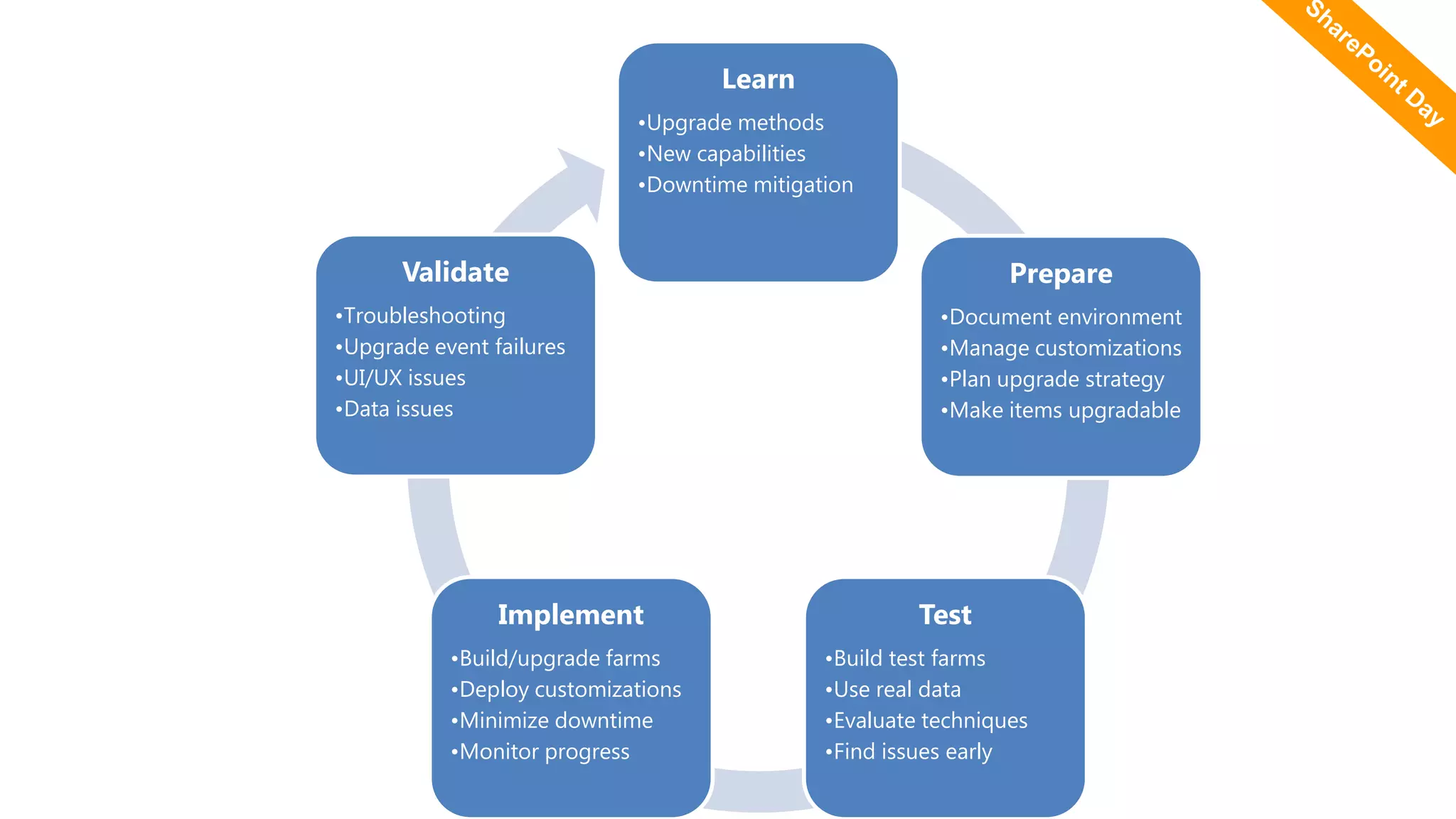
