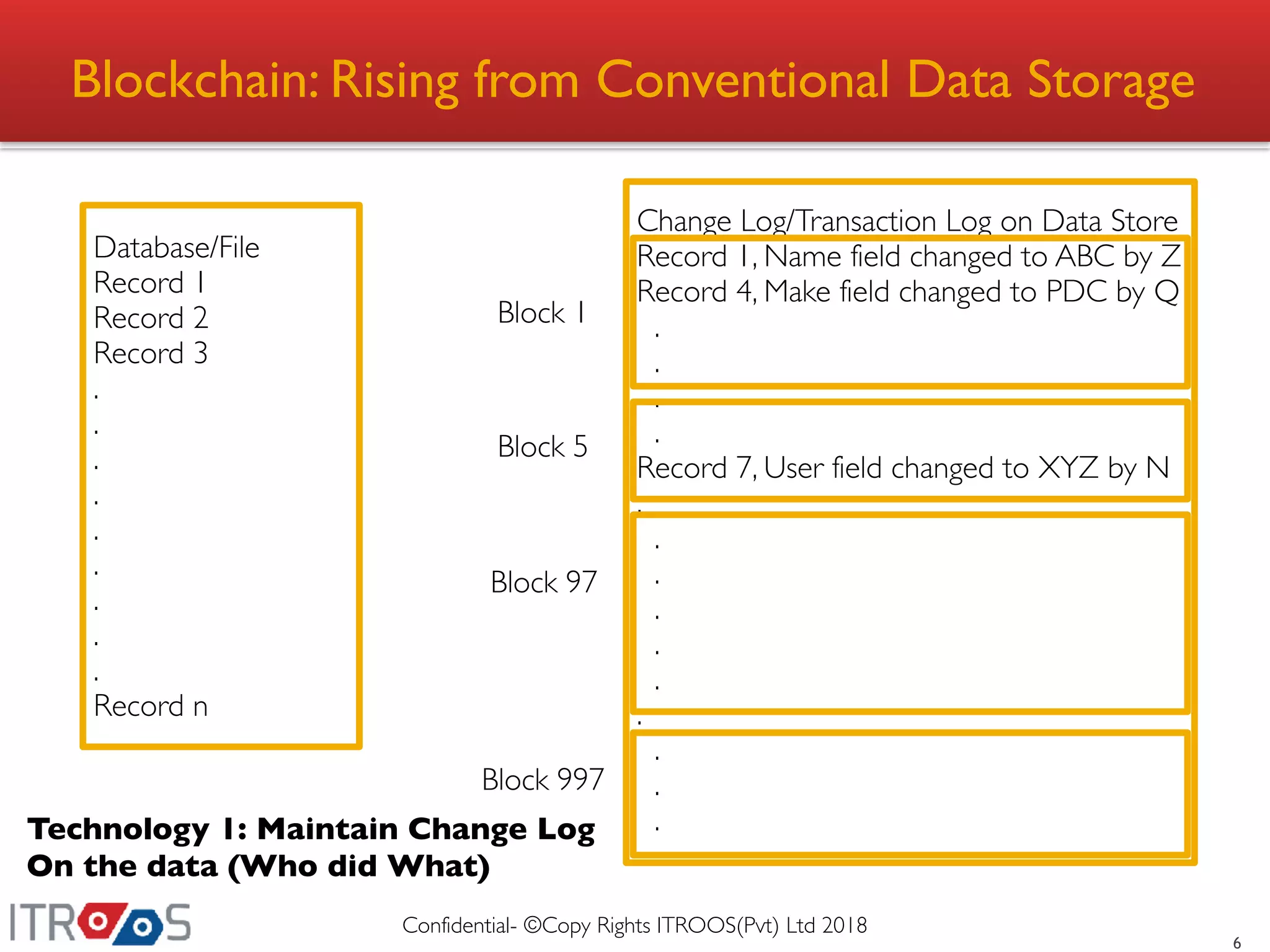
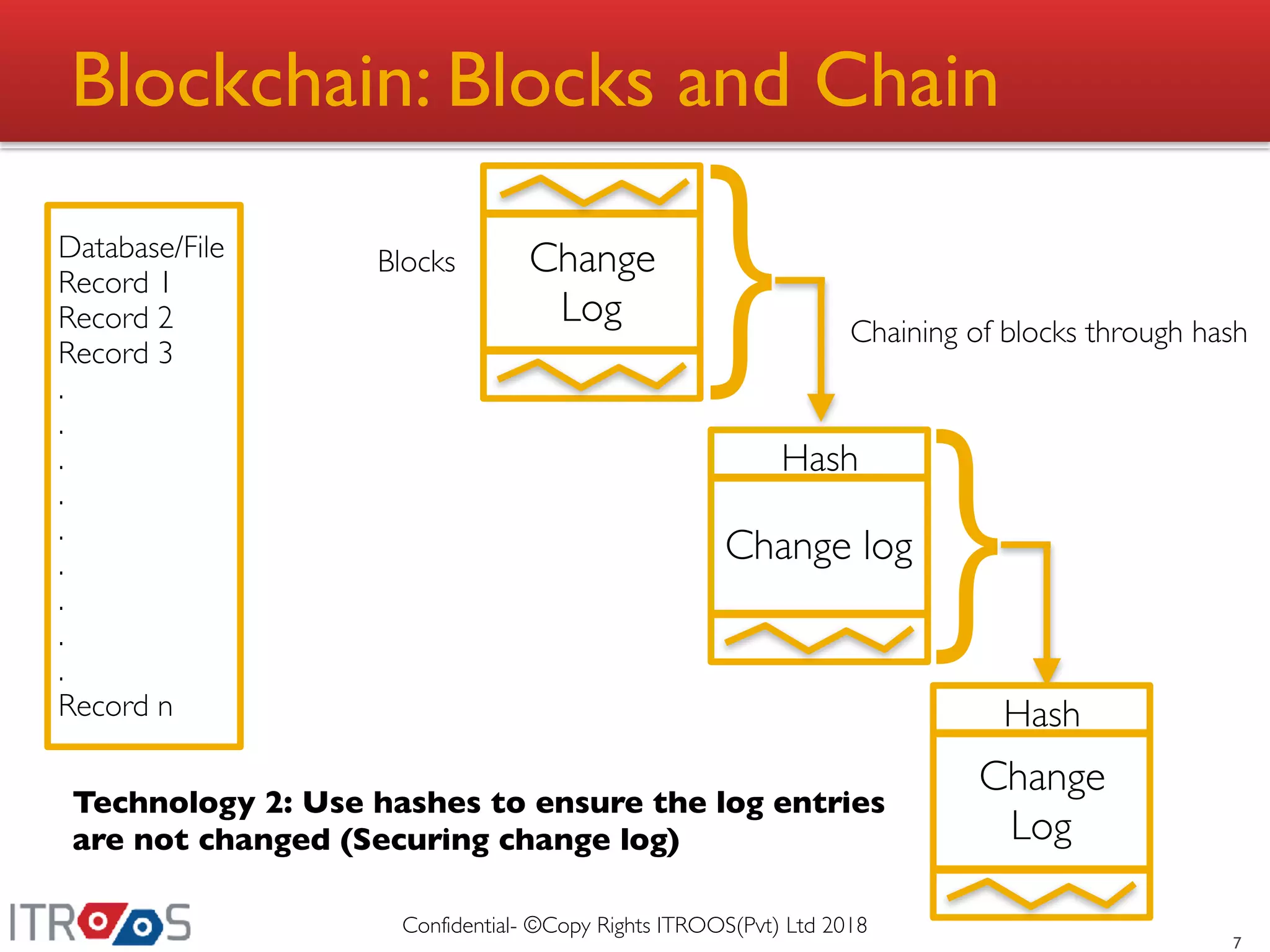
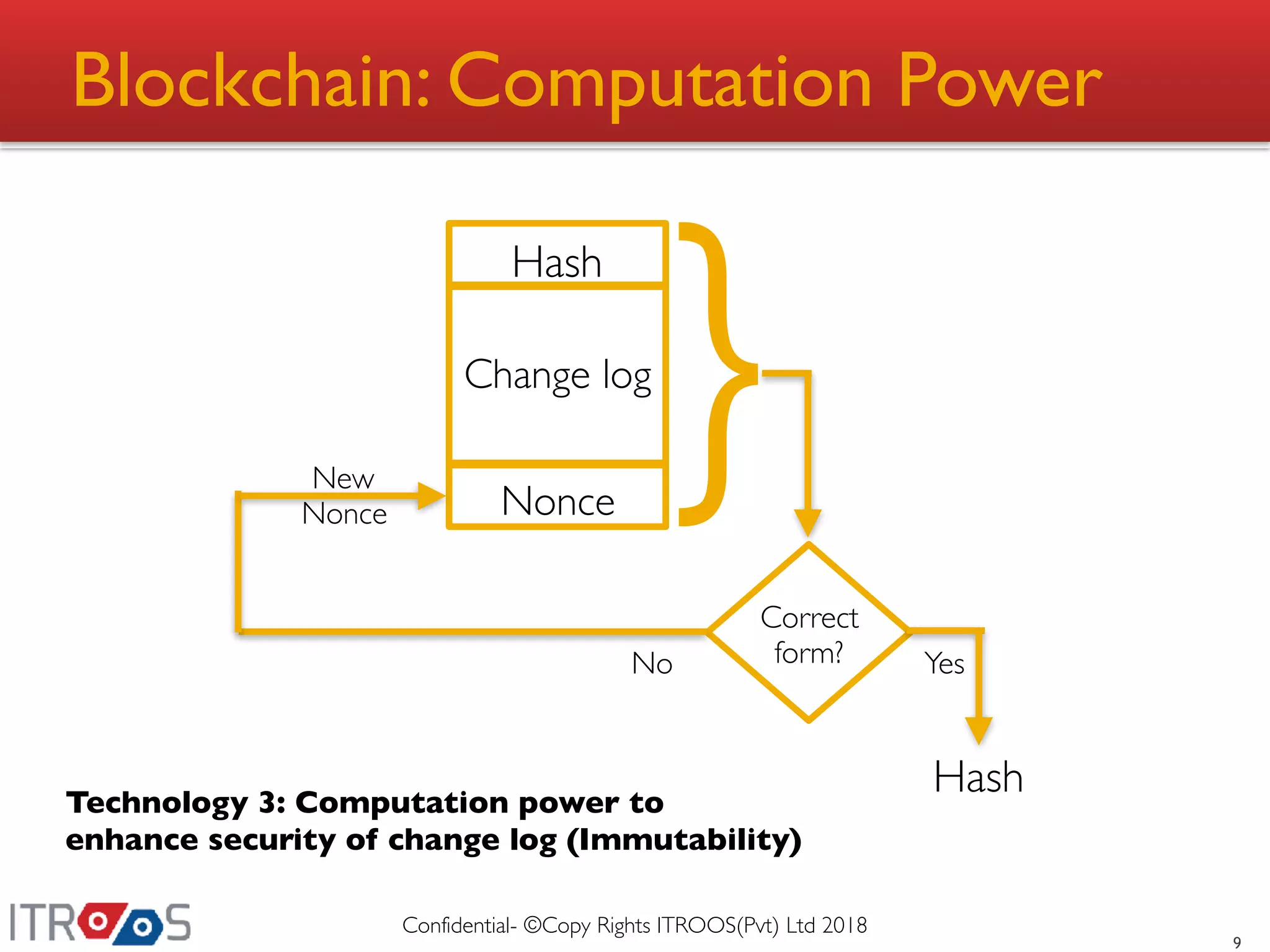
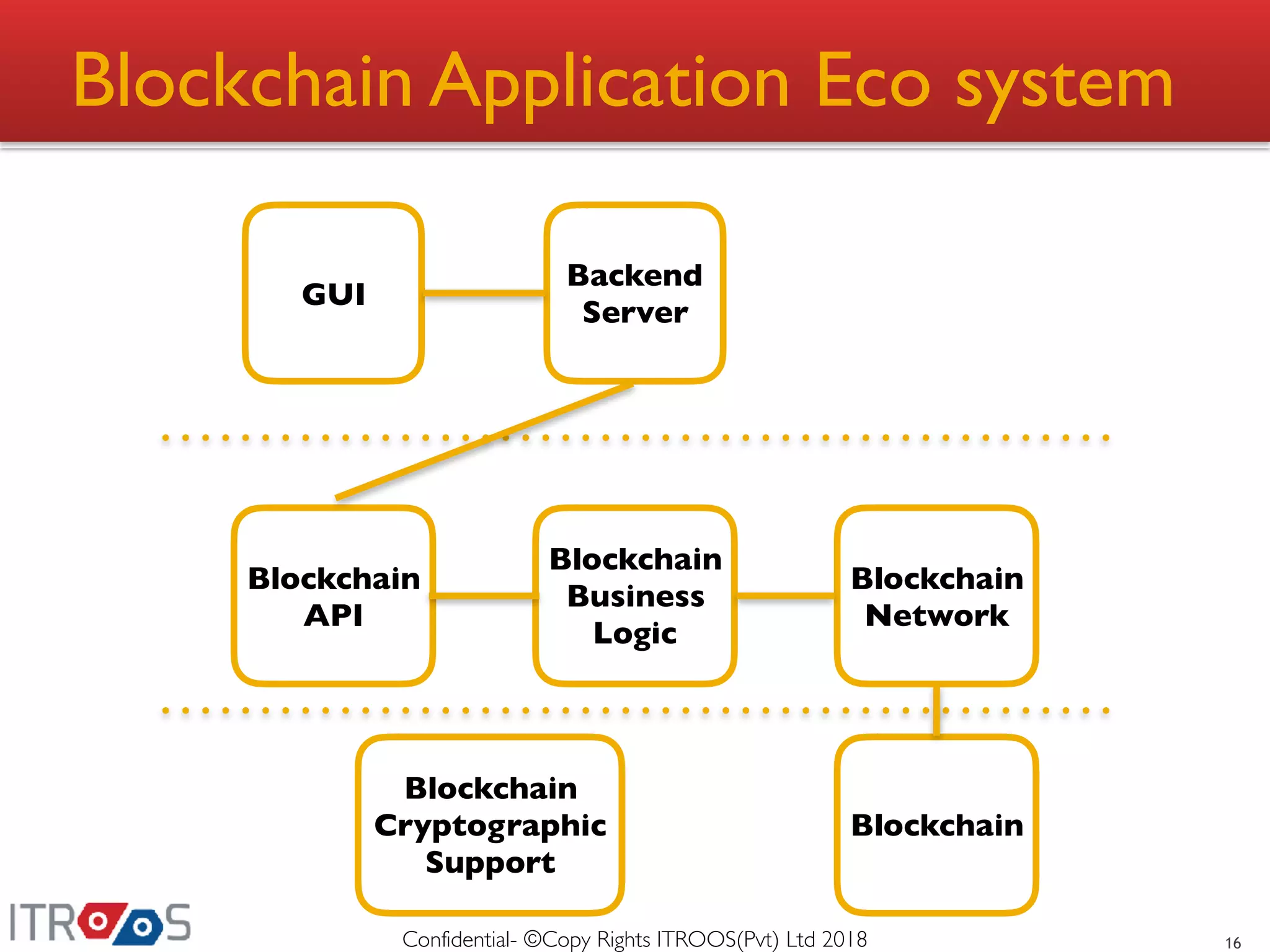
This document provides an overview of blockchain technology, including its advantages over conventional storage systems, such as enhanced security, immutability, and transparency. It discusses issues with traditional data storage, like trust and traceability, and explains how blockchain addresses these problems through mechanisms such as change logs, hashing, and peer consensus. The document also outlines the blockchain application ecosystem and its components.