Report
Share
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Astronomy 4.1 Energy formation and layers of the Sun - IT6230

Astronomy 4.1 Energy formation and layers of the Sun - IT6230
Similar to 16.3 solar activity
Similar to 16.3 solar activity (20)
The Biological Effects of Radiation to Humans on a Manned Mission to Mars

The Biological Effects of Radiation to Humans on a Manned Mission to Mars
Recently uploaded
Bioenergetics is an important domain in biology. This presentation has explored ATP production and its optimum utilization in biological systems along with certain theories and experiments to give a bird's eye view of this important issue.Energy is the beat of life irrespective of the domains. ATP- the energy curre...

Energy is the beat of life irrespective of the domains. ATP- the energy curre...Nistarini College, Purulia (W.B) India
Recently uploaded (20)
Module for Grade 9 for Asynchronous/Distance learning

Module for Grade 9 for Asynchronous/Distance learning
Cyathodium bryophyte: morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.

Cyathodium bryophyte: morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.
Porella : features, morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.

Porella : features, morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.
Site specific recombination and transposition.........pdf

Site specific recombination and transposition.........pdf
Pteris : features, anatomy, morphology and lifecycle

Pteris : features, anatomy, morphology and lifecycle
Role of AI in seed science Predictive modelling and Beyond.pptx

Role of AI in seed science Predictive modelling and Beyond.pptx
Human & Veterinary Respiratory Physilogy_DR.E.Muralinath_Associate Professor....

Human & Veterinary Respiratory Physilogy_DR.E.Muralinath_Associate Professor....
FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry

FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry
Energy is the beat of life irrespective of the domains. ATP- the energy curre...

Energy is the beat of life irrespective of the domains. ATP- the energy curre...
Use of mutants in understanding seedling development.pptx

Use of mutants in understanding seedling development.pptx
development of diagnostic enzyme assay to detect leuser virus

development of diagnostic enzyme assay to detect leuser virus
16.3 solar activity
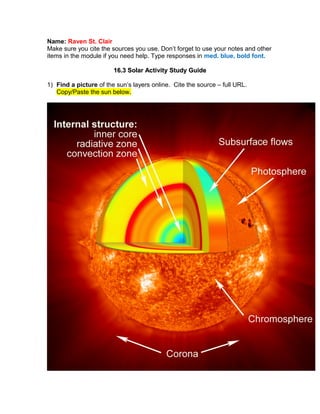
- 1. Name: Raven St. Clair Make sure you cite the sources you use. Don’t forget to use your notes and other items in the module if you need help. Type responses in med. blue, bold font. 16.3 Solar Activity Study Guide16.3 Solar Activity Study Guide 1) Find a picture of the sun’s layers online. Cite the source – full URL. Copy/Paste the sun below.
- 2. http://www.nasa.gov/images/content/171926main_heliolayers_label_lg.jpg 2) Explain the following properties or characteristics of the sun: a. Core: center of the sun, hot and dense, where nuclear fusion is made b. Radiative Zone: where energy is transported to outer layers by photons c. Convective Zone: where energy is transported by large bulks of gas through convection to outer cooler layers d. Photosphere: "light sphere" where photons make it to space e. Chromospere: thin, pink layer seen in solar eclipses where temperature rises away from the photosphere f. Corona: very hot crown that can be seen around the moon during a total solar eclipse 3) How do sunspots work? They occur where Sun's magnetic field rises from below Sun's surface and poke through. They are darker and cooler than the area around it. They can last for days or weeks. Sunspots can affect Earth a little in ways such as the power plants, knocking out satellites, and creating auroras. Find a picture, copy/paste it here and cite the source. http://www.exploratorium.edu/sunspots/images/active2.jpg 4) What is a prominence? An eruption of gas on the Sun's surface hundreds of thousands of miles into space that are caused by strong magnetic fields and may last for months. How does this differ from a flare? They are much stronger than flares. Flares only last for a few seconds or minutes and don't go as far out in the universe as prominences do. Find a picture, copy/paste it here and cite the source.
- 3. http://cdn.recomparison.com/images/community/topics/1299/129907222011135819.j pg 5) How does an aurora work? Auroras are caused solar winds that come close enough to Earth's atmosphere to brush up against it and spiral down into it. The gases from the solar winds light up when they hit Earth, forming the aurora. Find a picture, copy/paste it here and cite the source. http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/image/0710/aurora_kuenzli_big.jpg