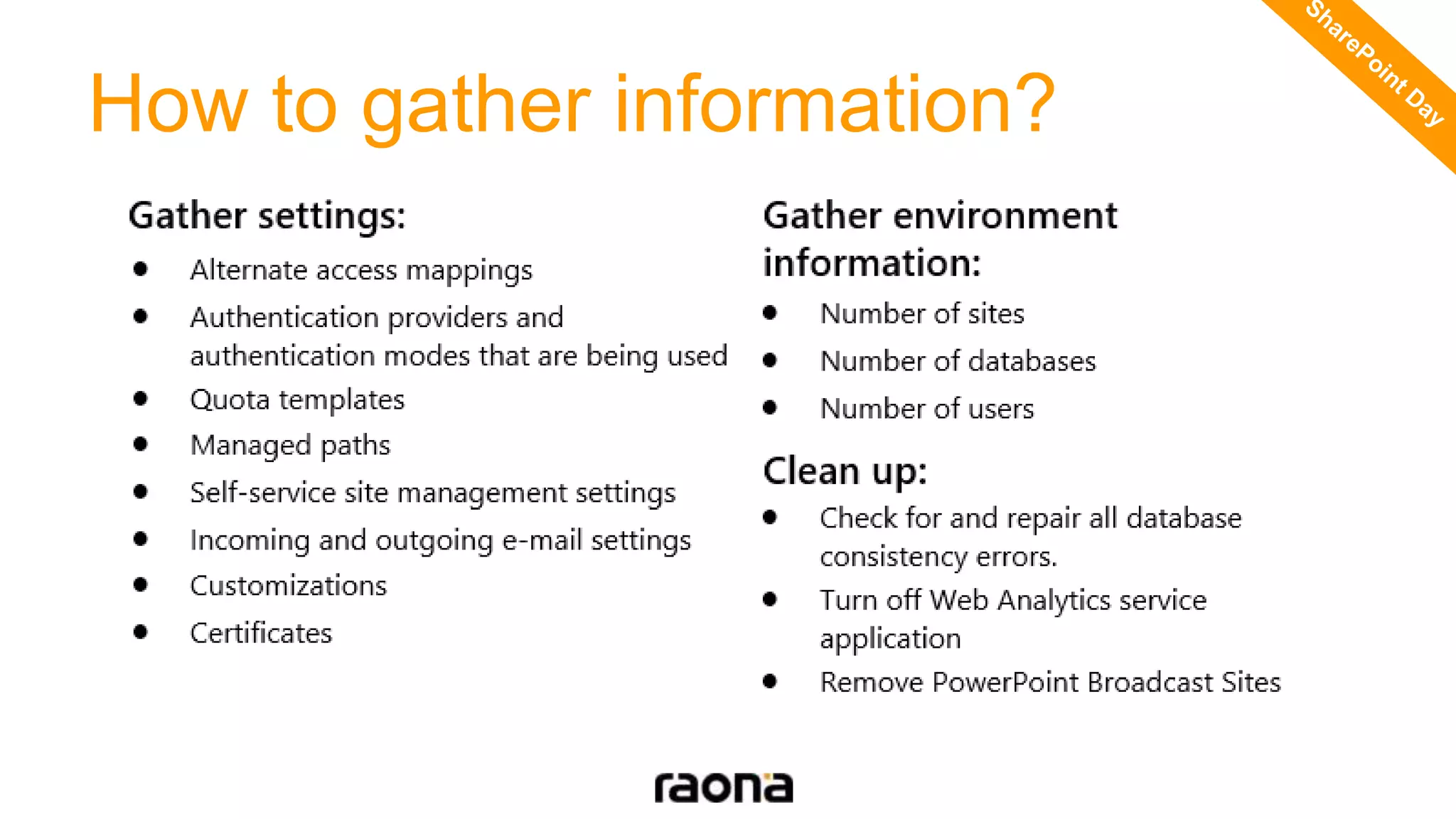
