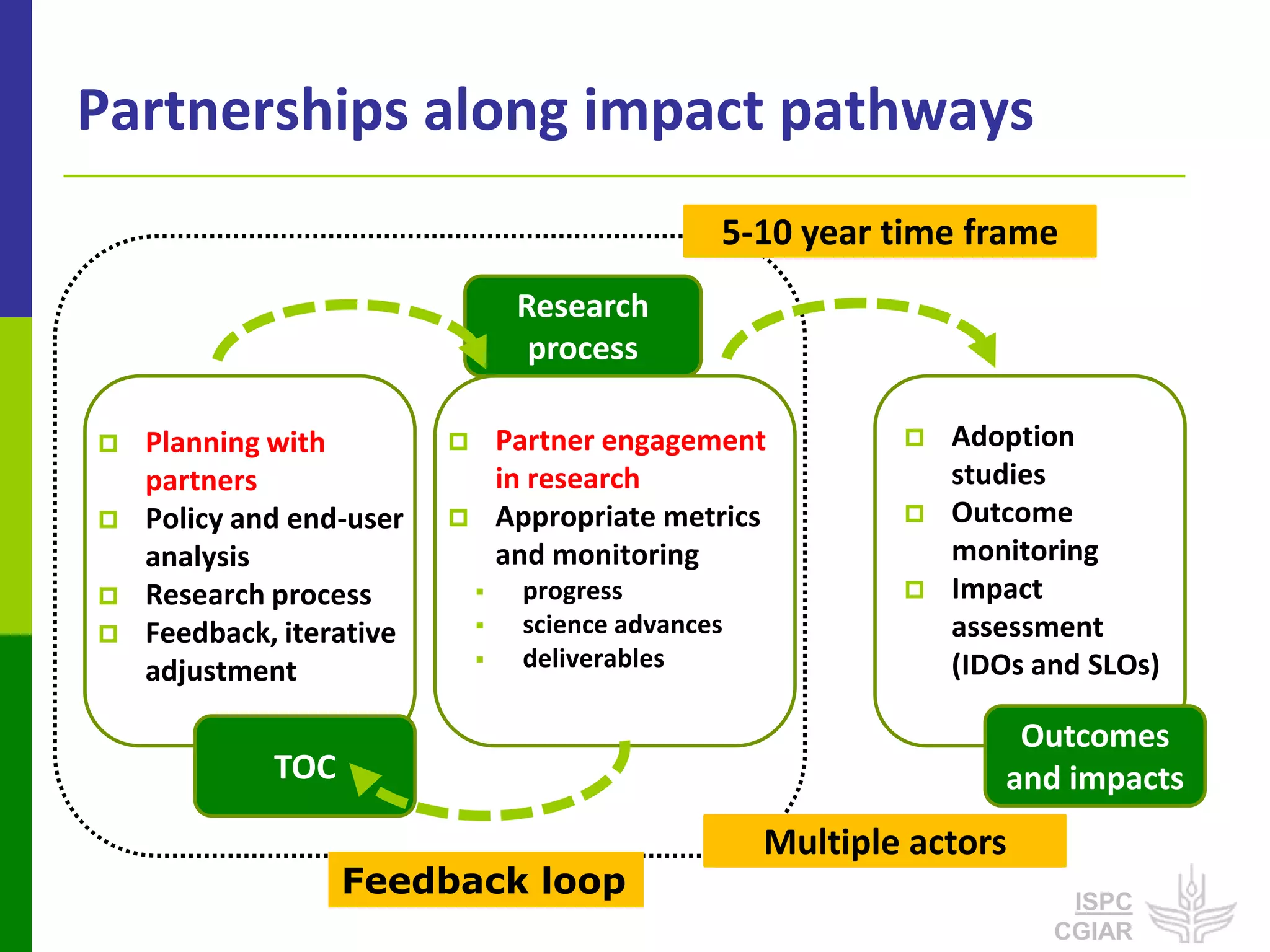
This document discusses partnerships that are important for achieving the CGIAR's System-Level Outcomes of reducing rural poverty, improving food security, improving nutrition and health, and sustainably managing natural resources. It emphasizes that long-term impact pathways depend on partnerships with local actors. It also highlights the ISPC's role in convening discussions, assessing research programs, and identifying issues of integration that benefit from effective partnerships.