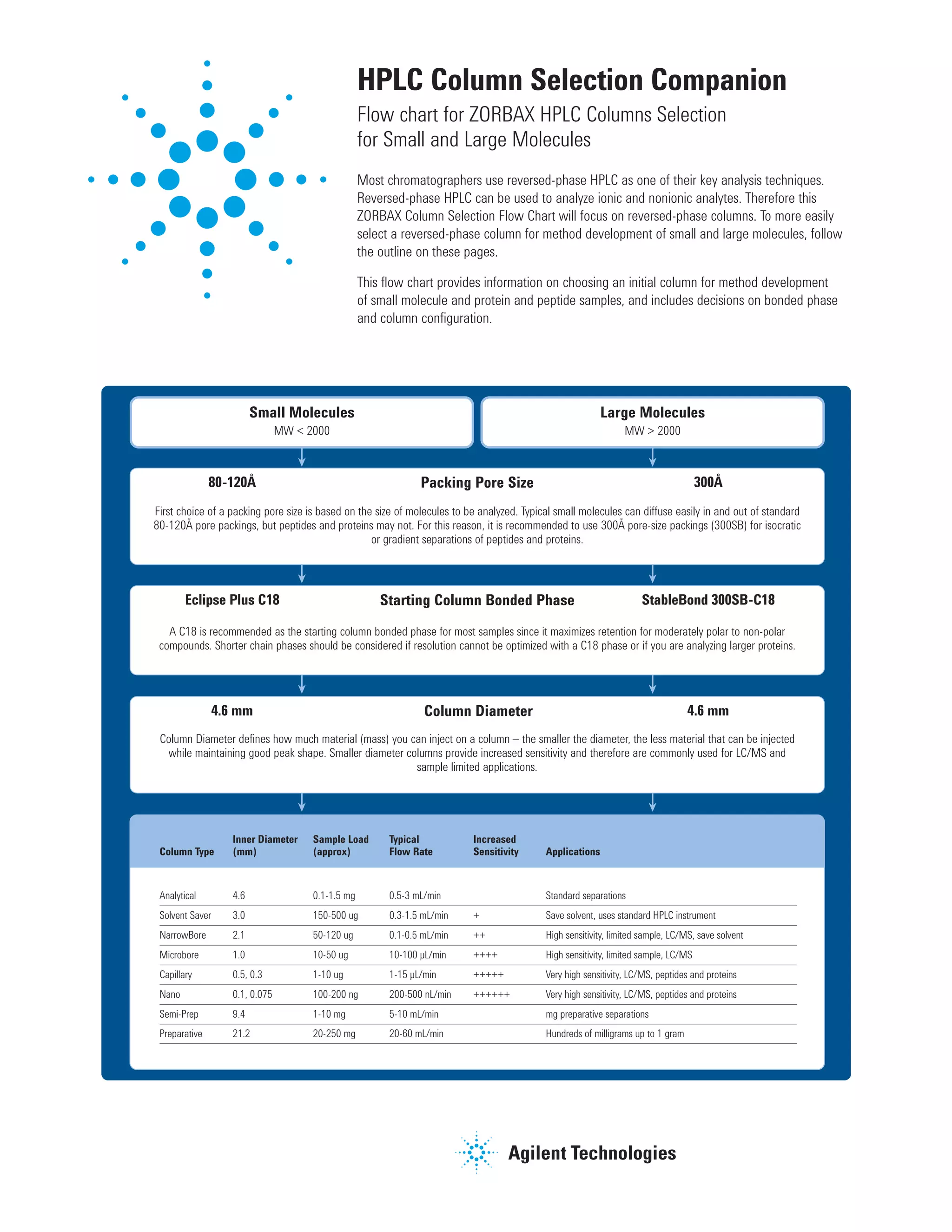
This document provides a flow chart to help chromatographers select reversed-phase HPLC columns for analyzing small molecules or large molecules like proteins and peptides. It recommends starting with a ZORBAX 300SB-C18 column with 300Å pores for large molecules, and provides guidance on selecting column dimensions, particle size, bonded phase, and length based on the analyte size and whether standard or fast analysis is needed.