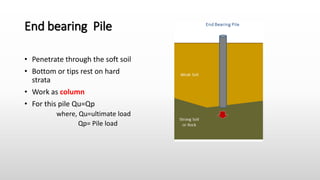
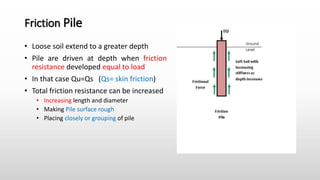
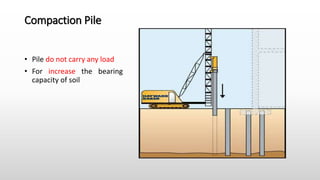
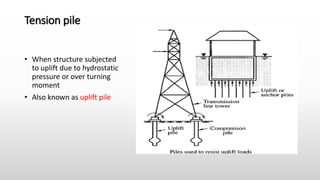
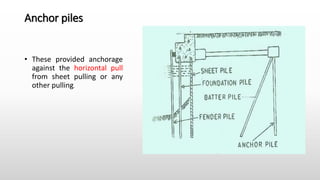
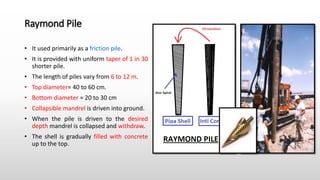
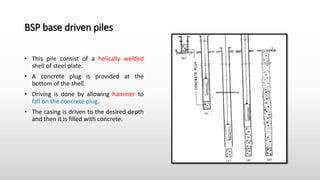
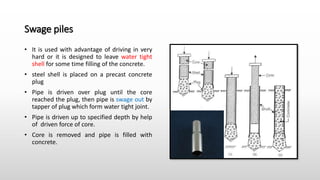
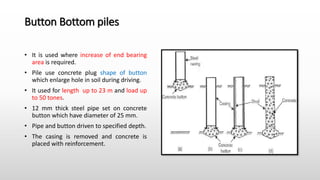
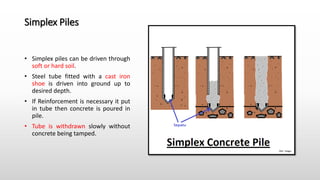
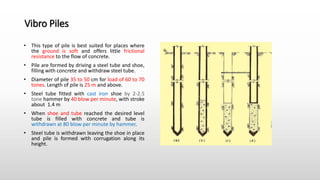
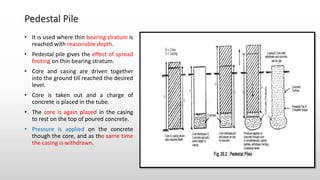
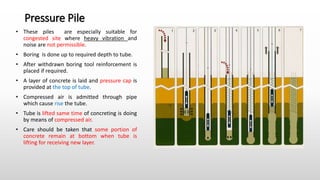
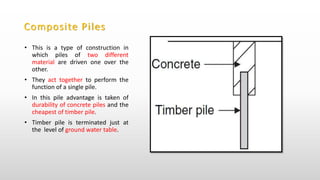
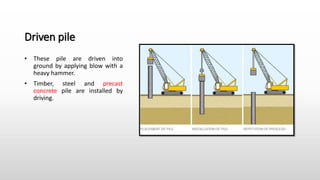
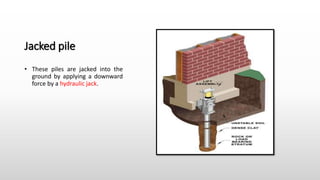
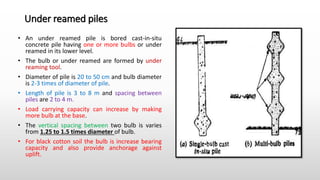
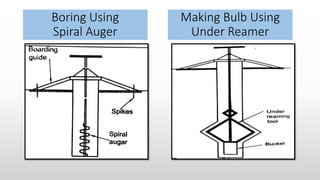
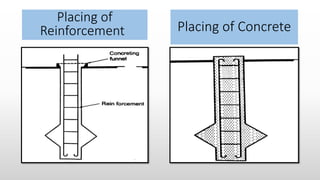
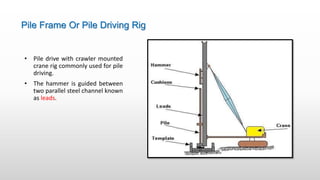
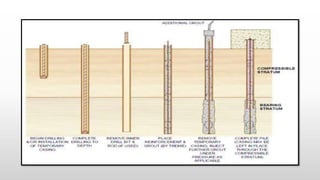
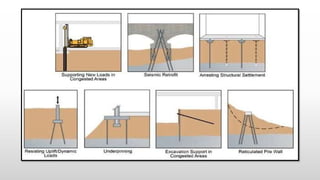
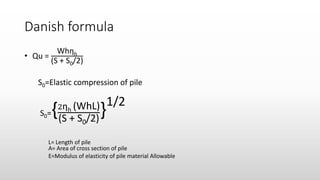
The document provides an extensive overview of pile foundations, detailing their purpose, types, construction methods, and applications. It explains various types of piles—such as timber, concrete, and steel—and their respective installation techniques, including driven and cast-in-situ methods. Additionally, the document addresses factors affecting the selection of piles and common causes of failure in pile foundations.