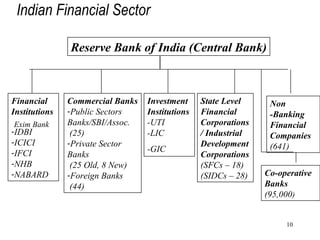
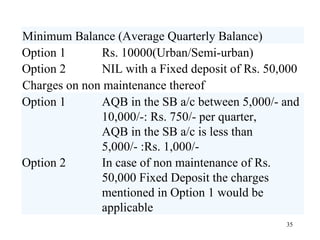
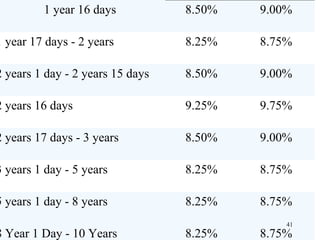
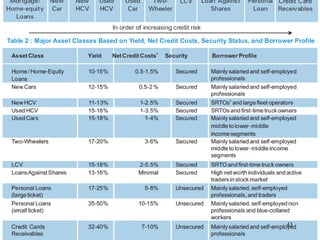
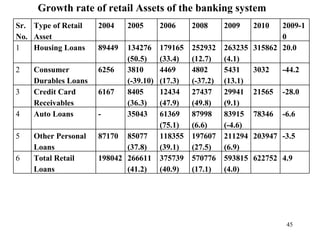
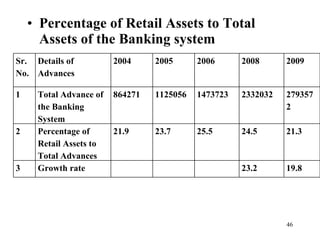
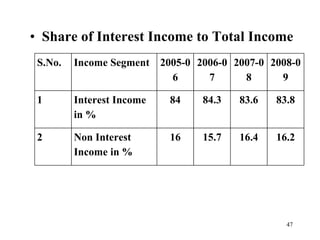
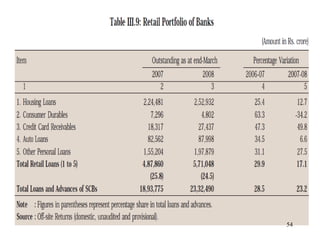
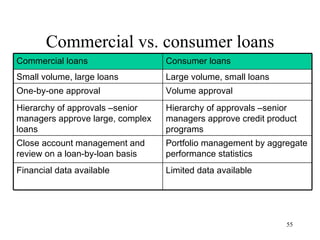
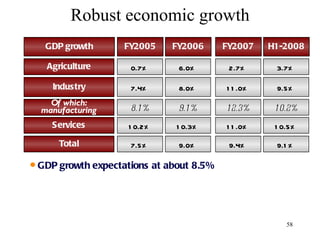
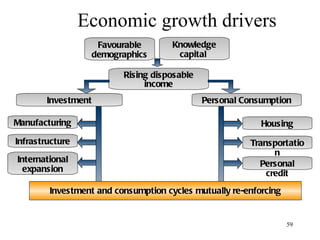
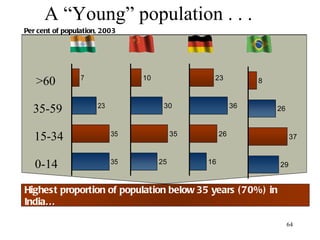
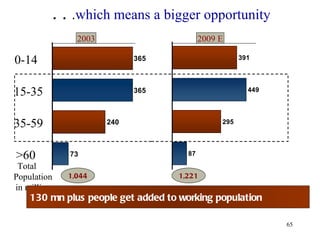
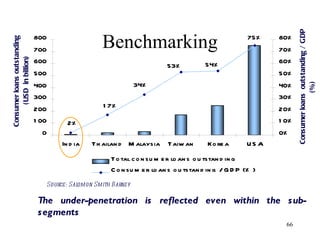
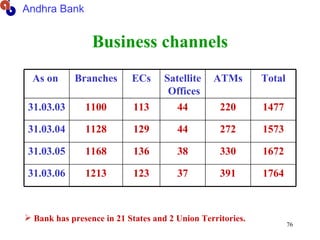
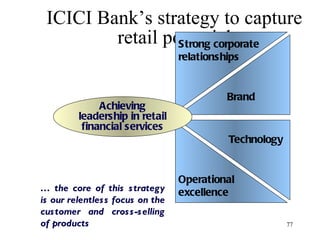
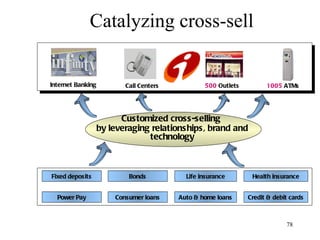
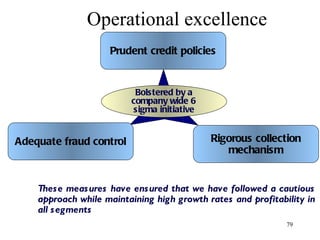
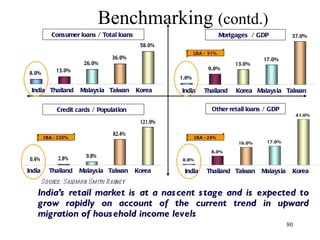
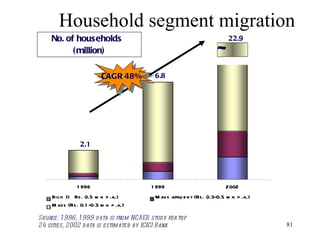
The document discusses various types of banking in India including retail banking, commercial banking, cooperative banking, development banking, and investment banking. It explains the key differences between retail banking and wholesale banking. Retail banking deals with individual customers through products like savings accounts, credit cards, personal loans, mortgages, and car loans. Wholesale banking serves large corporations and institutions through products like working capital loans, trade finance, treasury services, and cash management.