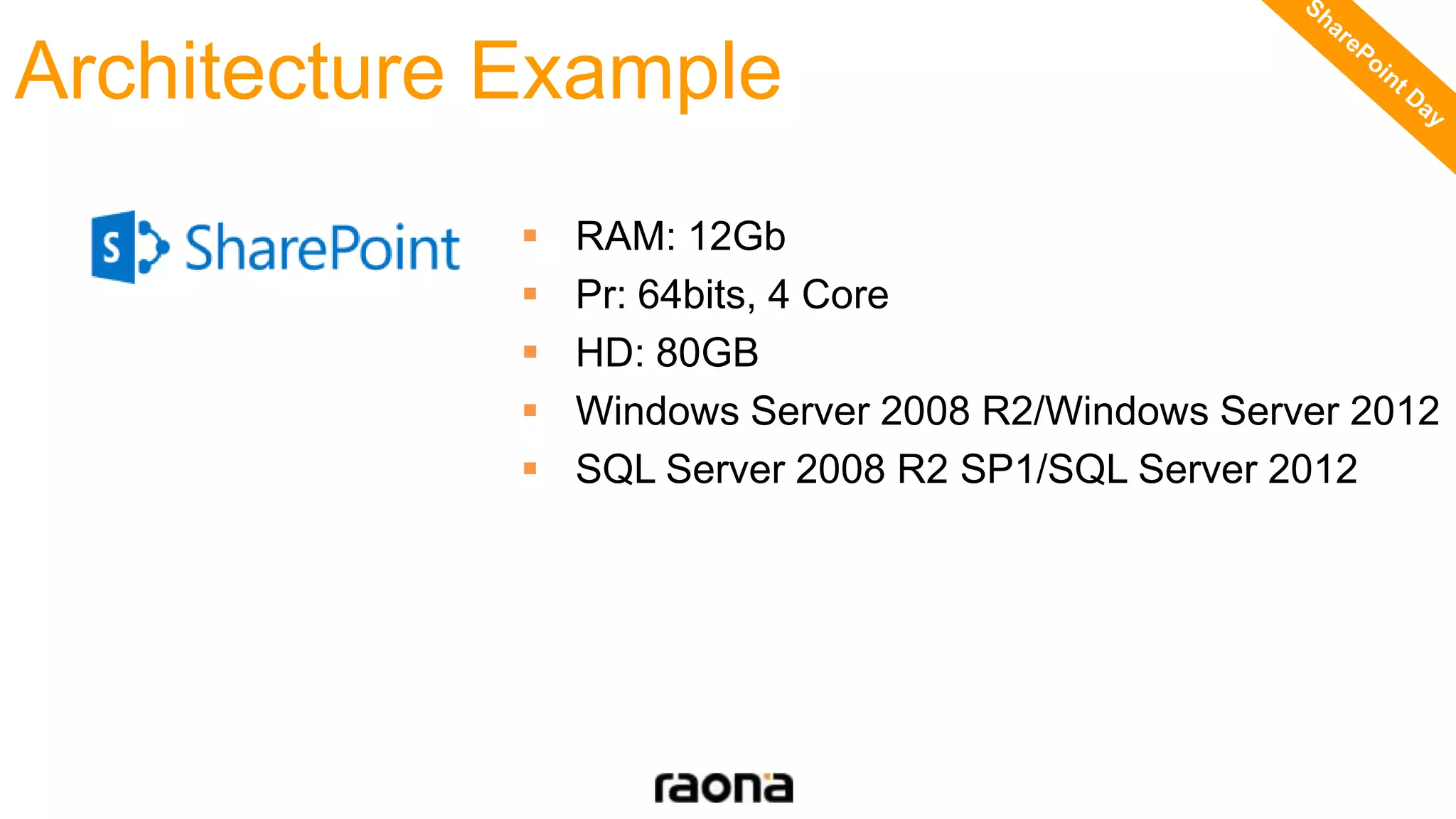
