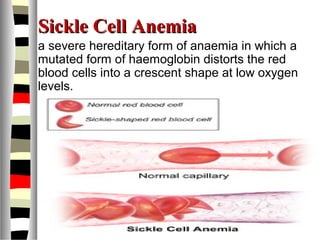
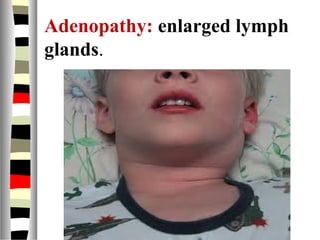
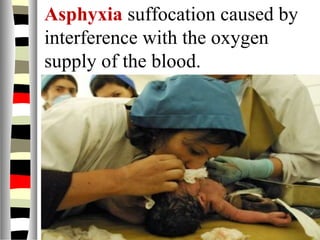
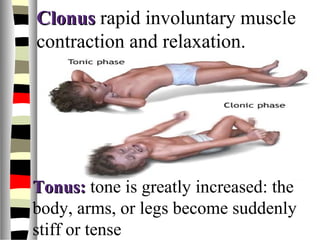
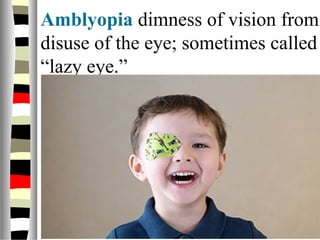
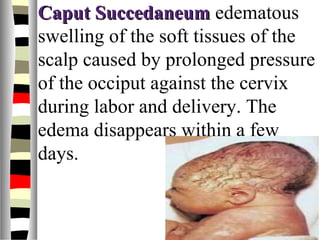
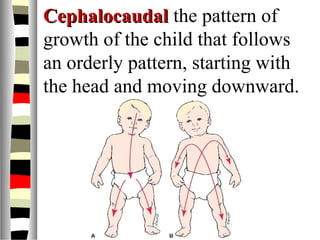
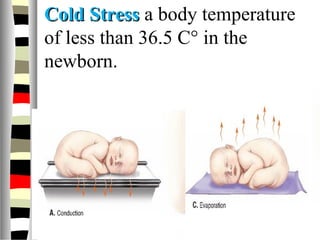
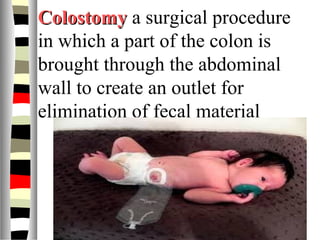
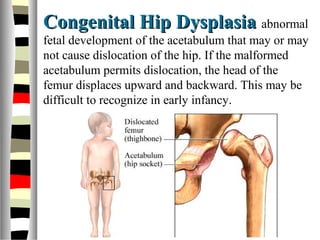
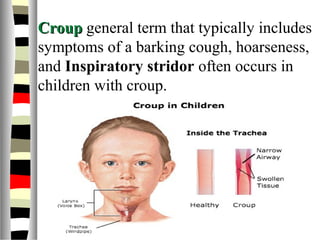
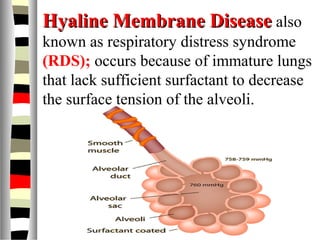
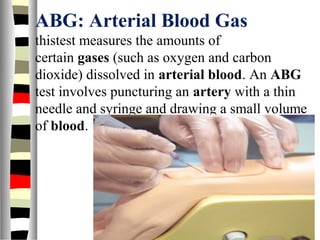
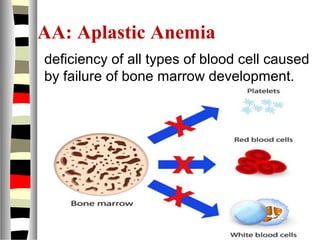
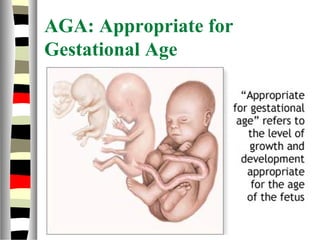
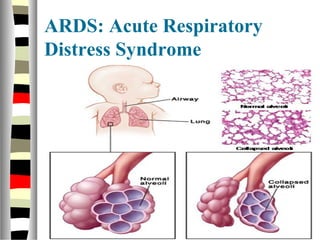
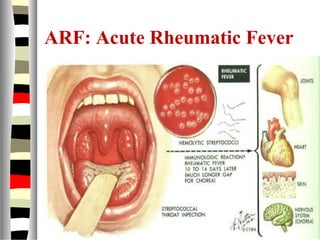
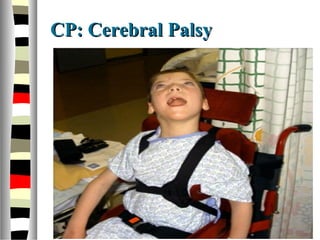
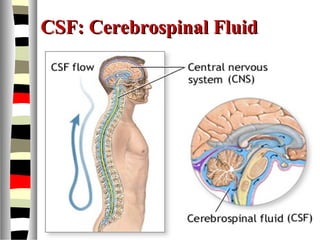
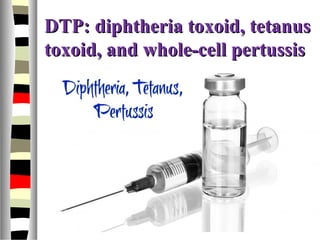
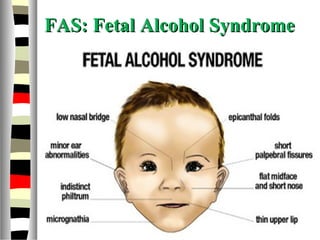
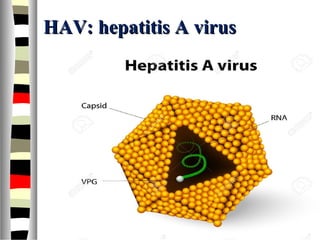
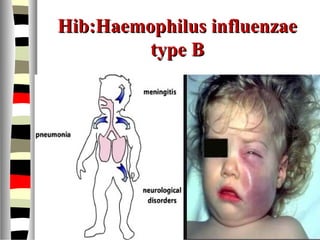
