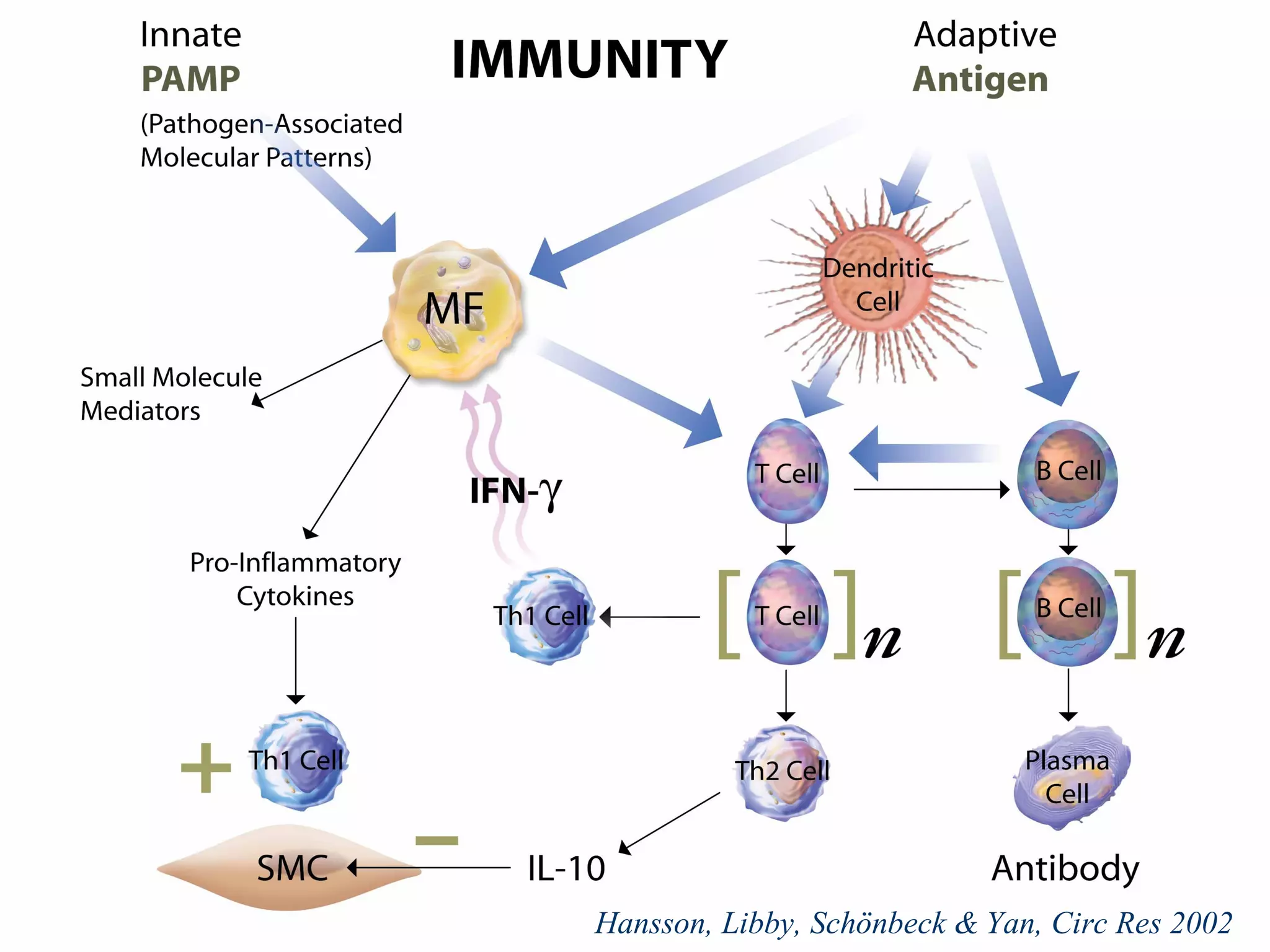
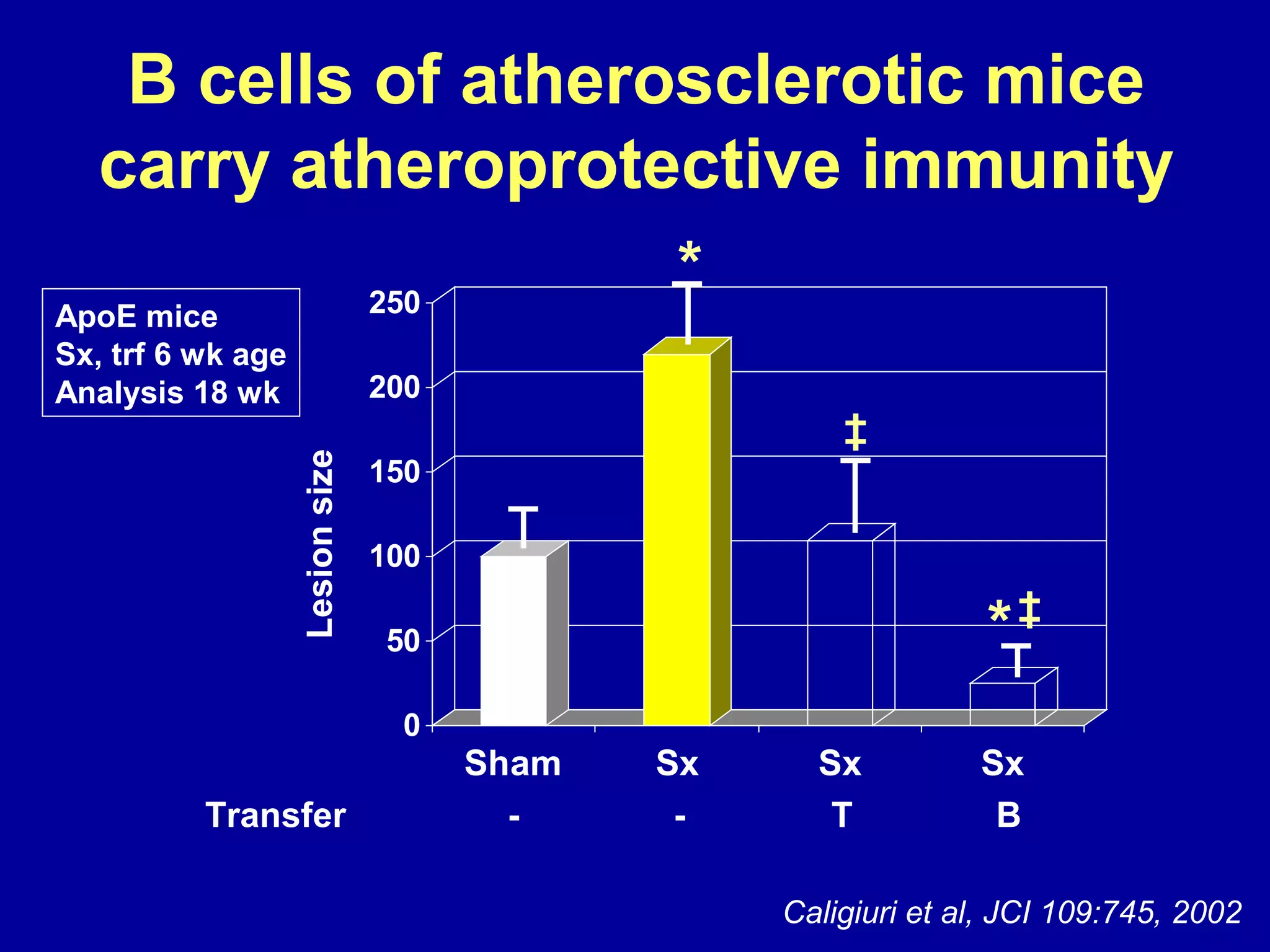
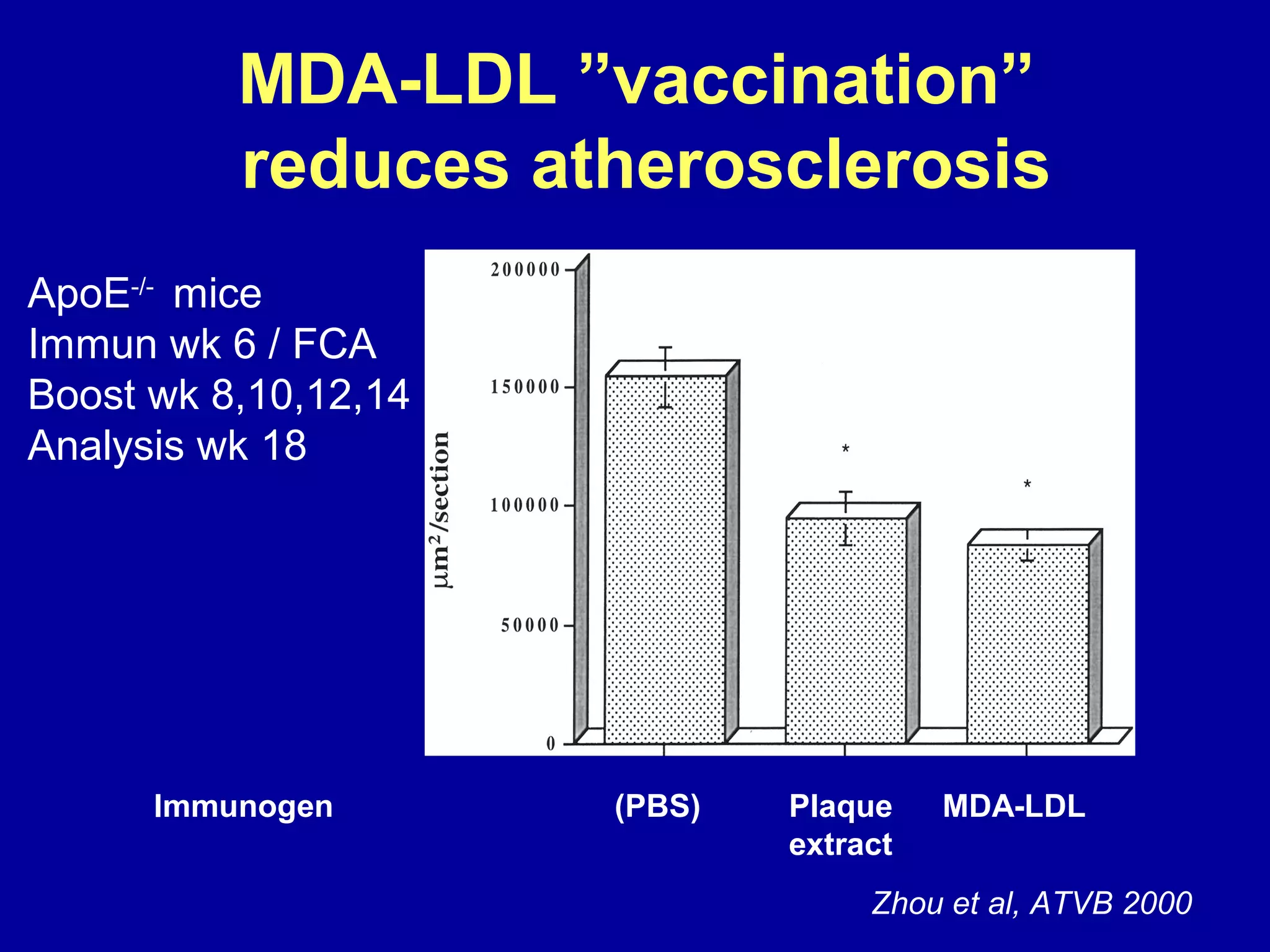
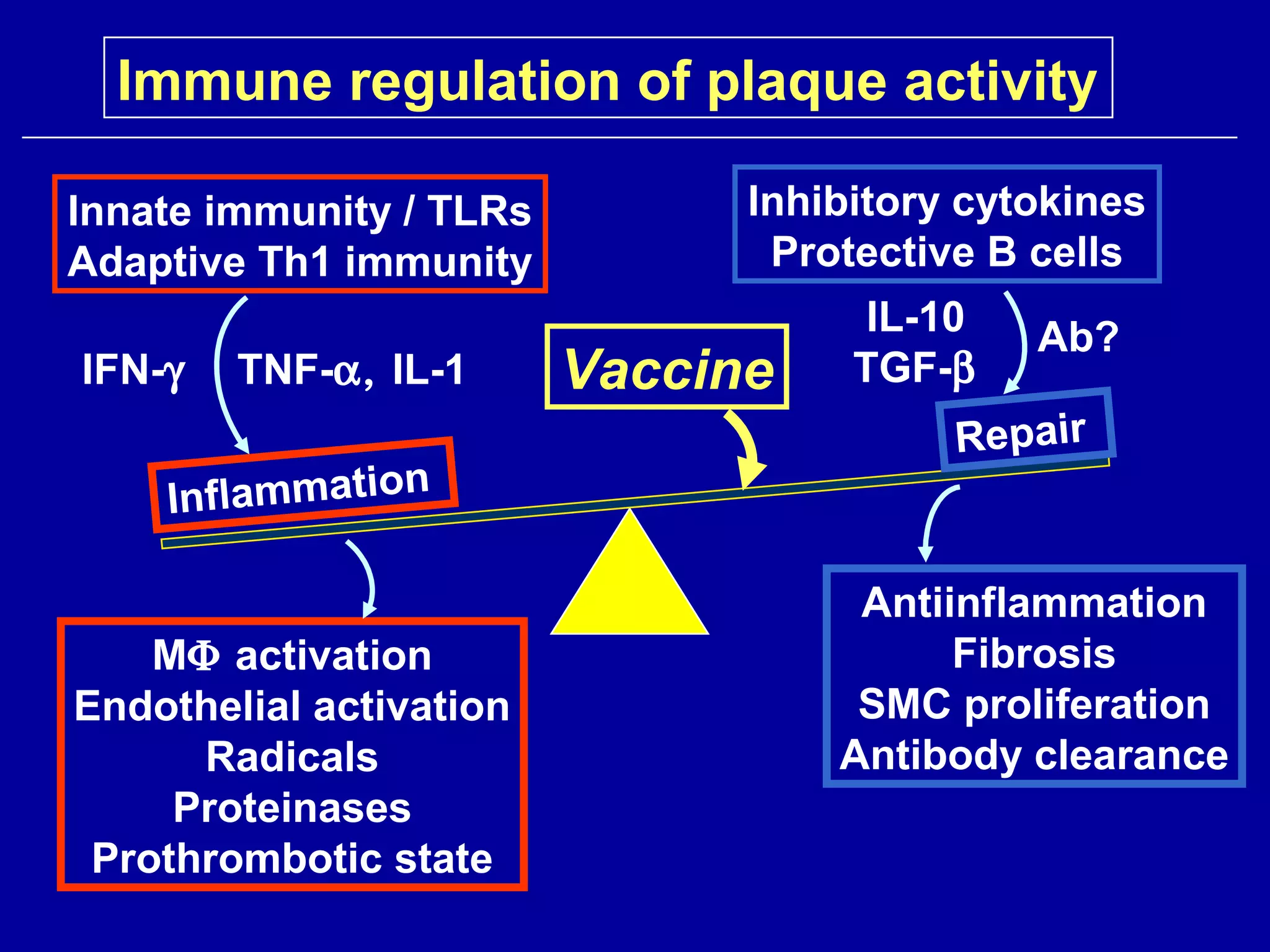
