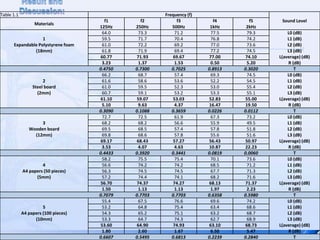
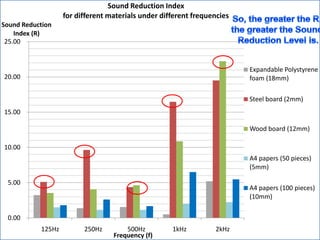
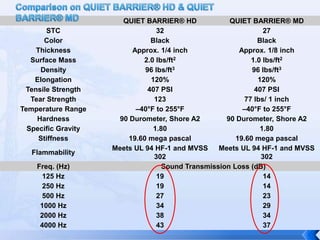
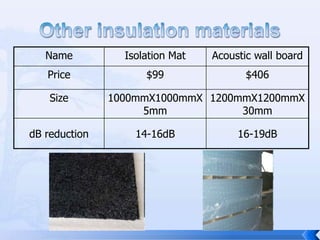
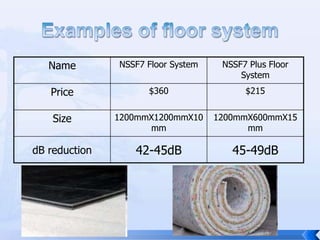
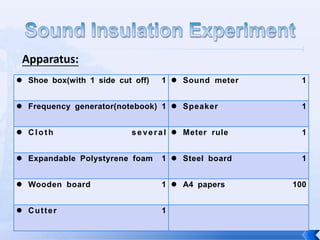
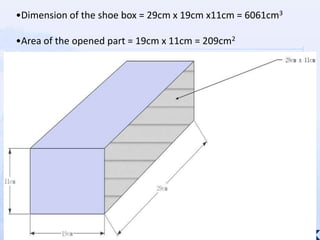
The document summarizes an experiment that tested the effectiveness of different common materials for sound insulation. The materials tested included expanded polystyrene foam, stainless steel, wood, and paper. The experiment measured the sound reduction index and transmitted coefficient of each material at different frequencies. The results showed that stainless steel was the most effective at sound insulation, while expanded polystyrene foam and paper were the least effective. Common soundproofing techniques for homes using different materials were also discussed.













![Decibel meterusing a decibel meter, we can measure the sound level (in dB) of different sound source. sound level (L) L = 10 log10 [ I/I0 ]…………………(1)sound reduction index (R): R = 10 log10 [ 1 / T ] (dB)…………(2) T: Transmitted sound energy / Incident sound energy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soundinsulationexperiment-110312222214-phpapp02/85/Sound-insulation-experiment-16-320.jpg)