This document discusses mobile computing and related concepts:
- Mobile computing allows access to network services anywhere via user and device portability between locations and networks. It includes technologies like laptops, phones, and PDAs.
- Ubiquitous computing integrates computation into the environment rather than distinct computer objects, enabling more natural interaction.
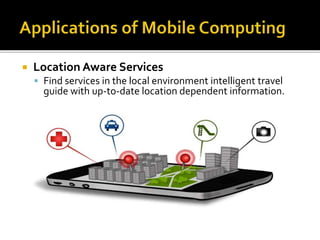
- Examples of mobile computing applications include web access, location-aware services, entertainment, vehicle telematics, medical, sales, and emergency response.
- Challenges include limited battery life, interference issues, bandwidth constraints, dynamic network changes, and ensuring security and interoperability across standards.