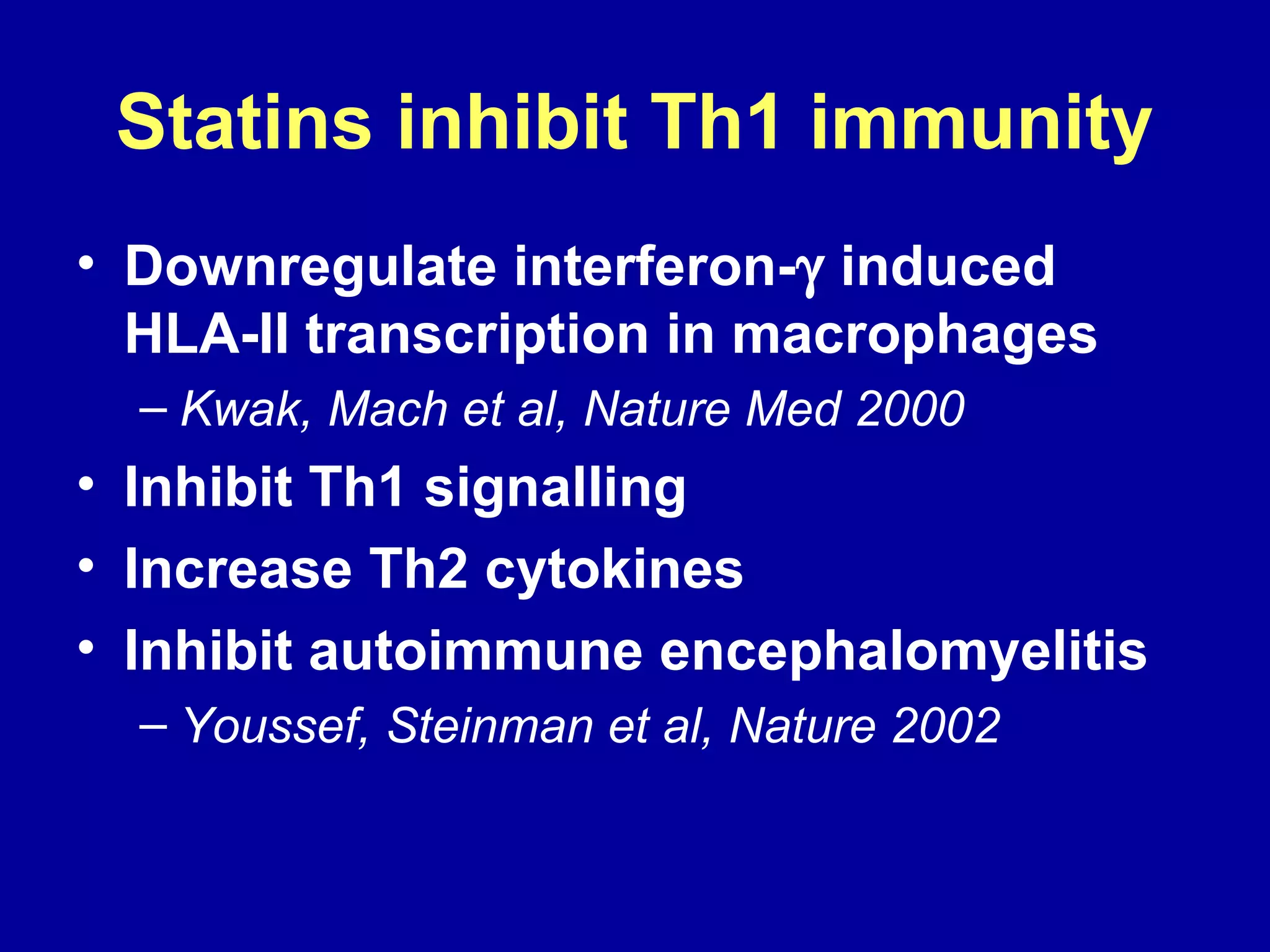
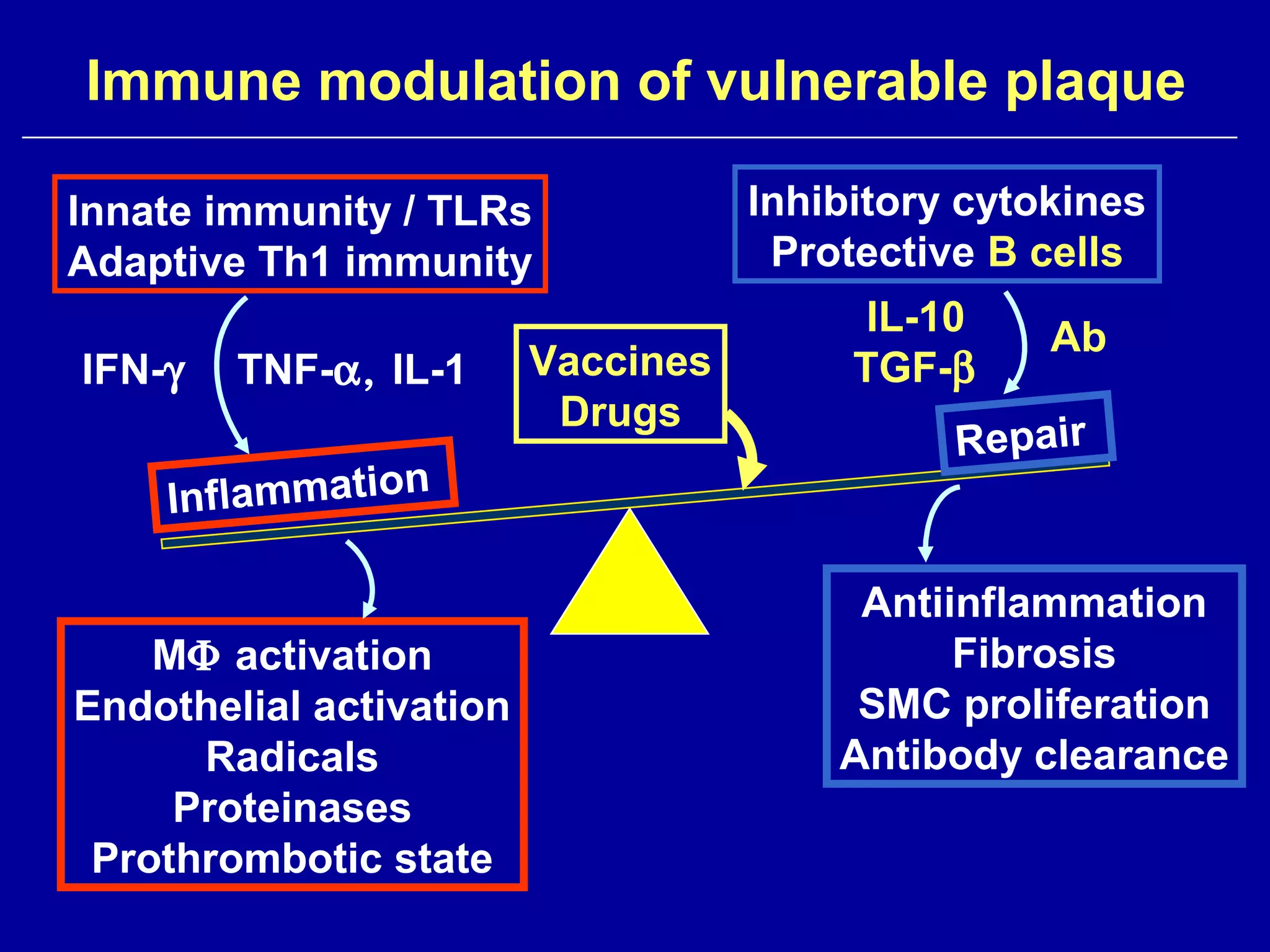
This document discusses potential immune-based therapies for