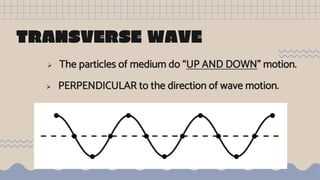
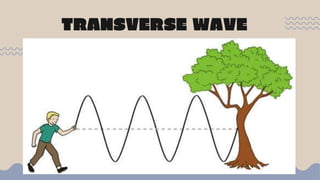
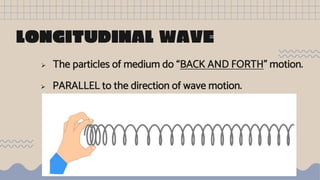
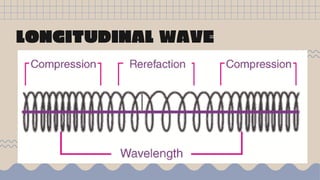
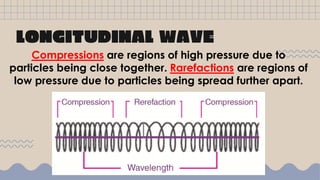
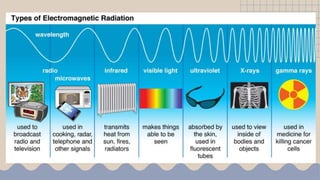
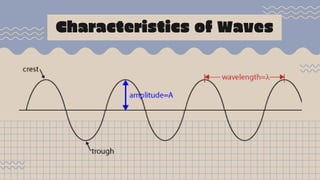
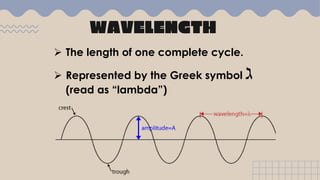
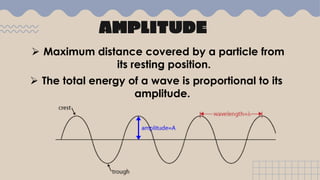
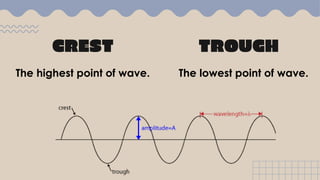
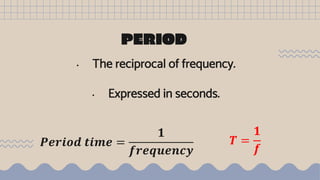
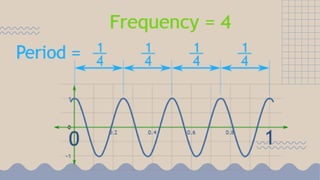
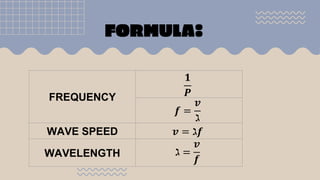
Waves transfer energy from one place to another as a disturbance that travels through a medium or space. There are two main types of mechanical waves: transverse waves, where the particle motion of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of wave travel, and longitudinal waves, where particle motion is parallel. Characteristics of waves include wavelength, amplitude, frequency, period, and wave speed, which can be calculated using the formulas relating these properties.