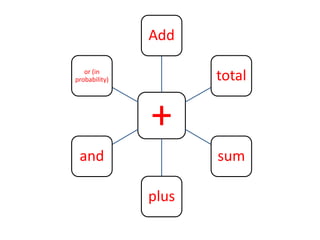
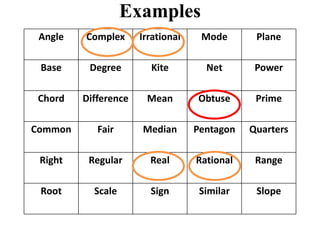
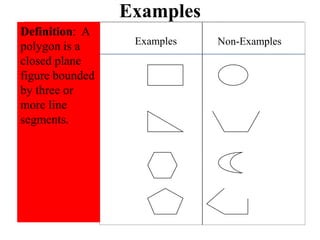
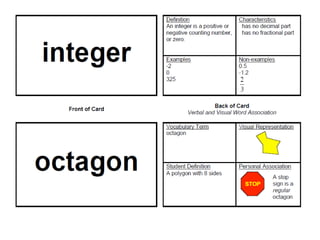
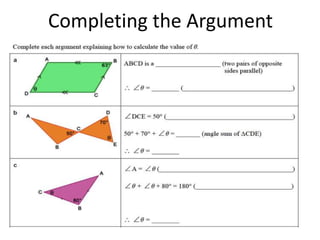
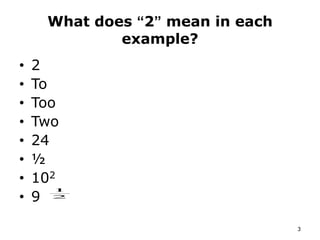The document discusses the significance of language in mathematics, emphasizing vocabulary development in understanding mathematical concepts. It outlines three categories of mathematical terms: those that are the same as in everyday English, those unique to math, and those with different meanings. Various strategies, such as graphic organizers and cloze passages, are suggested to enhance mathematical literacy and comprehension.