modulating atherosclerosis and vulnerable plaque. It summarizes that:
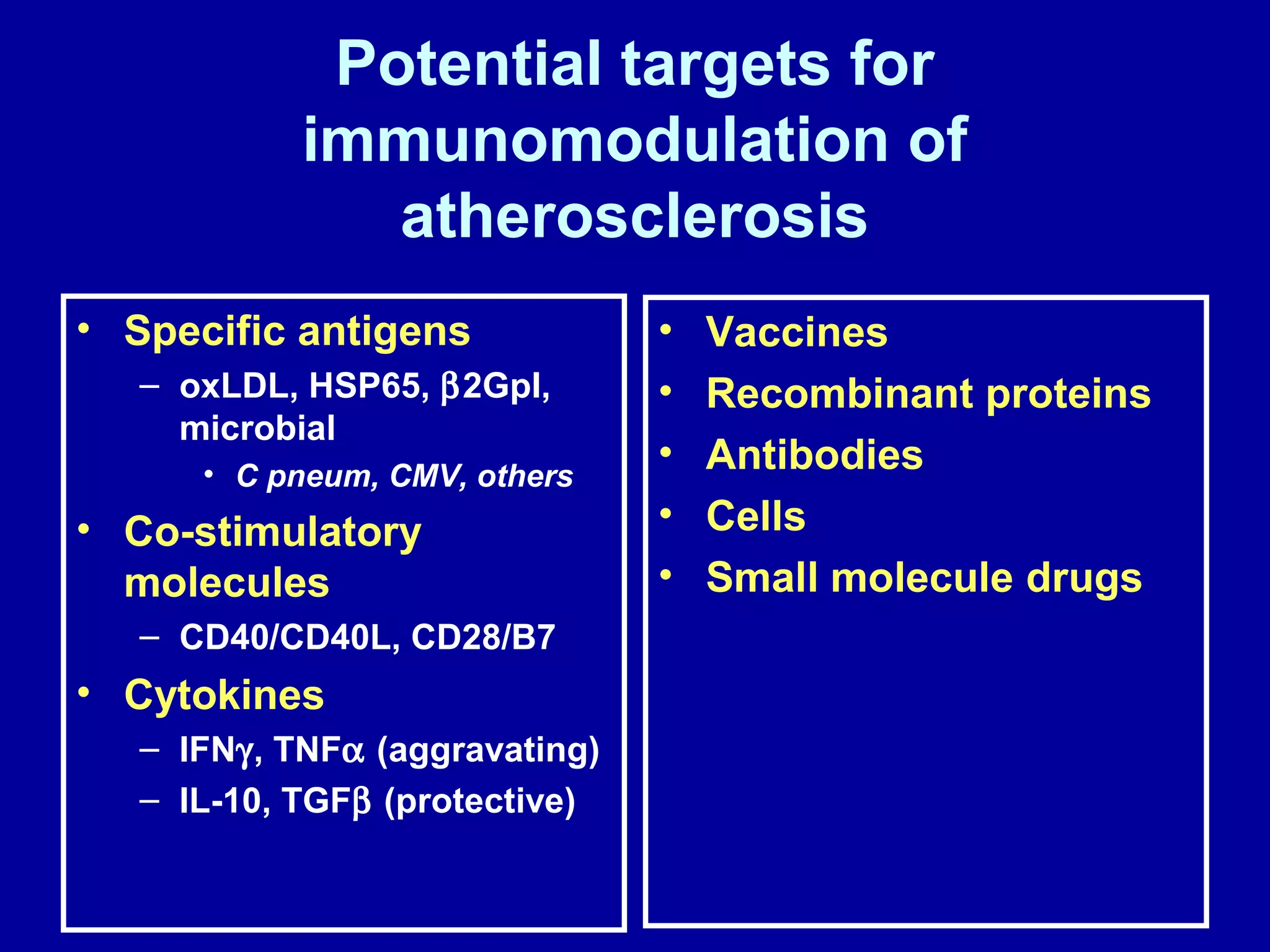
1. Specific antigens, co-stimulatory