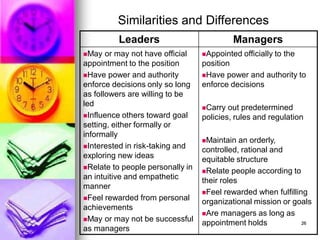
The document discusses key concepts in nursing management and leadership. It defines management as coordinating people, time, and supplies to achieve desired outcomes through problem-solving and decision-making. The main roles of a nurse manager are described as a customer service provider who creates a caring environment, a team builder, resource manager, decision-maker and problem-solver, and a change agent. Effective leadership and management requires technical, human, and conceptual skills including clinical expertise, working well with people, and understanding the overall organization.