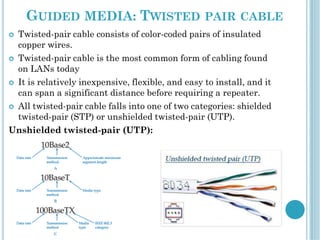
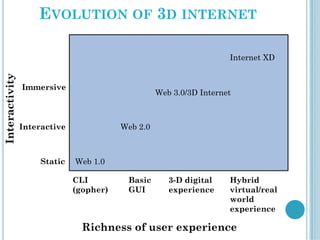
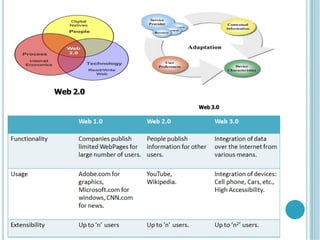
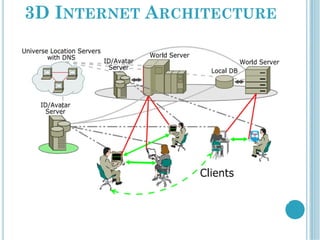
The document discusses the evolution of the internet from 2D to 3D and the concept of a 3D internet. It describes how a 3D internet would combine the power of the internet with 3D graphics to create an immersive virtual environment for interaction and communication. The key components of a 3D internet architecture are described as world servers to host 3D environments, avatar servers to manage user identities and profiles, and client programs to access the virtual worlds. Examples of applications for a 3D internet include social networks, virtual tourism sites, and streaming 3D content.