molecules, cytokines, vaccines, recombinant proteins, antibodies, and cells could be potential targets for immunomodulation of atherosclerosis.
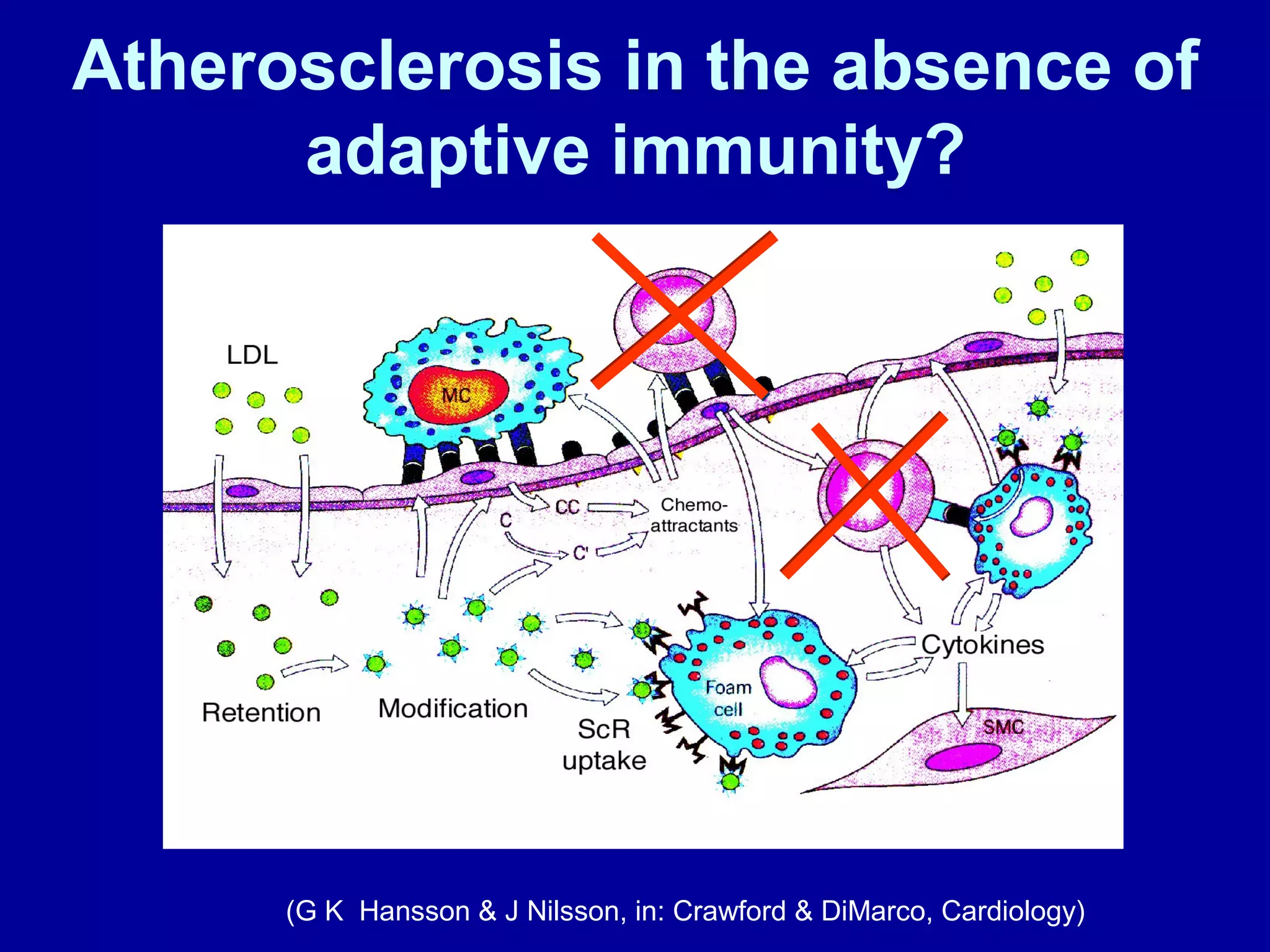
