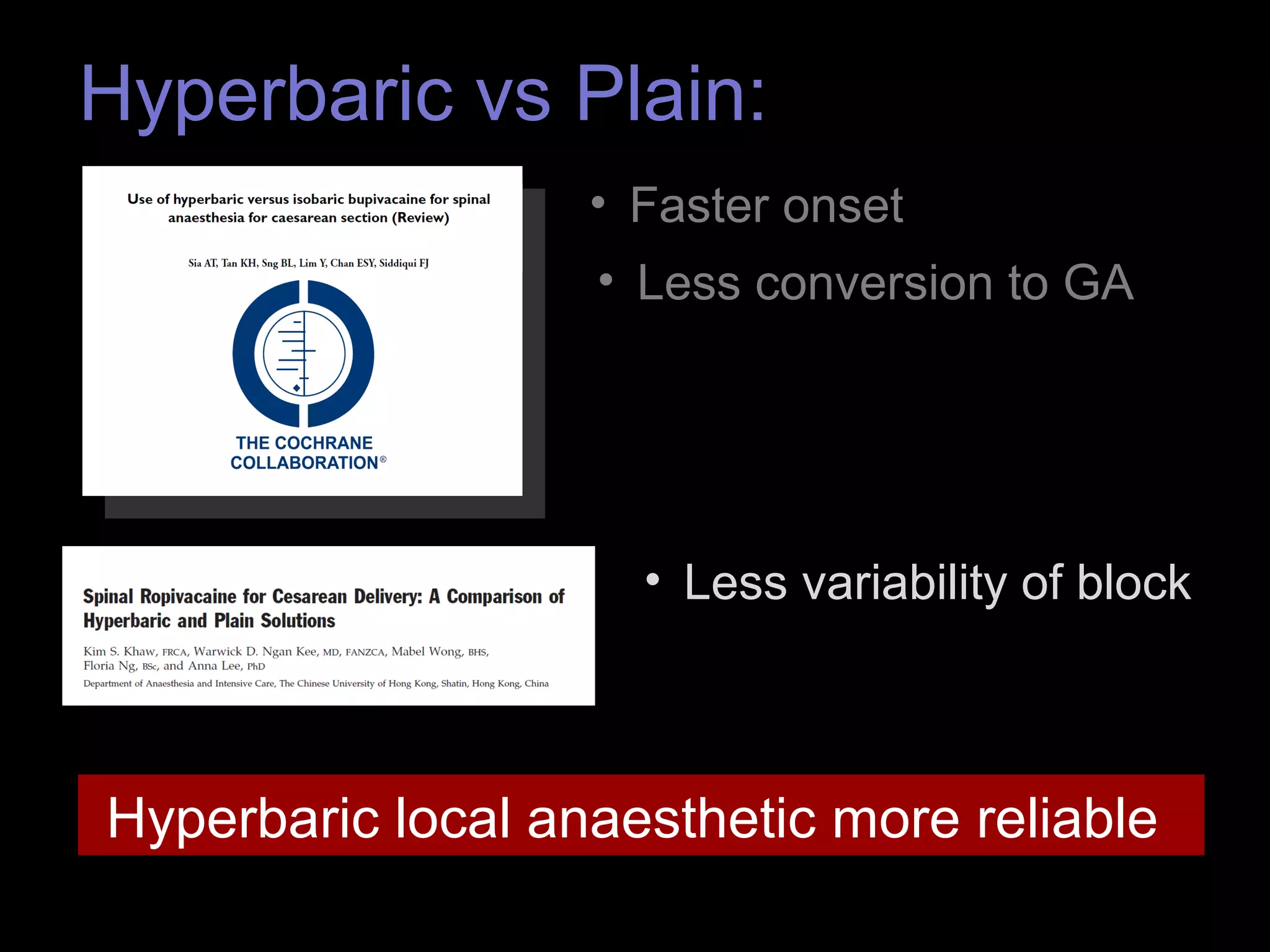
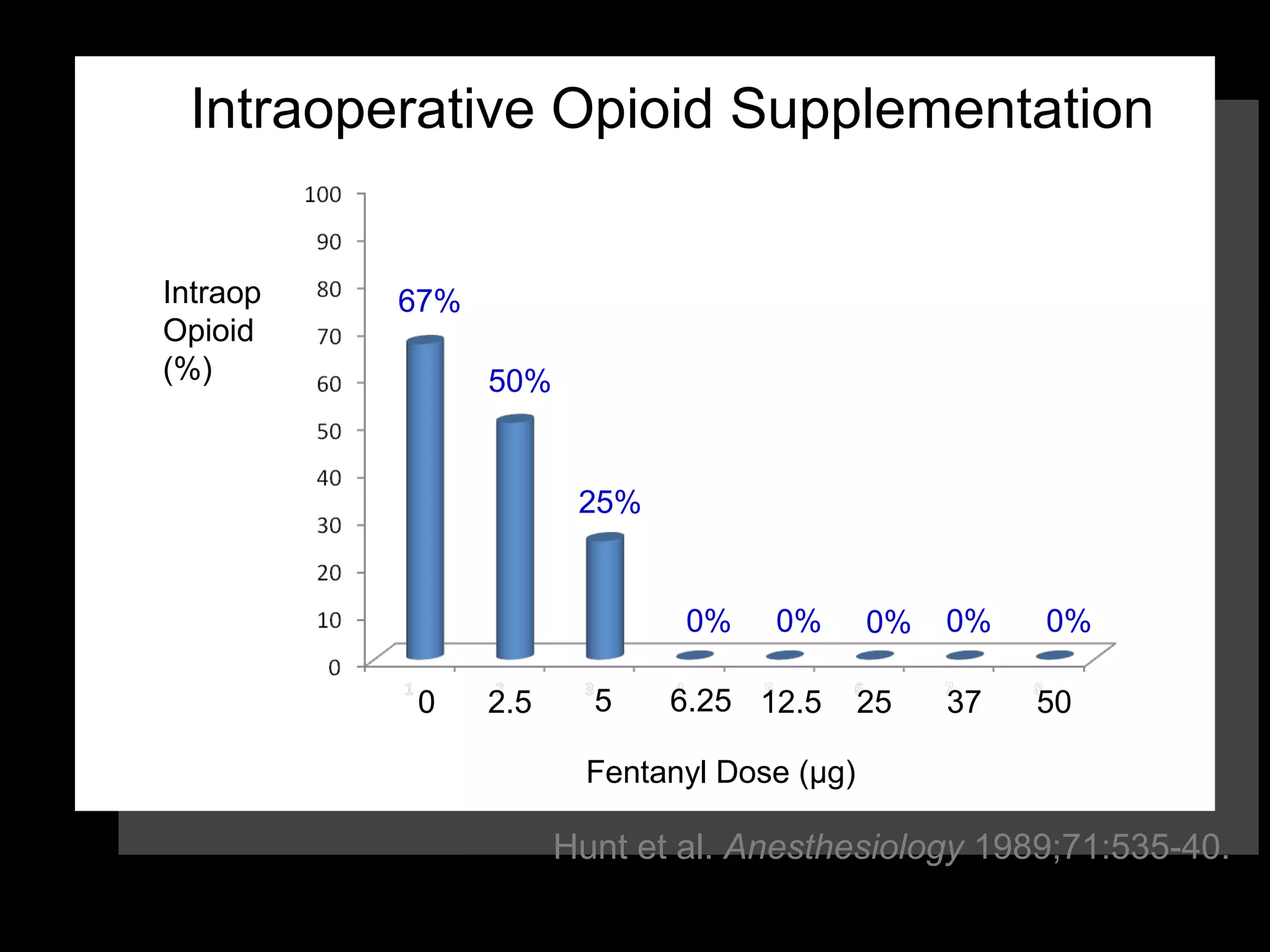
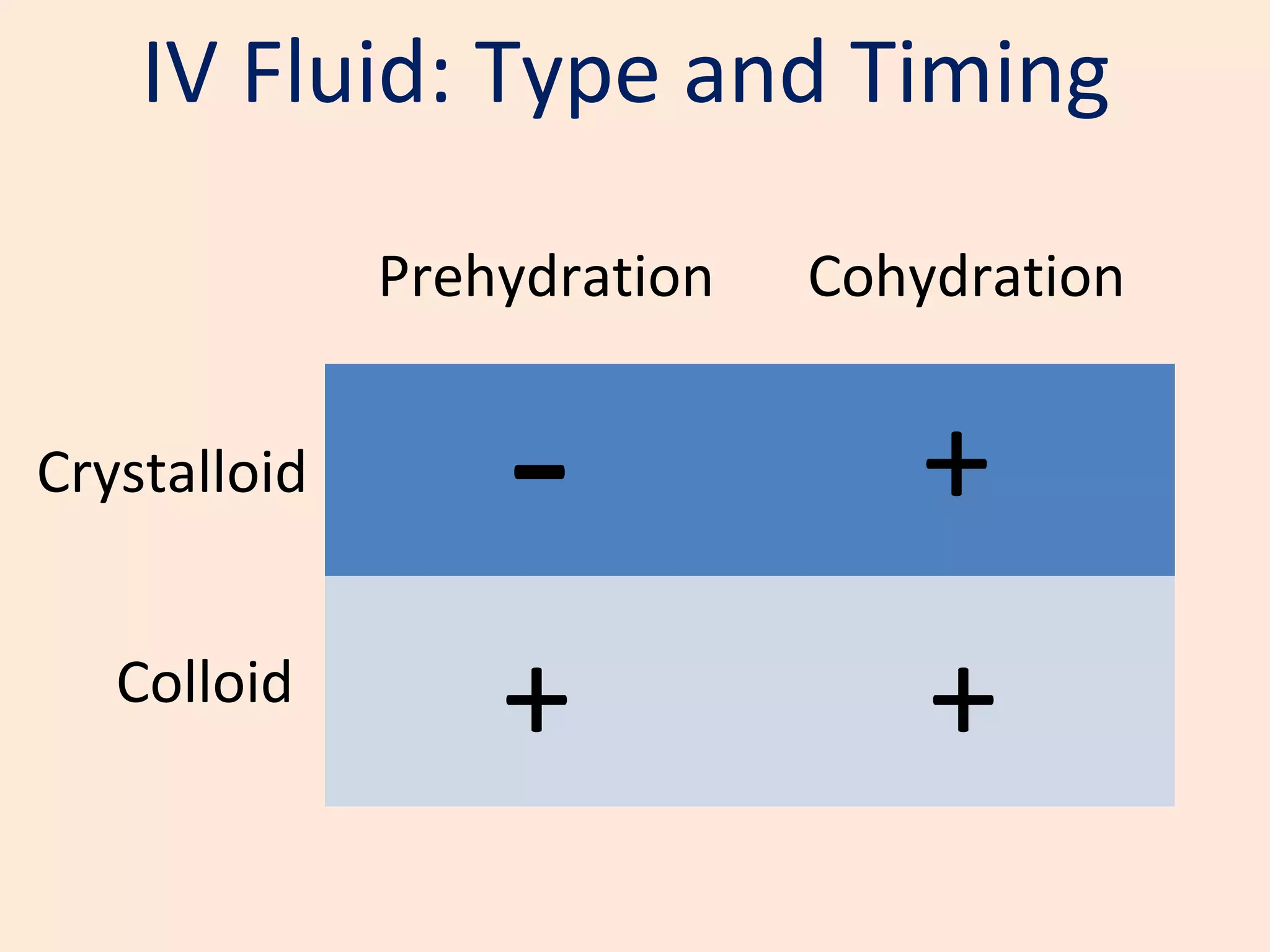
