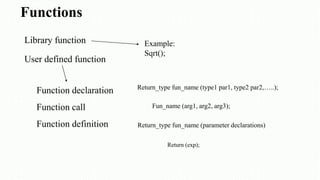
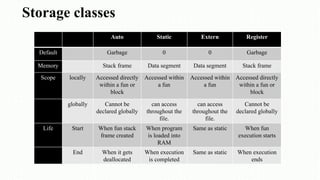
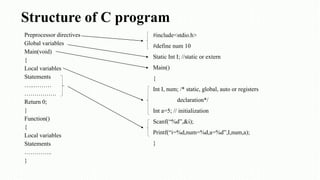
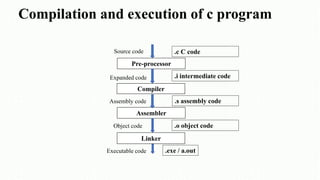
The document serves as an introduction to the C programming language, covering its structure, data types, operators, control statements, error types, functions, and storage classes. It describes how to compile and execute C programs and details various constructs like loops, conditionals, and arrays with examples. Additionally, it explains compiler errors and different data types, emphasizing the organization and functionality of C programming.


![Operators
• Arithmetic operator ( + , - , * , / , % ) – binary – doesn’t change the value – result (value)
• Relational operator ( > , >= , < , <= , == , != ) – binary – doesn’t change the value – result (0 or 1)
• Logical or Boolean operator (&& , || , ! ) – binary – doesn’t change the value – result (0 or 1)
• Conditional operator ( [? :] ) – ternary – doesn’t change the value – result (true stat or false stat)
• Bitwise operator ( & , | , ~ , << , >> ,^ ) – binary – changes the value
• Increment and decrement operator ( ++ , -- ) – unary – changes the value
• Size of operator ( sizeof() ) –unary –doesn’t change the value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1introductiontocprogram-190907073907/85/1-introduction-to-c-program-6-320.jpg)









![Arrays
Data_type array_name [index];
No of elements
in the array
To scan
For (i=0 ; a[i] ; i++)
{
Scanf(“%d”,&a[i]);
}
To print
For (i=0 ; a[i] ; i++)
{
printf(“%d”,a[i]);
}
Array representation
A[i]=i[a]=*(a+i)
Example:
Int a[6];
Int a[6] = {10,20,30,40,50,60};
1D array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1introductiontocprogram-190907073907/85/1-introduction-to-c-program-24-320.jpg)
![2D array
To scan
For (i=0 ; i<n ; i++)
{
for(j=0 ; j<m ; j++)
Scanf(“%d”,&a[i]);
}
To print
For (i=0 ; a[i] ; i++)
{
for(j=0 ; j<m ; j++)
printf(“%d”,a[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1introductiontocprogram-190907073907/85/1-introduction-to-c-program-25-320.jpg)
![Strings
Data_type string_name [index];
Example:
char s[6];
char s[6] = “hello”;
No of elements
in the string
To scan
For (i=0 ; s[i] ; i++)
{
Scanf(“%c”,&s[i]);
}
Or
Scanf(“%s”,s);
To print
For (i=0 ; s[i] ; i++)
{
printf(“%c”,s[i]);
}
Or
Printf(“%s”,s);
It is a collection of characters terminated by a null symbol (‘o’)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1introductiontocprogram-190907073907/85/1-introduction-to-c-program-26-320.jpg)