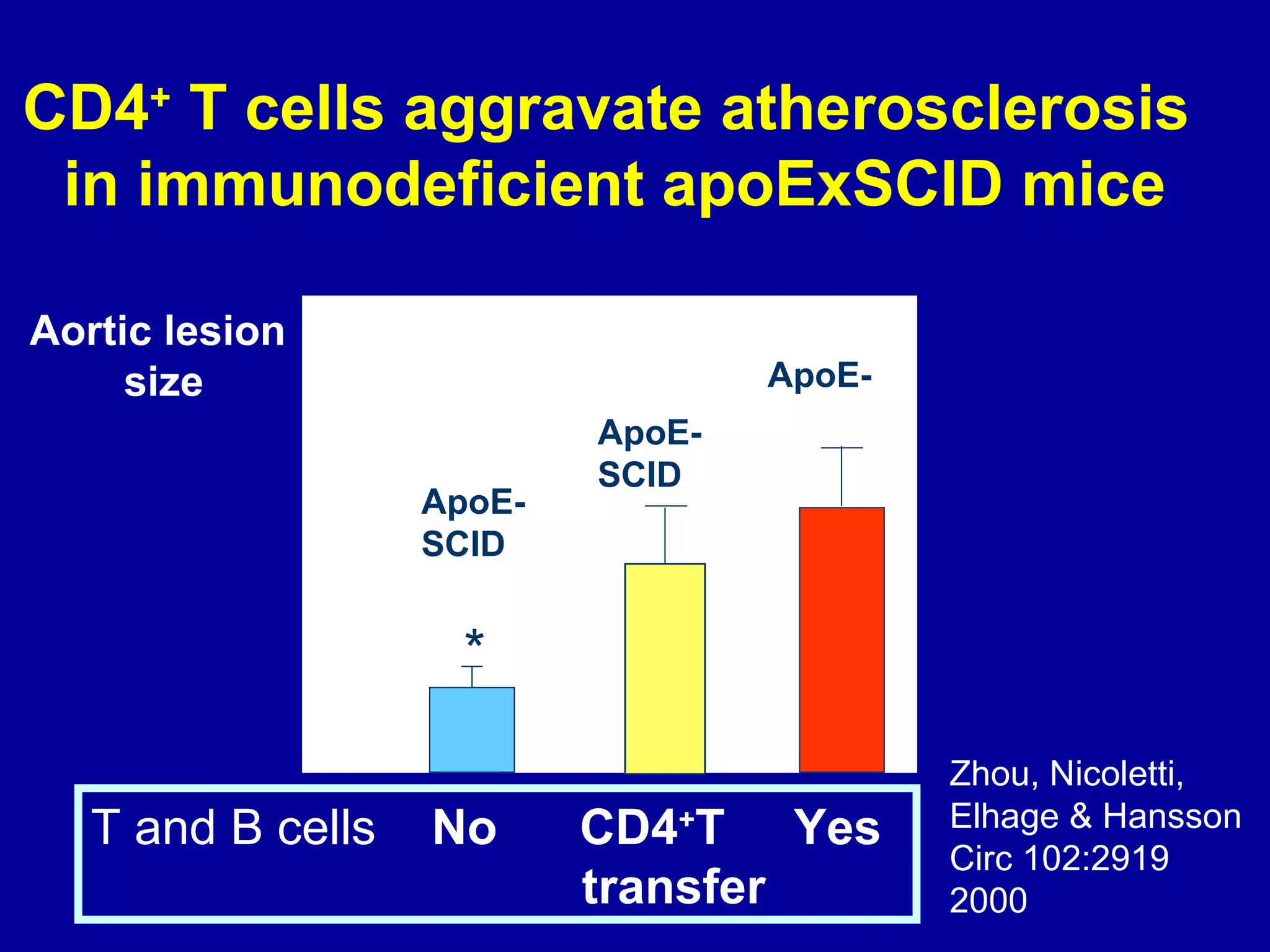
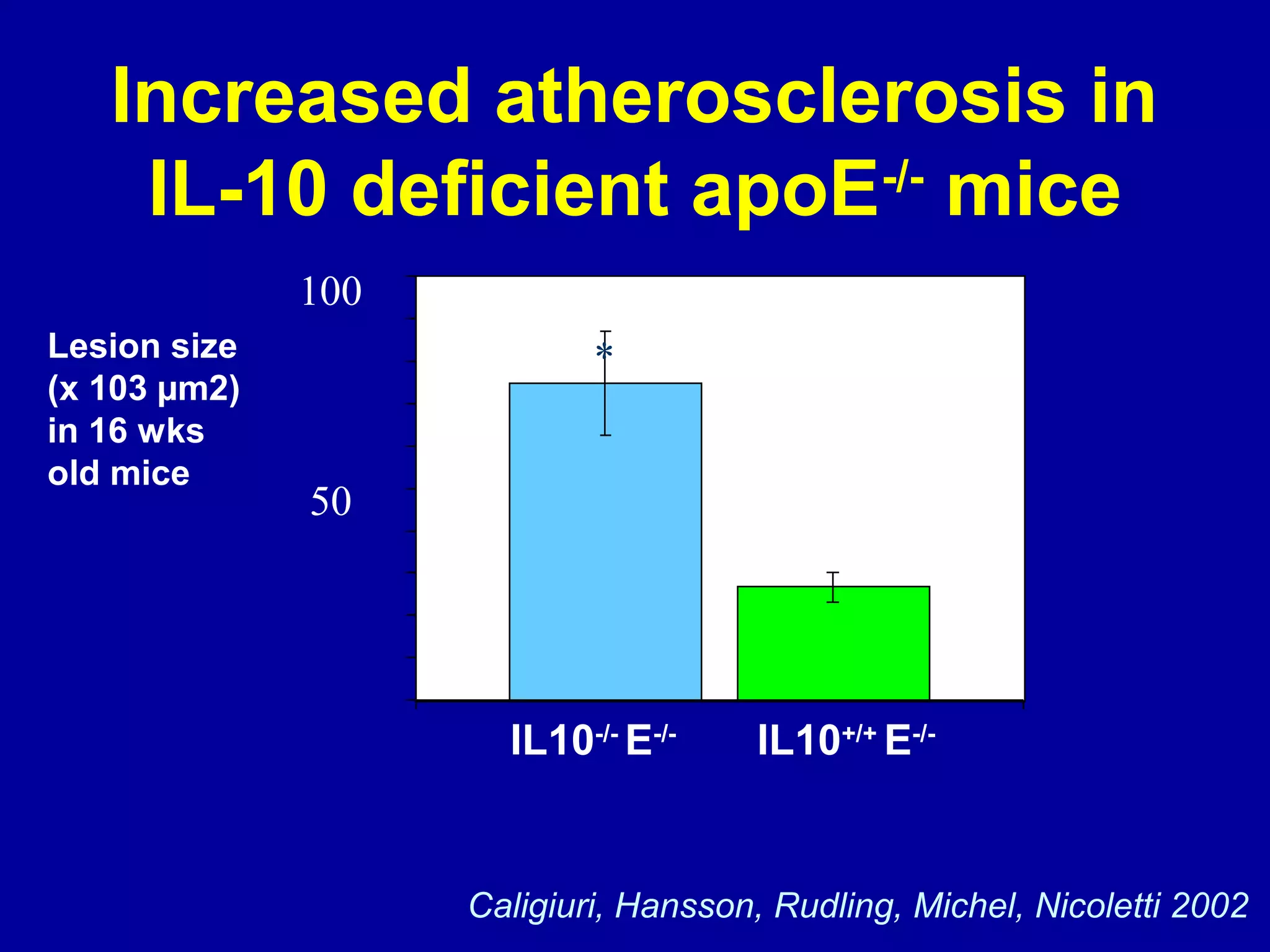
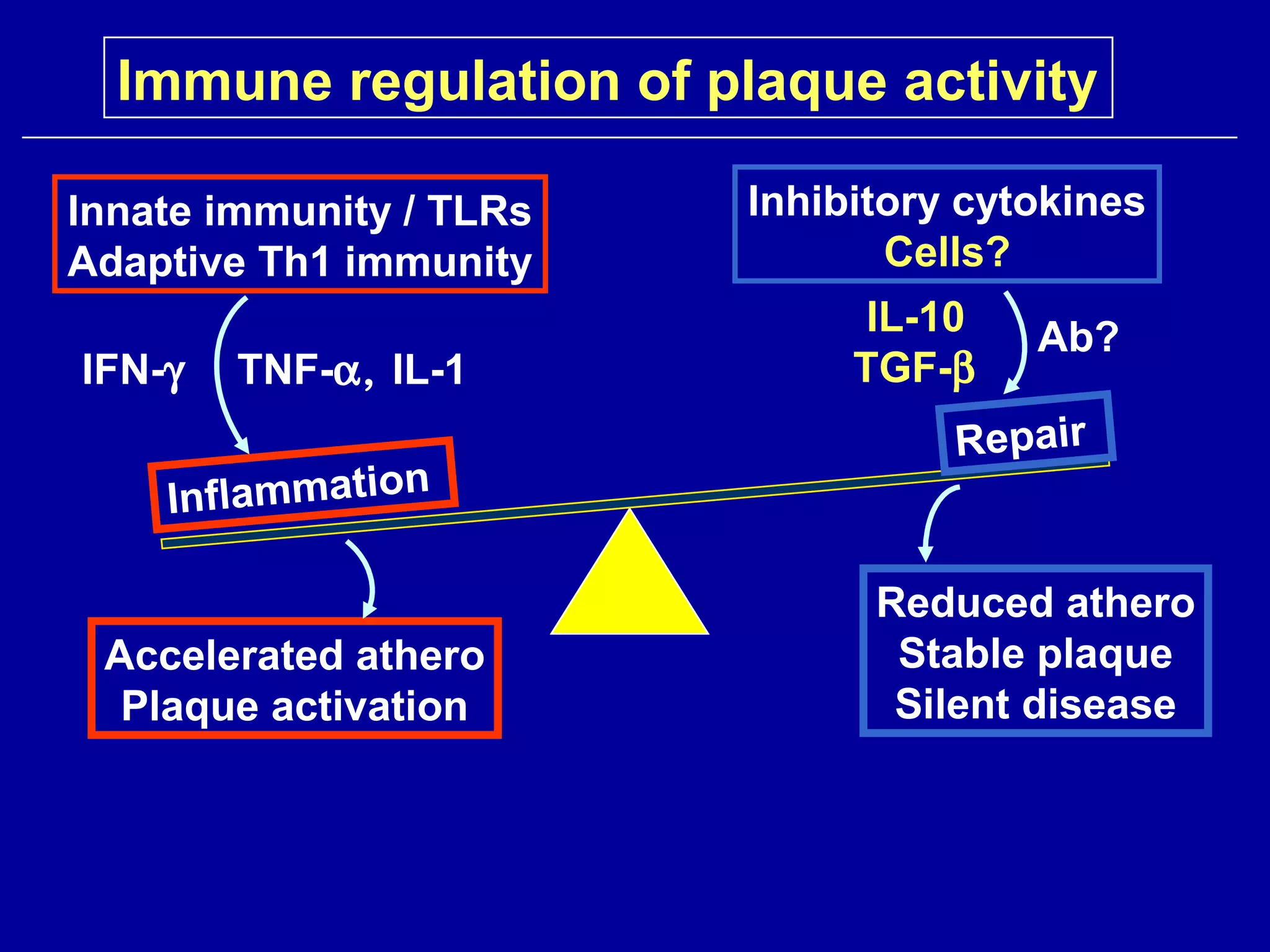
