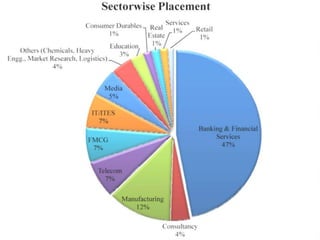
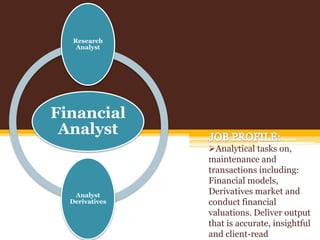
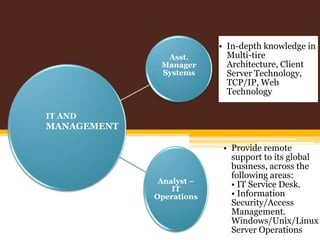
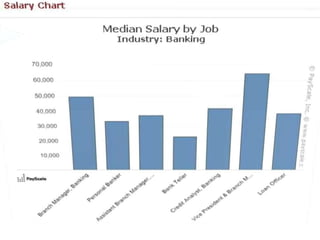
This document provides an overview of the banking sector in India. It discusses the history and evolution of banking in India including the establishment of public sector banks, private sector banks, foreign banks, cooperative banks, and other financial institutions. It also summarizes the roles of the Reserve Bank of India and provides examples of prominent public and private sector banks in India as well as foreign banks operating in the country. Finally, it outlines various career opportunities and job profiles for MBAs in the promising banking sector.