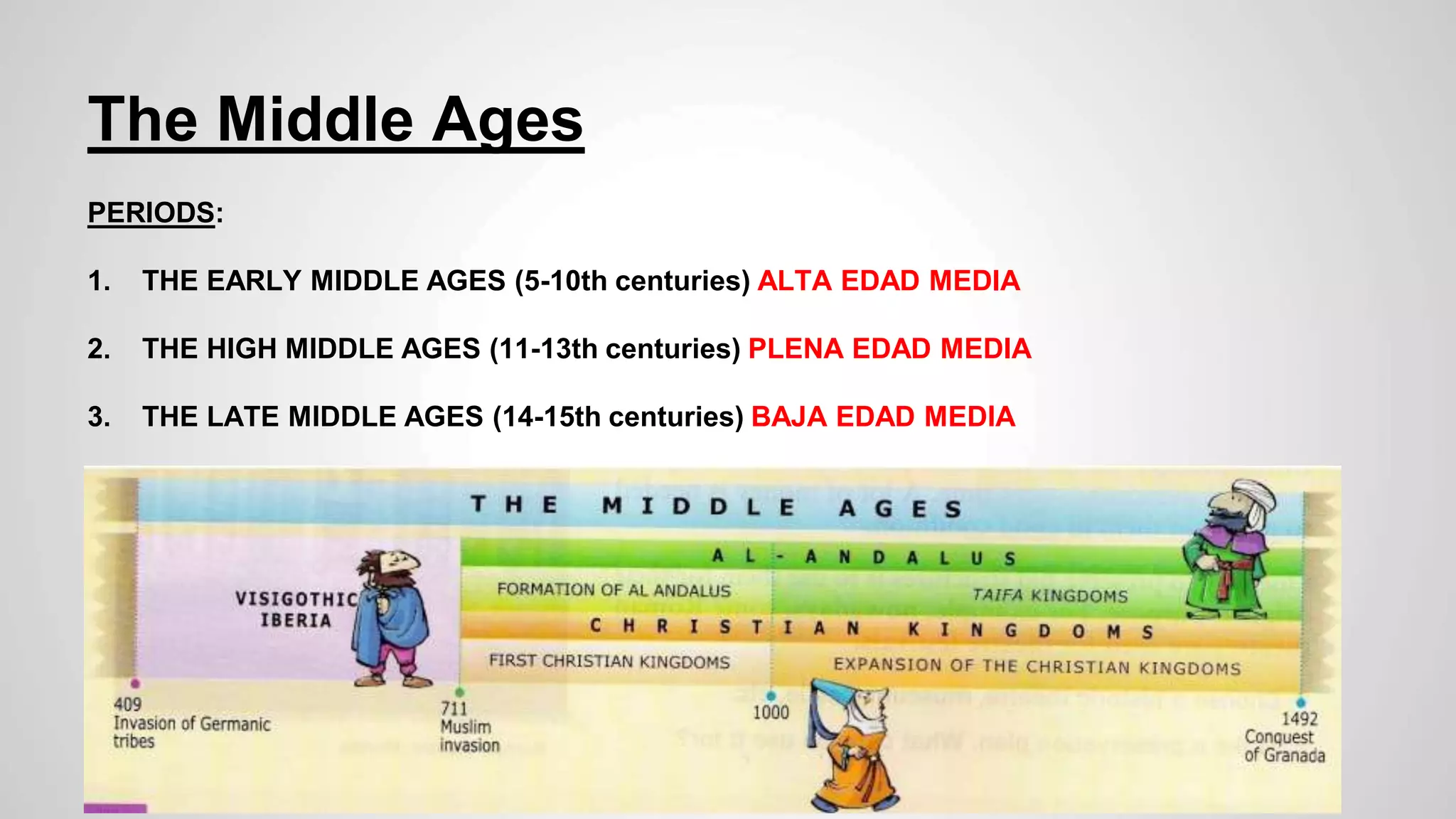
The document summarizes key periods and developments during the Middle Ages in Europe. It describes the division of the Roman Empire in 395 which led to the creation of the Byzantine Empire in the East. It then discusses the expansion of Islam under Muhammad and the early Islamic Empire. Finally, it outlines the rise of the Carolingian Empire under Charlemagne who was crowned Holy Roman Emperor in 800 and his division of the empire after his death among his three sons.