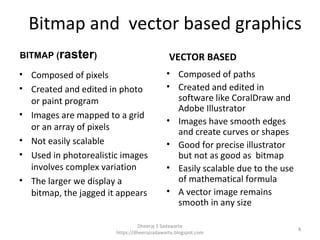
The document provides an overview of computer graphics, including its mathematical and computational foundations for synthesizing and manipulating visual content. It covers key concepts such as image representation, rasterization, bitmap vs vector graphics, and applications in various fields like digital art and medical imaging. Additionally, it discusses display devices like cathode ray tubes and the graphic rendering pipeline.