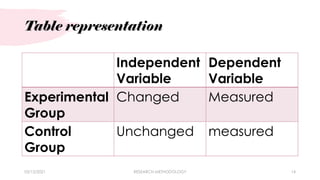
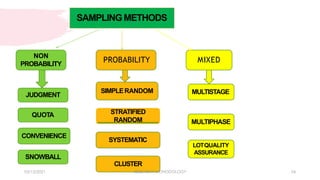
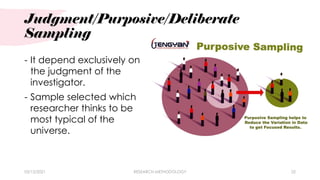
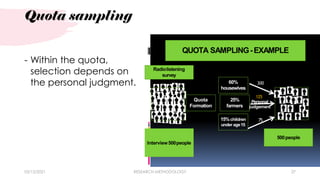
This chapter discusses research methodology and its key components. It identifies 6 main parts of chapter 3: 1) research design, 2) locale of the study, 3) population and sampling technique, 4) data gathering procedure, 5) research instrument, and 6) statistical treatment of data. It describes the different research designs including descriptive, experimental, and qualitative designs. It also explains concepts like research locale, population, sampling techniques, data collection procedures, types of research instruments including questionnaires, interviews and checklists, and the importance of statistical treatment of data.