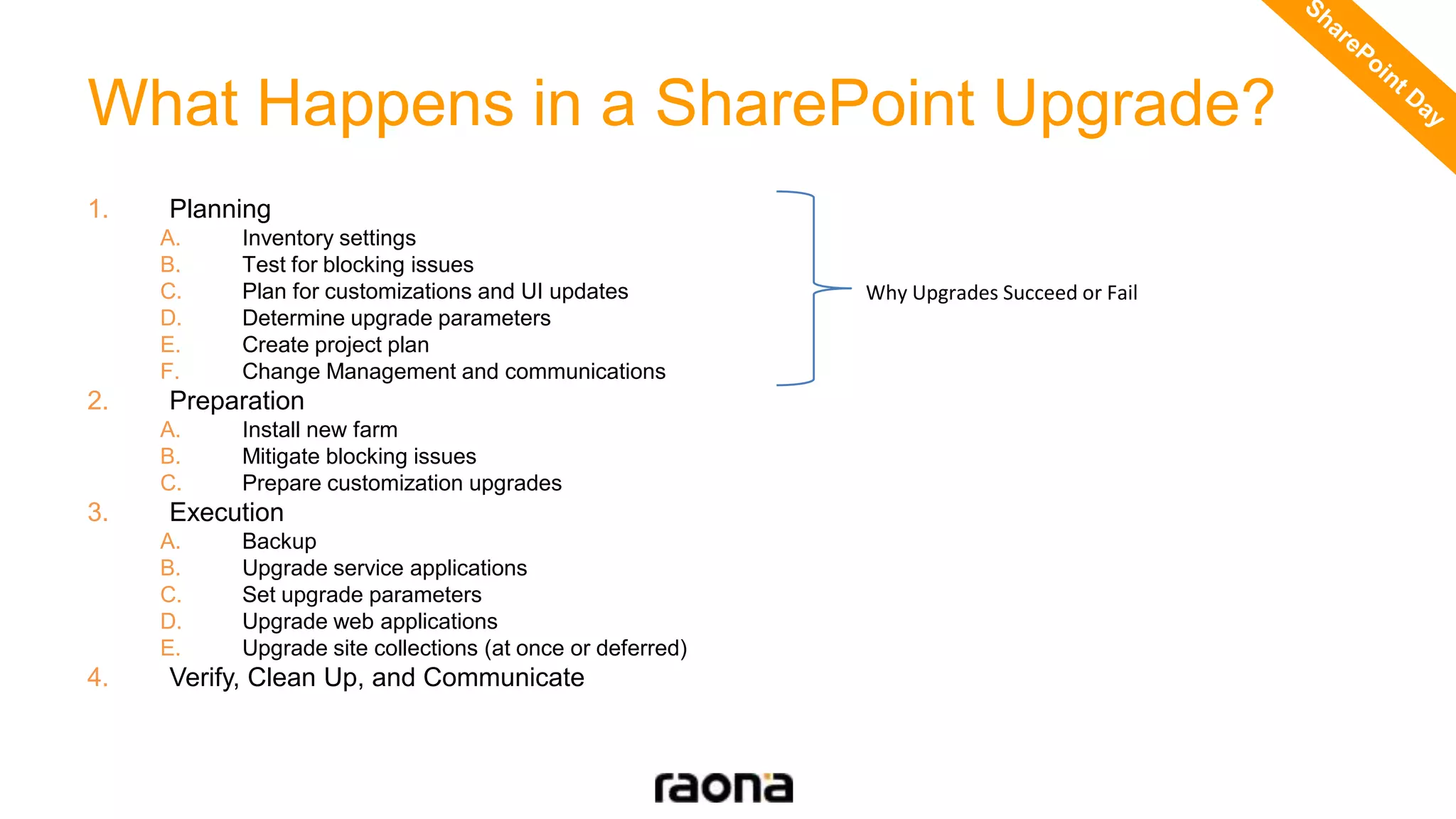
