This document discusses the in situ synthesis of titanium carbide (TiC) nanoparticles within an aluminum matrix during mechanical alloying using nanodiamond powders as carbon precursors. The study demonstrates that the optimal combination of materials for synthesis is aluminum (30 g) and TiC (40 g), resulting in nanoparticles averaging around 30 nm, which are uniformly distributed in the matrix. Differential scanning calorimetry shows that the developed composites maintain thermal stability, making them suitable for applications in casting technologies.

![ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT
1
In situ synthesis of TiC nano-reinforcements in aluminum matrix composites during
mechanical alloying
Vladimir A.Popov1
*, Manfred Burghammer2
, Martin Rosenthal2
, Anton Kotov1
1
National University of Science and Technology “MISIS”, Leninsky prospect, 4, 119049
Moscow, Russia
2
ESRF, 71 avenue des Martyrs, 38000 Grenoble, France
*corresponding author e-mail address: popov58@inbox.ru
Abstract
In this paper the possibility of fabrication of titanium carbide reinforcing nanoparticles inside
an aluminum matrix by in situ synthesis during mechanical alloying will be discussed. The
application of nanodiamond particles as carbon precursor for synthesis allowed obtaining TiC
particles in nanosized form due to the size of initial nanodiamond particle of 4-6 nm. The
developed composites were investigated by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffractometry,
and differential scanning calorimetry.
Keywords: A: Metal-matrix composites (MMCs); Particle-reinforcement; B: Microstructures;
D: Electron microscopy
1. Introduction
The advancement of science and technology requires the development of new materials. On
the one hand, modernized materials enhance the quality of various products and increase their
service life, while on the other hand they create new technical solutions that are fundamentally
different when compared to existing ones. Metal matrix composites [1-18] provide a new level of
properties unattainable in conventional non-reinforced metals and alloys. However, composites
with powder-like reinforcing particles still deserve considerable attention. Multiple studies have
been dedicated recently to the development of nanocomposites. e.g., composites with nano-sized
reinforcing particles. However, nano-powders in this application display a number of features,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09f8706f3115125a5879c0d4cc9afed9-220109151712/85/09f8706f3115125a5879c0d4cc9afed9-2-320.jpg)
![ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT
2
such as an increased surface area and high activity of the material, which results in a large
amount of foreign matter and contamination on the surface of the nanoparticles. Contamination
at the interface between the metal matrix and the reinforcing particle is one of the major reasons
preventing a wider application in industry. This is explained by the fact that despite being an
insignificant amount, these contaminations and inclusions considerably reduce the bonding
strength between the composite components.
In casting technologies, contaminations and inclusions on the surface of nanoparticles result
in reduced dampening between the components which, at the very least, causes irregular
distribution of reinforcing particles in the matrix, and more often leads to them being removed
from the melt along with the slag.
To reduce contamination at the interface between the metal matrix and the reinforcing
particle, various methodologies have been developed. A promising approach is the in situ
synthesis of nanoparticles in the matrix. In this case, the synthesized nanoparticles have no
contact with air, and thus no contamination between the reinforcing particle and the metallic
matrix is formed.
Recently, titanium carbide has been generating increased interest due to its good mechanical
characteristics. The literature includes reports on in-situ studies of the synthesis of titanium
carbide reinforcing particles during the mechanical alloying process [11-13]. In the described
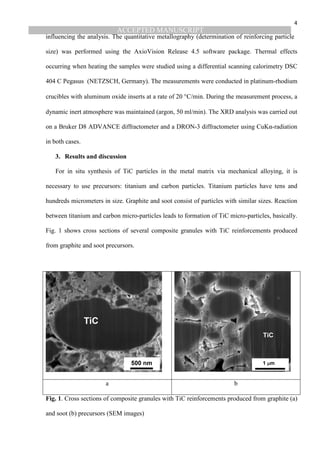
processes, titanium and graphite (or soot) particles were used as precursors. The synthesis is
often carried out when annealing granules after mechanical alloying.
The hereby presented work is intended to study the in-situ synthesis of nanoparticles of
titanium carbide in an aluminum matrix during mechanical alloying when using nanodiamond
powders and titanium particles as precursors. The extremely small size of nanodiamond particles
and their exceptional hardness are those characteristics of nanodiamonds (ND) that led to their
choice for the experiment [19-29]. The exceptional hardness and the quantity of nanodiamonds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09f8706f3115125a5879c0d4cc9afed9-220109151712/85/09f8706f3115125a5879c0d4cc9afed9-3-320.jpg)
![ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT
3
results in intensification of the mechanical alloying process, and their small size has a positive
effect upon the size reduction of synthesized titanium carbide particles.
2. Materials, equipment, and methodologies
The composites were fabricated by mechanical alloying [30-34]. In the studies, commercially
available aluminum, titanium and detonation-synthesized nanodiamond powders were used as
initial materials. A technical grade aluminum powder was applied to the matrix, with an initial
particle size of 30-100 µm. As precursors for the synthesis of titanium carbide particles,
technical grade titanium powders were used with a particle size of 100 µm, alongside detonation-
synthesized nanodiamond powders manufactured by Kombinat Elektrohimpribor (FSUE).
Primary nanodiamond particles are near-spherical in shape; in general, they are 4-6 nm in size. A
distinctive feature of nanodiamonds, just like most nanopowders, is that they can combine into
agglomerates reaching up to hundreds of micrometers in size. In terms of nanoparticle bonding
strength, there are primary and secondary (and sometimes tertiary) agglomerates. The strongest
are primary agglomerates. At the start of mechanical alloying, secondary agglomerates
deagglomeration into primary nanoagglomerates of up to 100 nm. A substantial period of time is
required for complete deagglomeration of the agglomerates.
A Retsch PM400 planetary mill with four tightly closed grinding jars was used for
mechanical alloying. Balls of 12 mm in diameter were used as the milling tool. The ratio of ball
weight to the weight of the processed material was 10:1. The rotation velocity of the grinding
jars around the common axis (rotation rate of the carrier) was 300 rpm. The drums were air-
cooled during operation. To prevent overheating, the planetary mill was stopped after every 10
minutes of operation for 5 minutes to cool-down. The processing time was deemed to be the time
when the mill was operating, disregarding the cool-down intervals.
The granules obtained after mechanical alloying were studied using a scanning electron
microscope Helios NanoLab™ 600i DualBeam™ (FEI). Secondary electrons registration mode
was used. For the studies, granules were cut by an ion beam to avoid surface contaminations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09f8706f3115125a5879c0d4cc9afed9-220109151712/85/09f8706f3115125a5879c0d4cc9afed9-4-320.jpg)