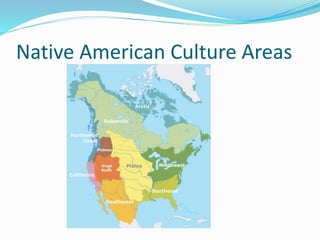
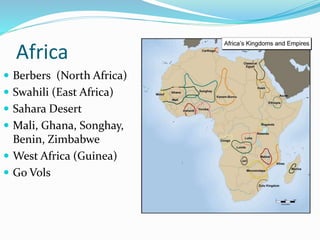
This document outlines the objectives and key concepts for a US History course covering the period up to 1865. It will introduce students to the societies and cultures of Western Europe, Native Americans, and West Africans in the 1400s. Students will learn about the reasons for European exploration and increasing conflicts between groups. They will compare the Spanish, French, Dutch, and English colonies and contrasts between New England and Chesapeake English colonies. Key themes like liberty, slavery, and European/Indian interactions will be examined.