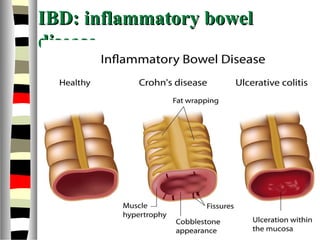
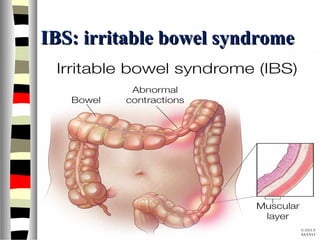
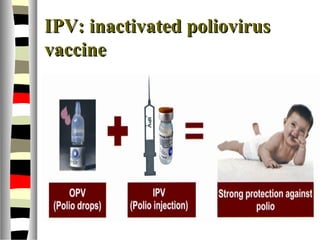
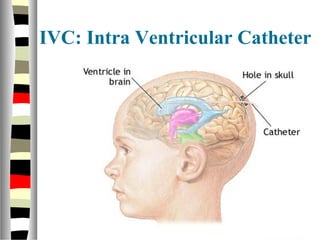
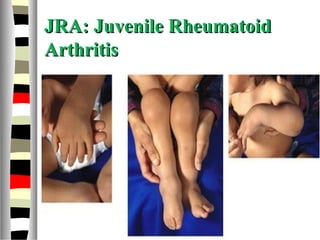
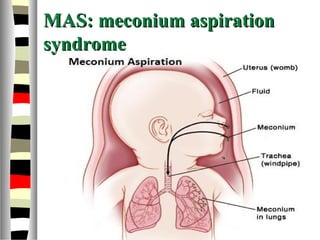
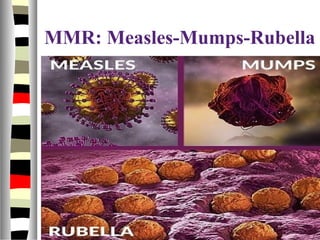
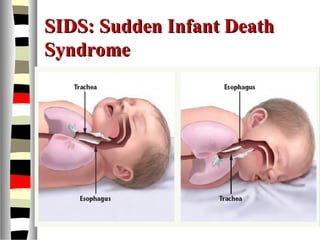
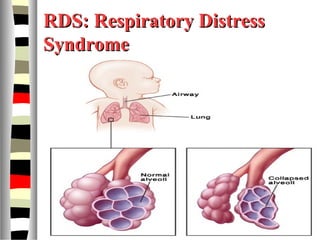
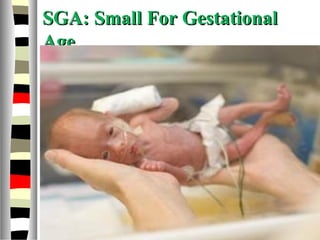
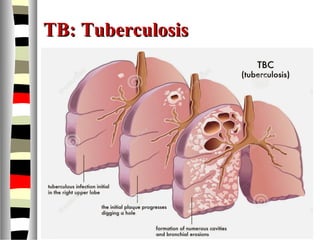
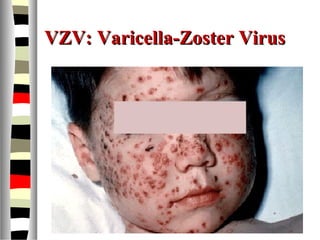
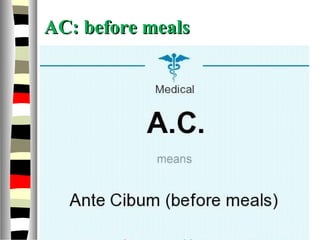
The document is an extensive list of pediatric terms and conditions, including definitions of various medical terminology relevant to children's health. It covers topics such as sickle cell anemia, separation anxiety, and definitions of numerous pediatric disorders like celiac syndrome and autism. Additionally, it includes abbreviations and medical terminology used in healthcare settings for pediatric care.