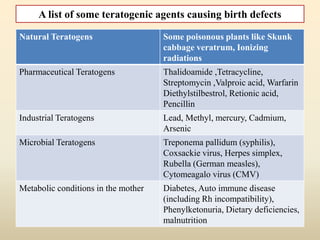
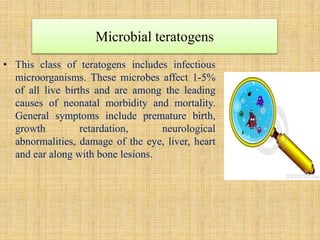
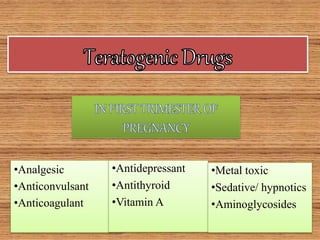
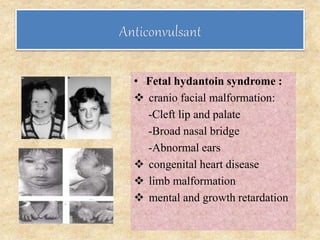
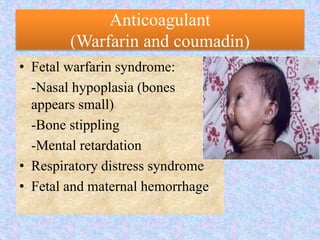
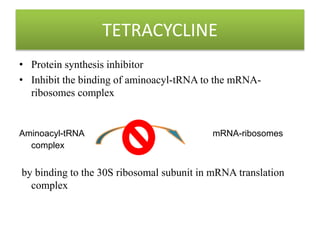
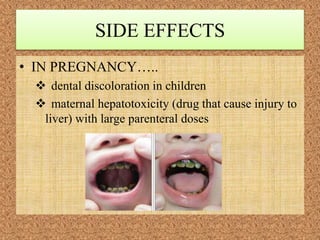
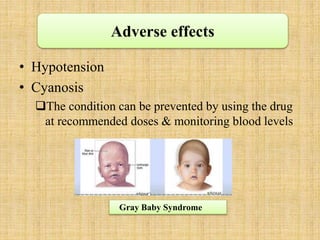
Microbial agents like rubella virus, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasma gondii, and Treponema pallidum can cause birth defects when a woman is exposed during pregnancy. These microbes may directly damage the fetus or disrupt the immune response. Common effects include premature birth, growth problems, neurological abnormalities, and damage to organs like the eyes, liver, heart and ears. While exposure to ionizing radiation is a potential risk, most diagnostic procedures expose the fetus to less than 50 mSv of radiation, which is a dose unlikely to increase risks. Prescription drugs are also a concern, as several classes of medications like tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, and anticonvulsants