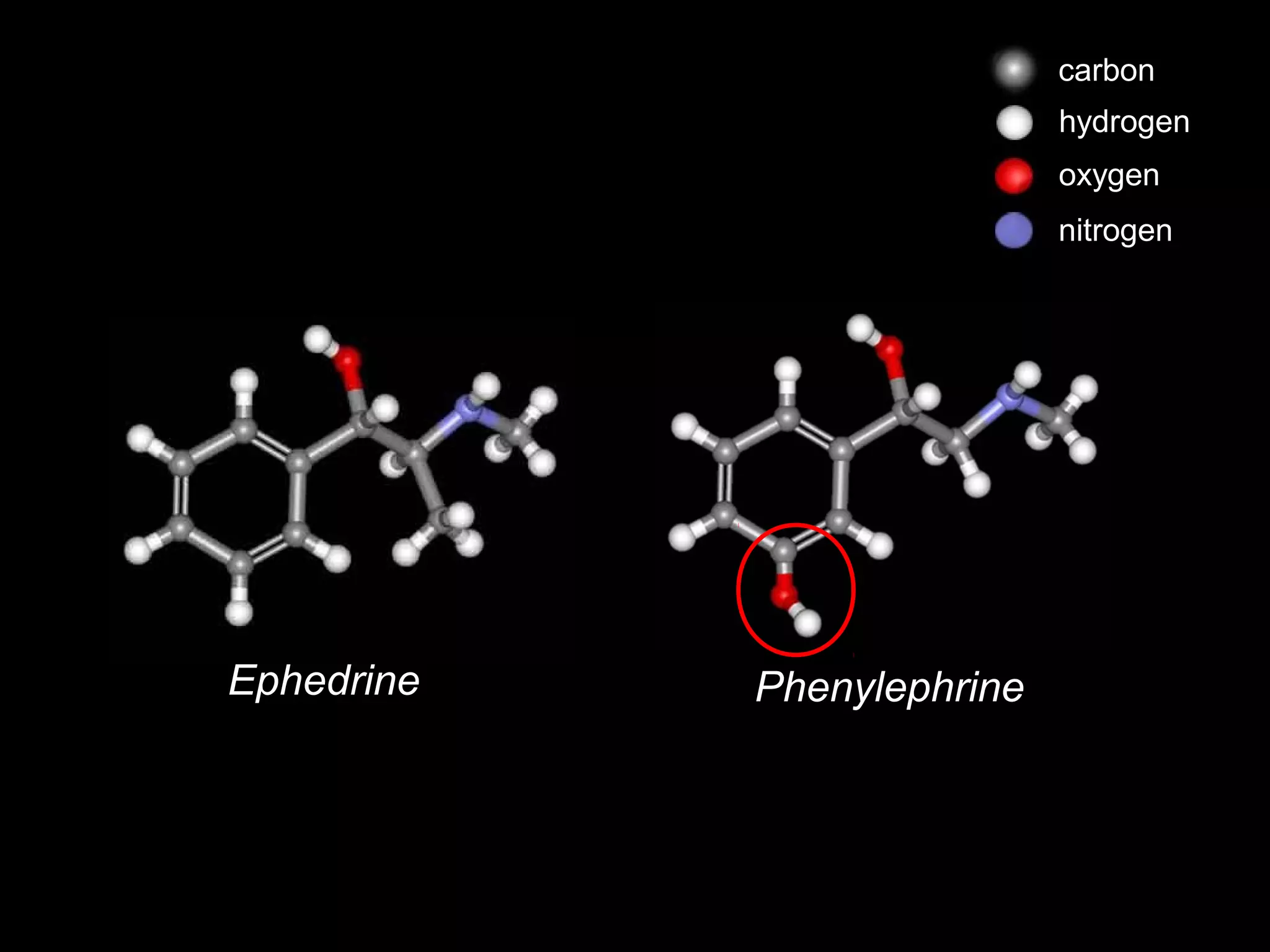
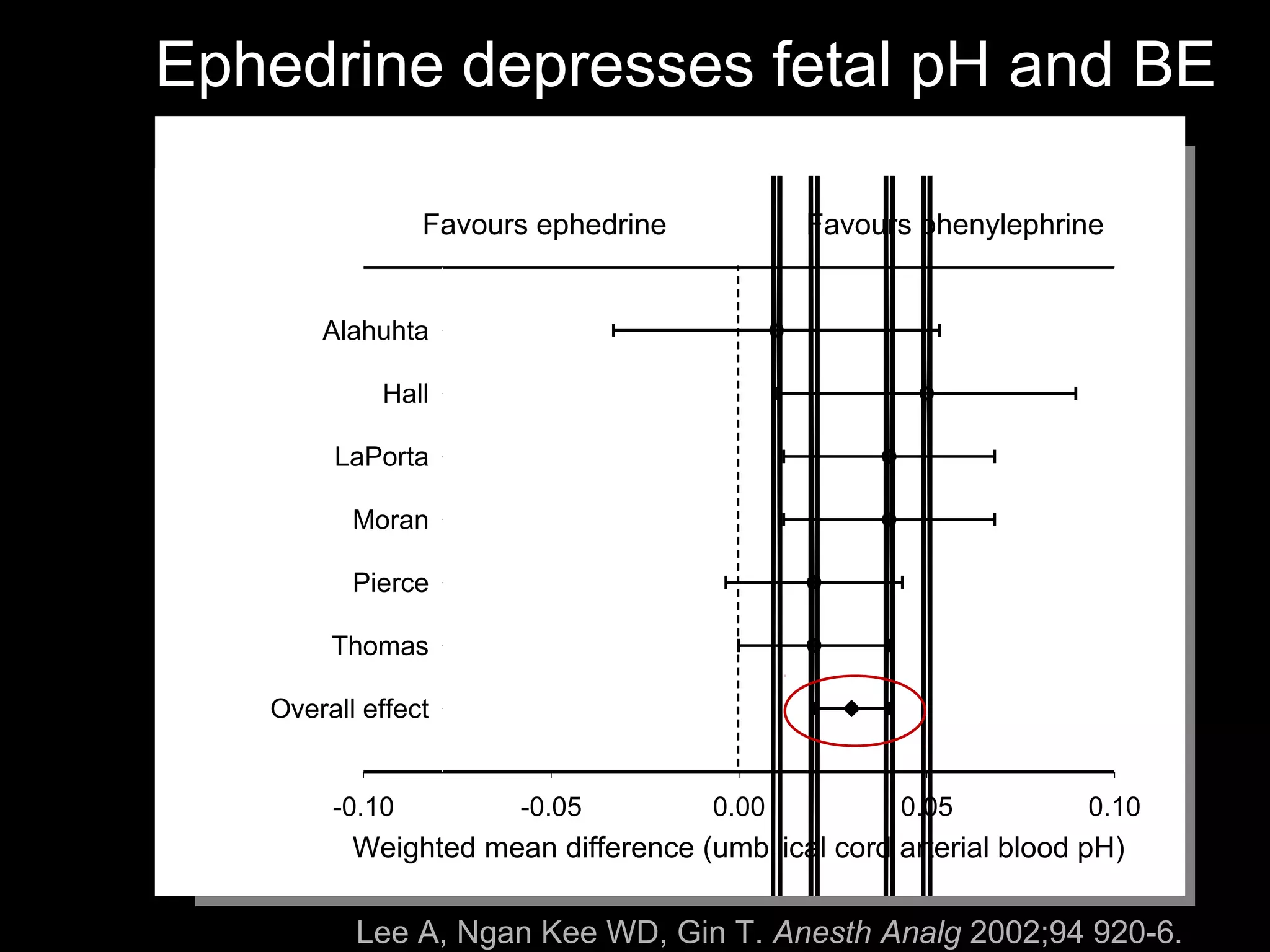
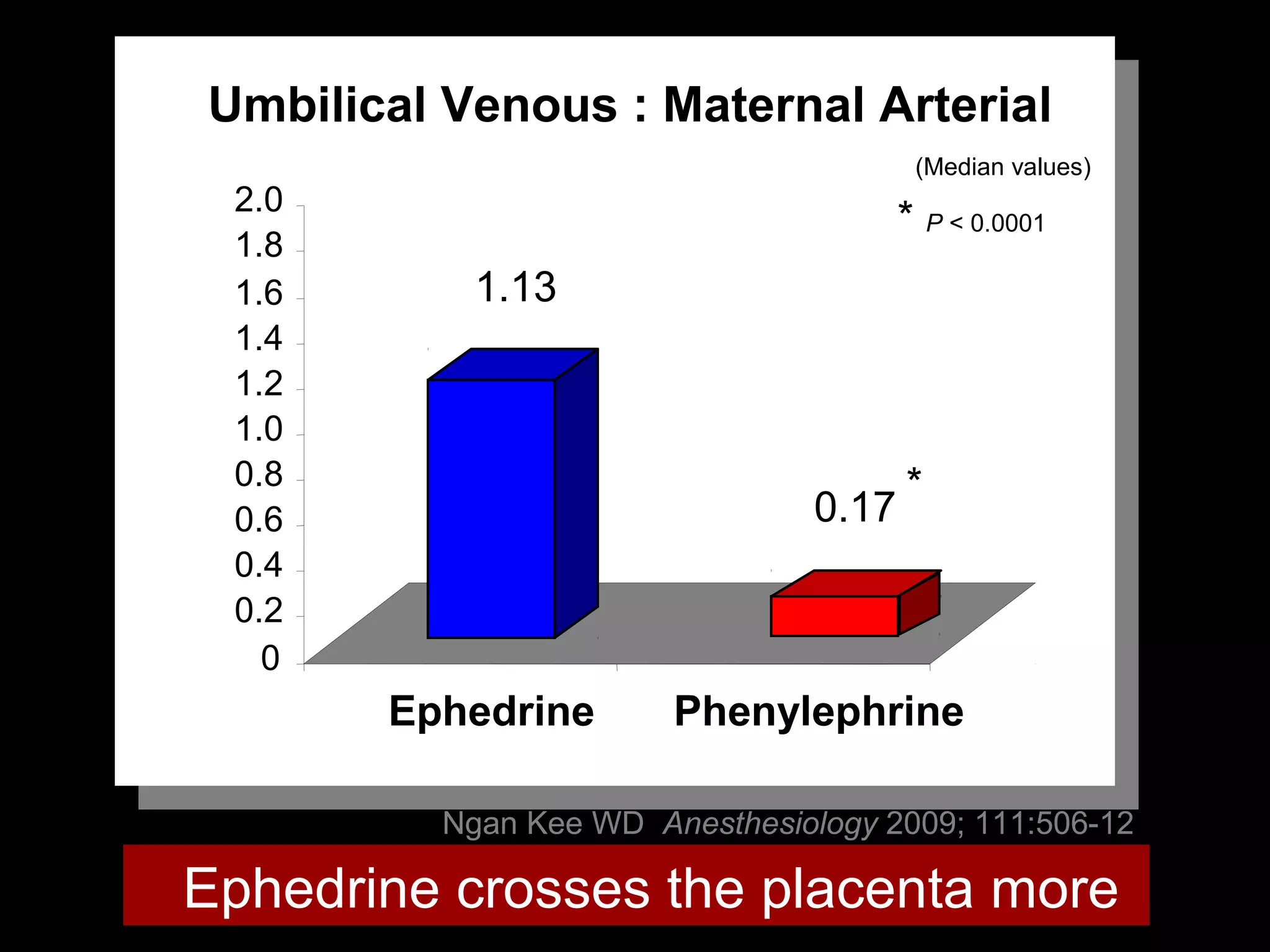
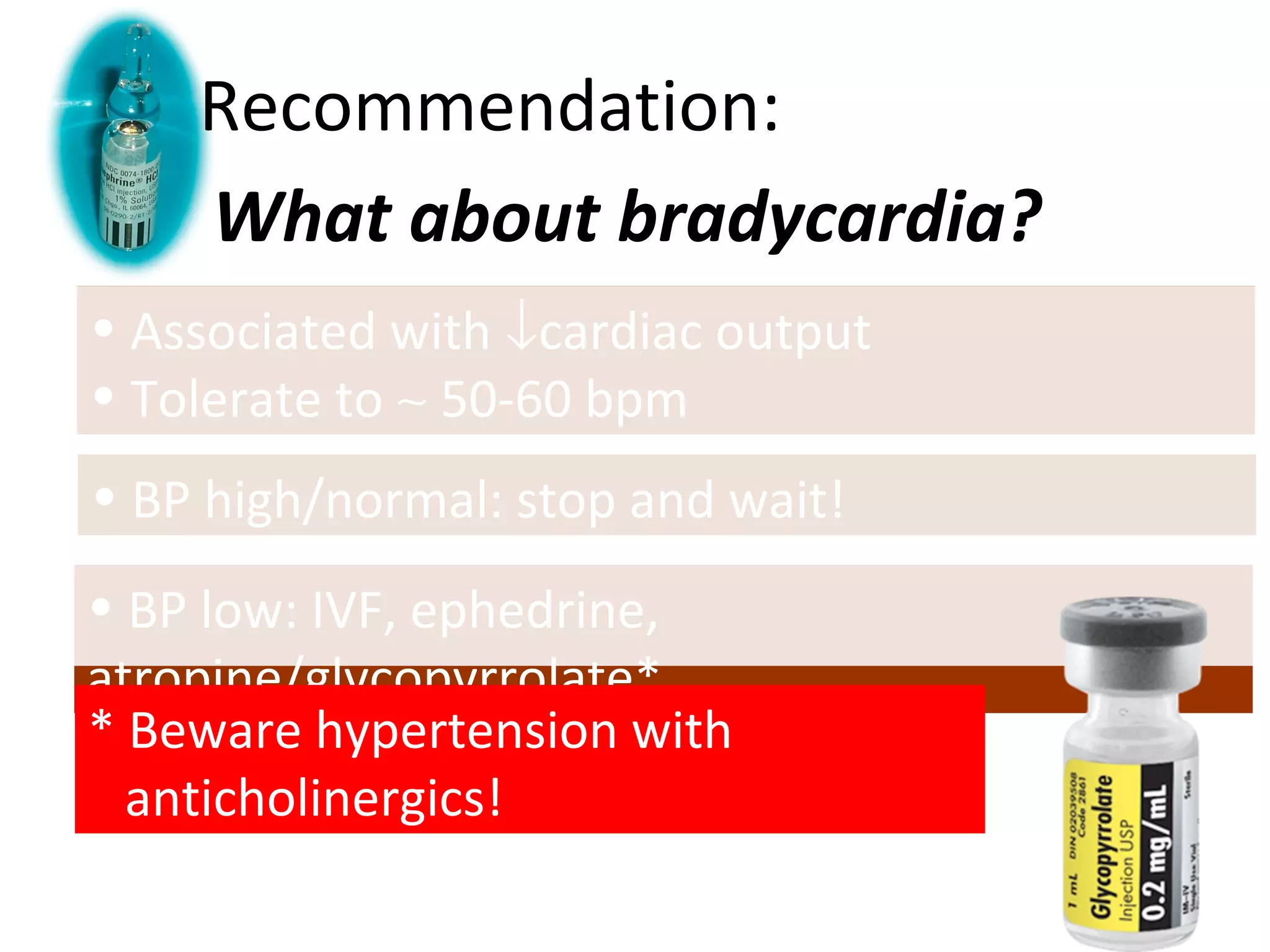