2. While general immunosuppression may reduce atherosclerosis in animal studies, it has substantial side effects for infections and direct vascular effects that make it unsuitable for chronic treatment in humans.
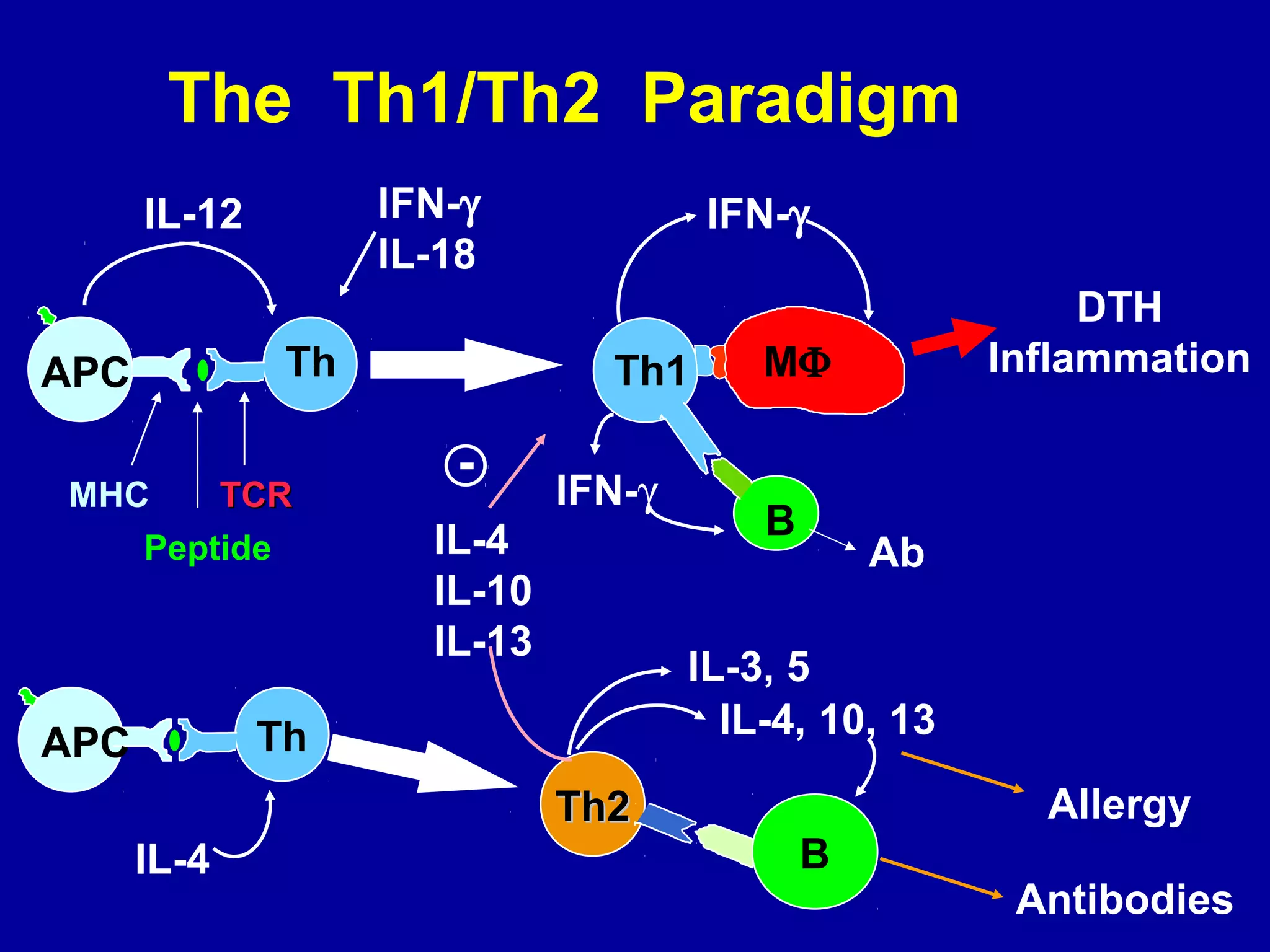
3. Modulating the Th1/Th2 balance, inducing protective antibodies through vaccination against oxidized LDL or heat shock proteins, and using small molecule drugs that inhibit Th1 responses like statins and pentoxifyllin are promising