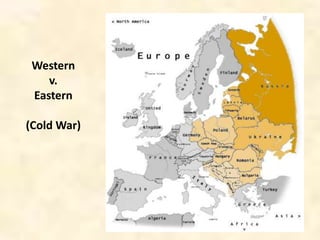
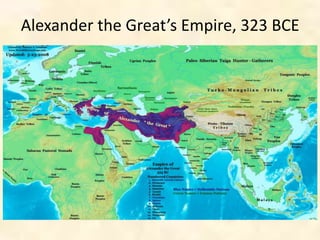
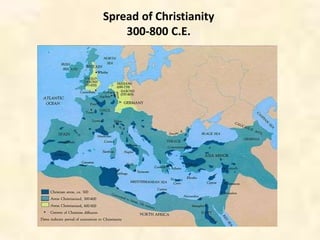
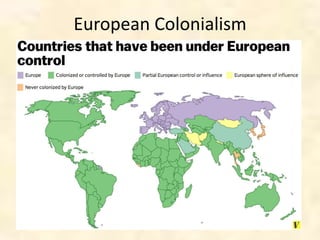
This document provides an overview of the concepts to be covered in an introductory Western Civilization course. It questions what is meant by "the West" and "civilization", noting that these terms are variable and contentious. The document explores different definitions of the geographic, political, cultural, and imperial boundaries of the West, touching on influences from ancient Greece and Rome, the spread of Christianity, and European colonialism. It examines changing borders of Europe over time and debates what constitutes the East versus the West. Key topics to be addressed in the class are identified.