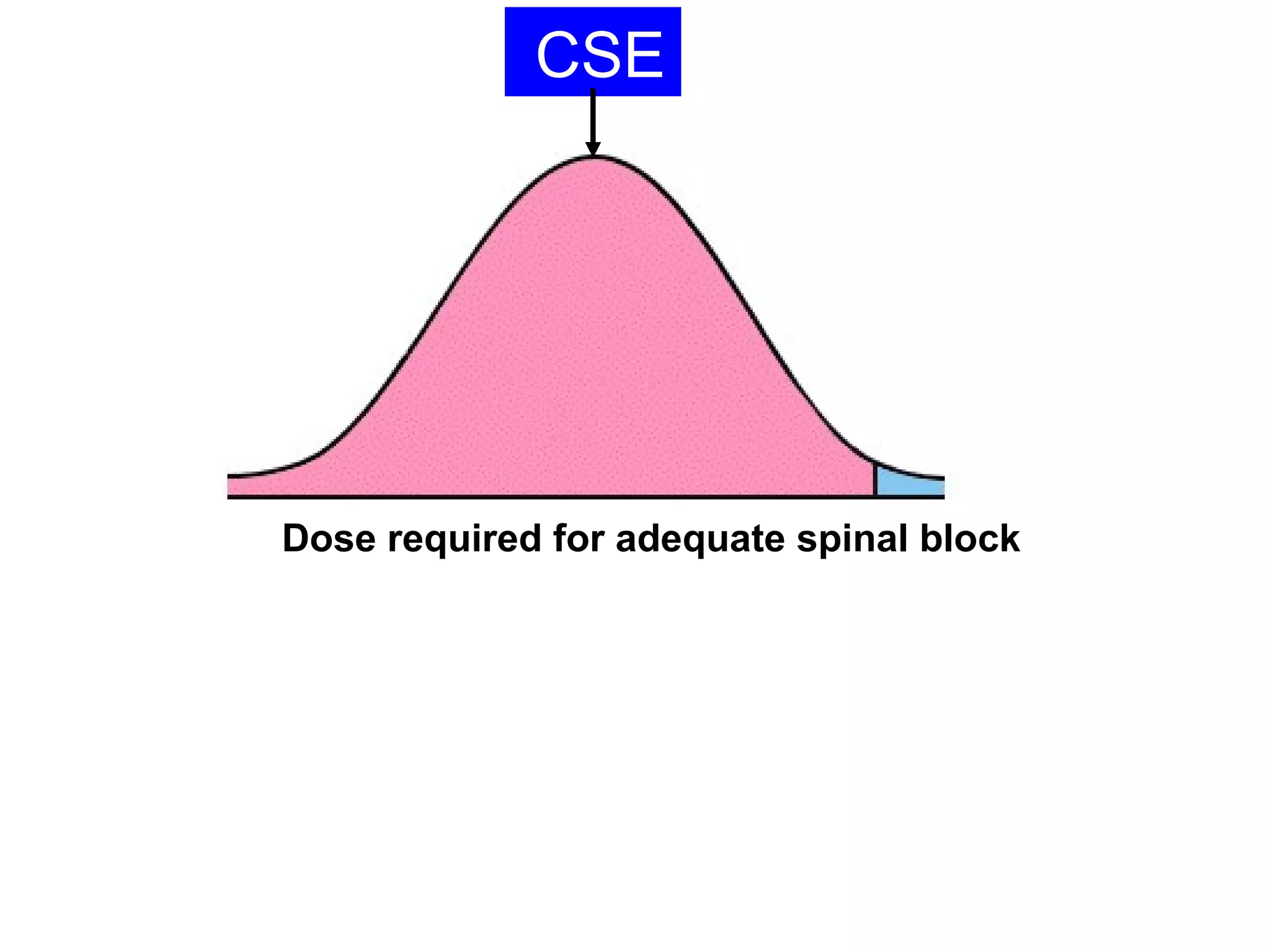
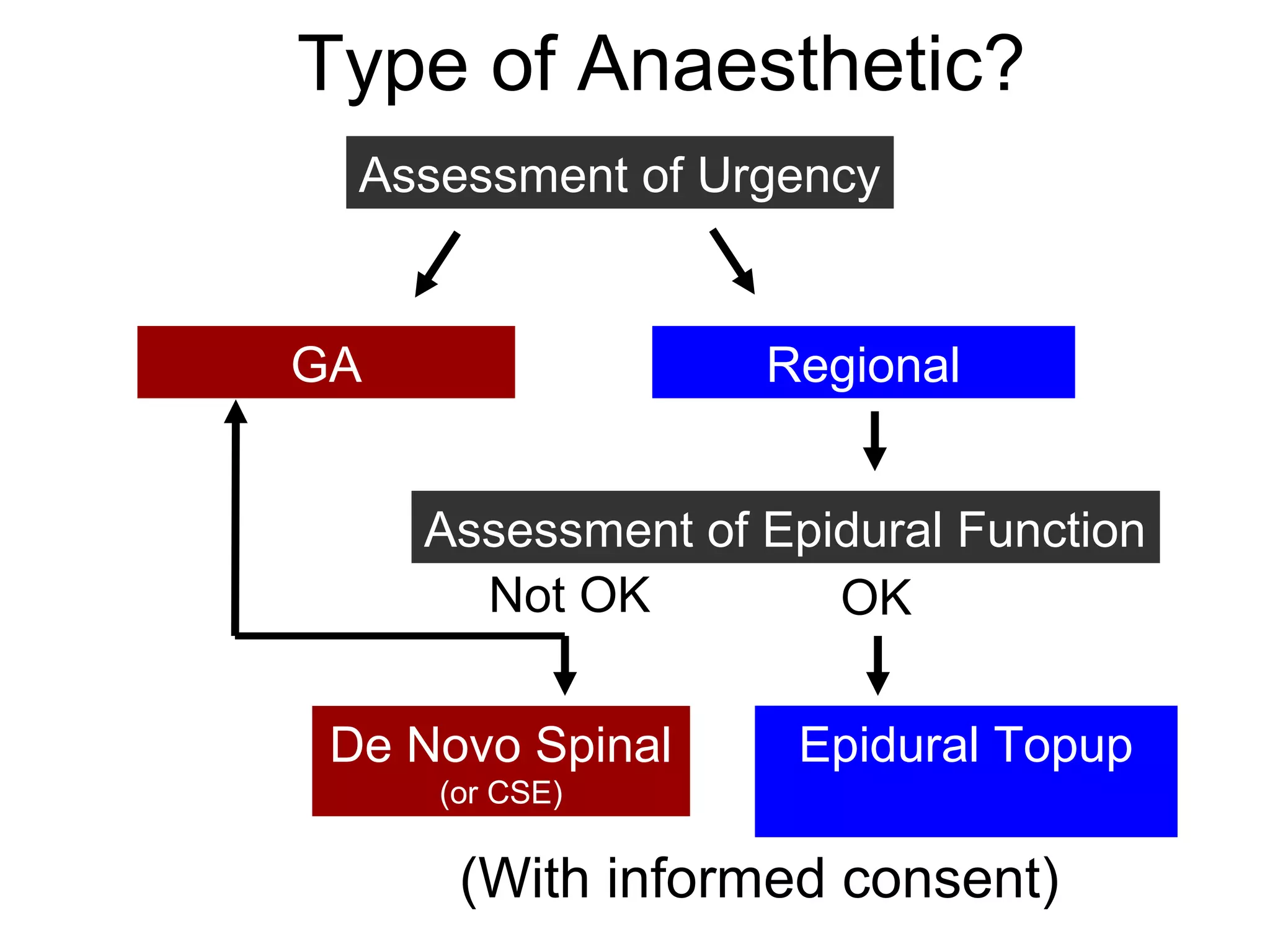
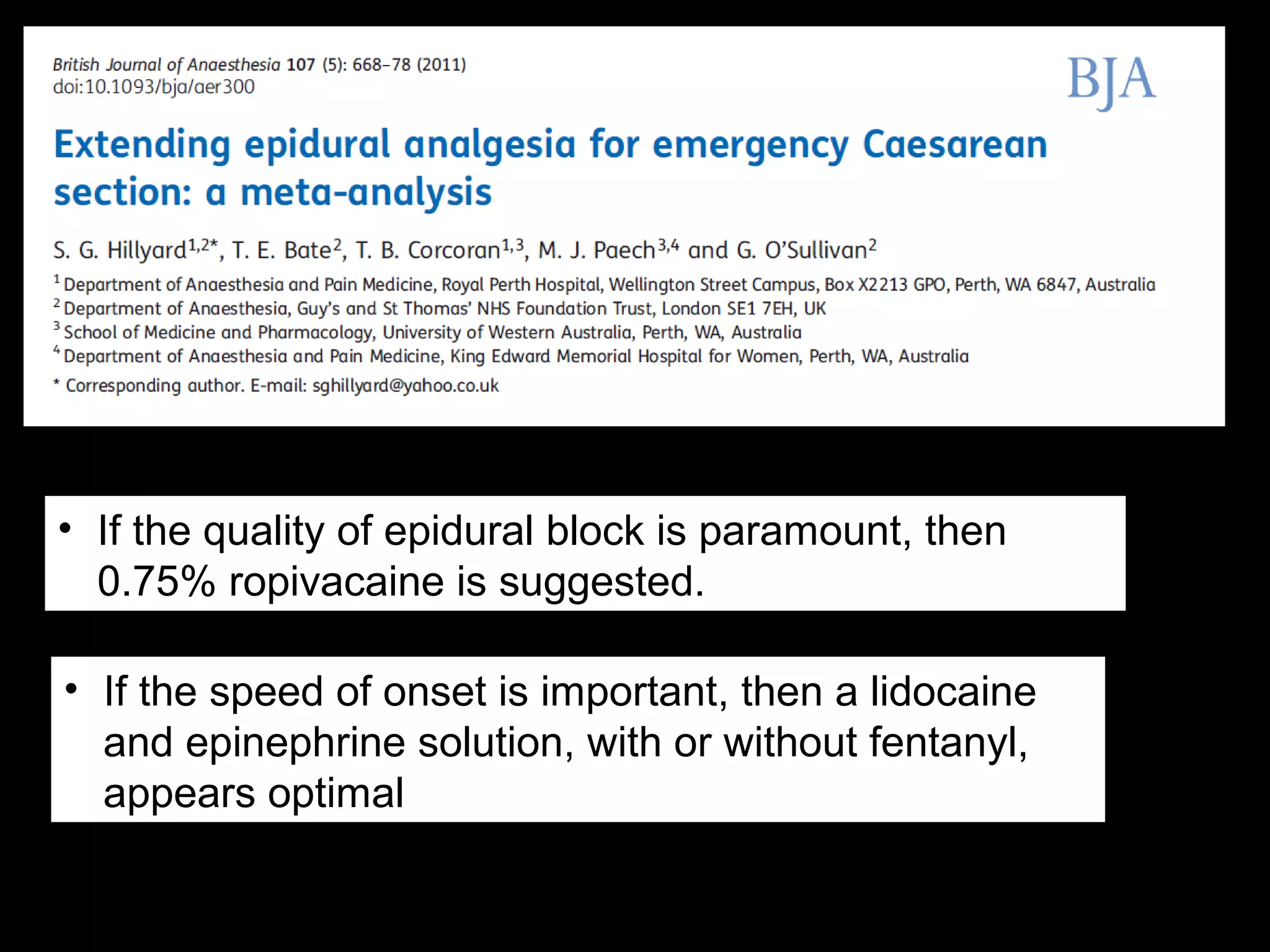
