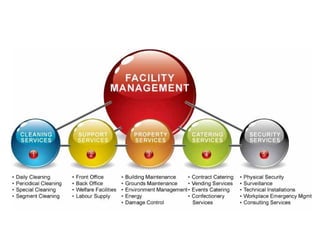
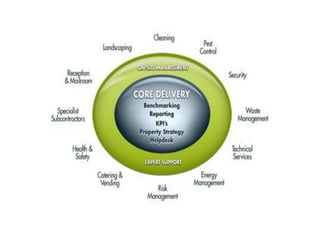
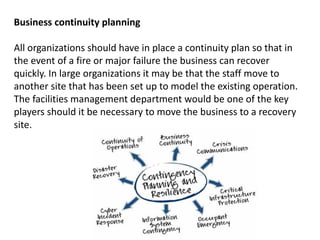
The document summarizes key statistics related to changes in the modern workforce and how they are impacting facility management. Some of the key points include:
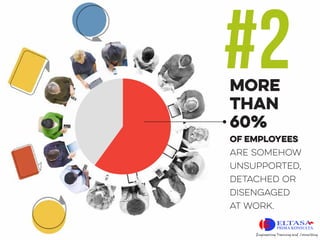
- Facility management costs like office space can cost up to $14,000 per employee annually. Over 60% of employees feel unsupported or disengaged at work.
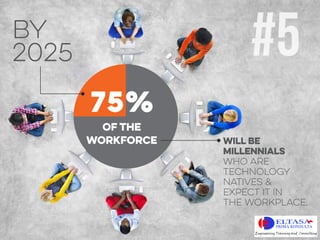
- By 2025, millennials who expect technology in the workplace will make up 75% of the workforce. The average American spends 5.2 hours online daily and 80% of North Americans use the internet.
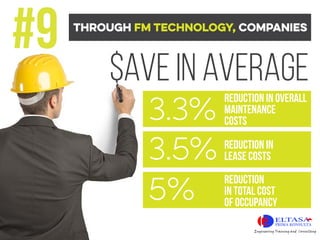
- Through facility management technology, companies can save on average 5% in maintenance costs, 3.5% in lease costs, and 3.3% in total occupancy costs. The