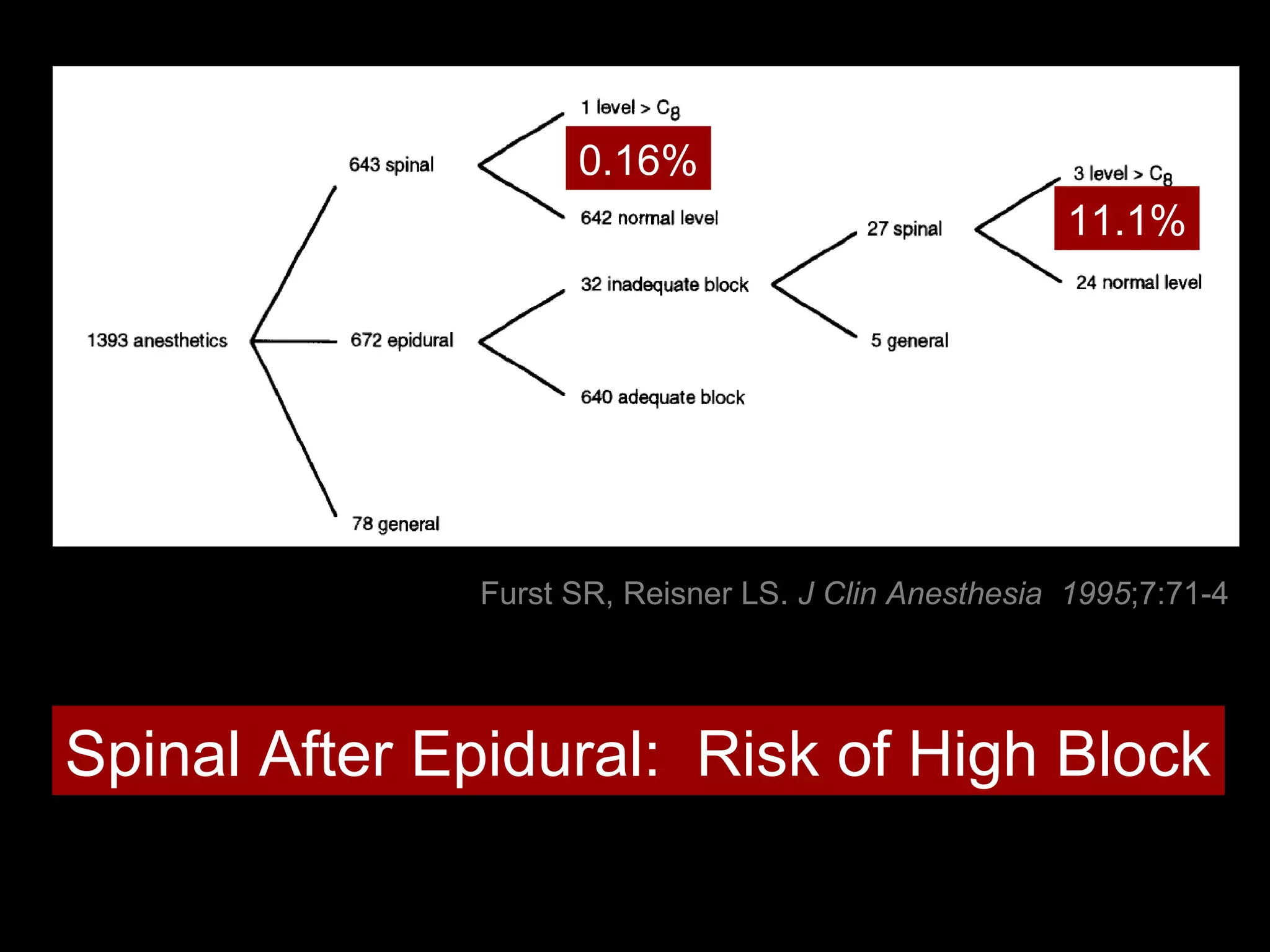
The document discusses regional anesthesia techniques for caesarean section. It recommends using hyperbaric bupivacaine with fentanyl for spinal anesthesia. It suggests crystalloid cohydration for intravenous fluids and using phenylephrine instead of ephedrine as the vasopressor. The document also recommends combined spinal-epidural anesthesia to reduce spinal doses and improve hemodynamic stability. It provides guidance on epidural top-ups or converting to spinal anesthesia if the epidural fails. The key points emphasize optimal drug choices, fluid management, hemodynamic control and contingency plans for regional anesthesia during caesarean sections.