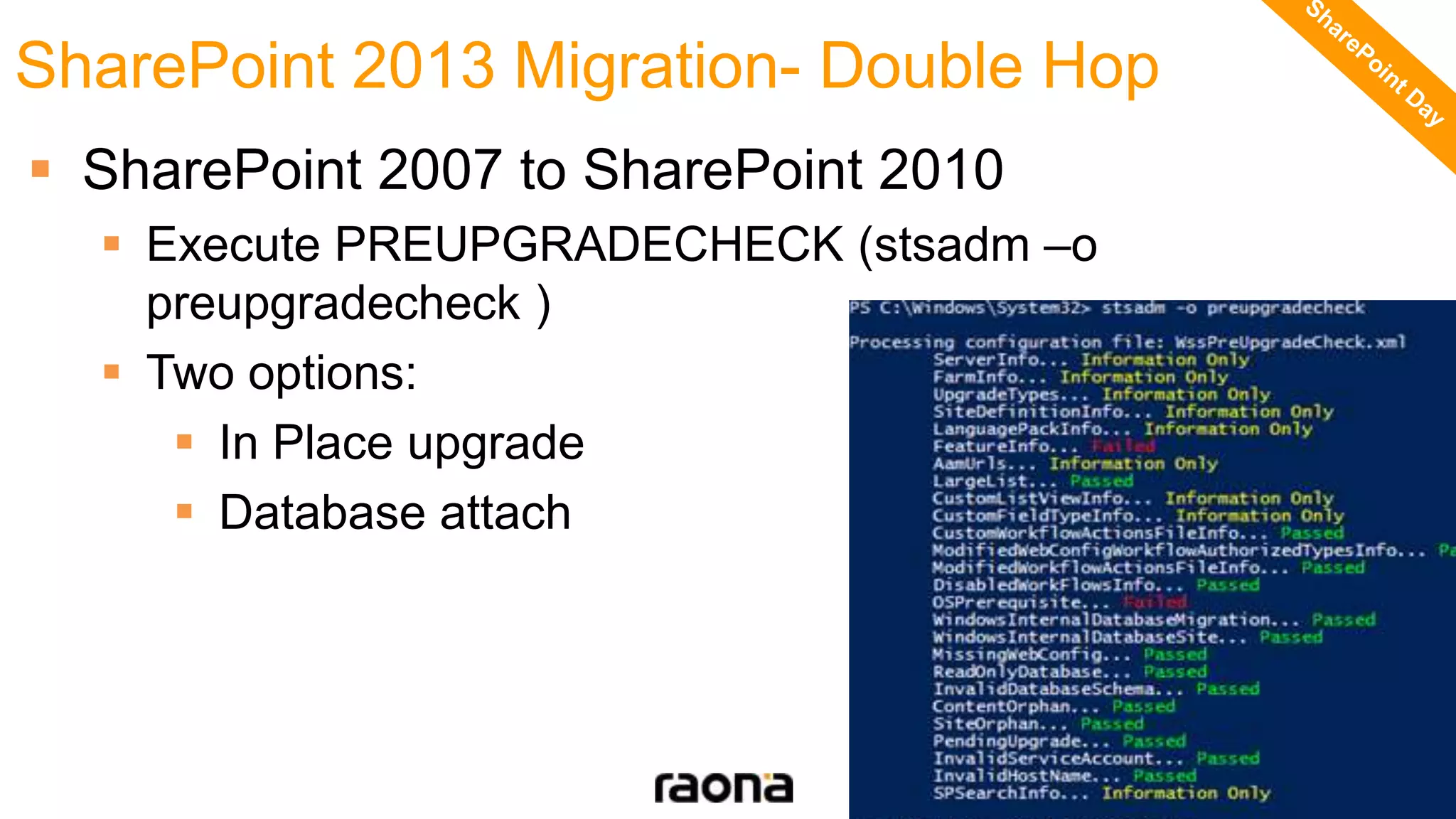
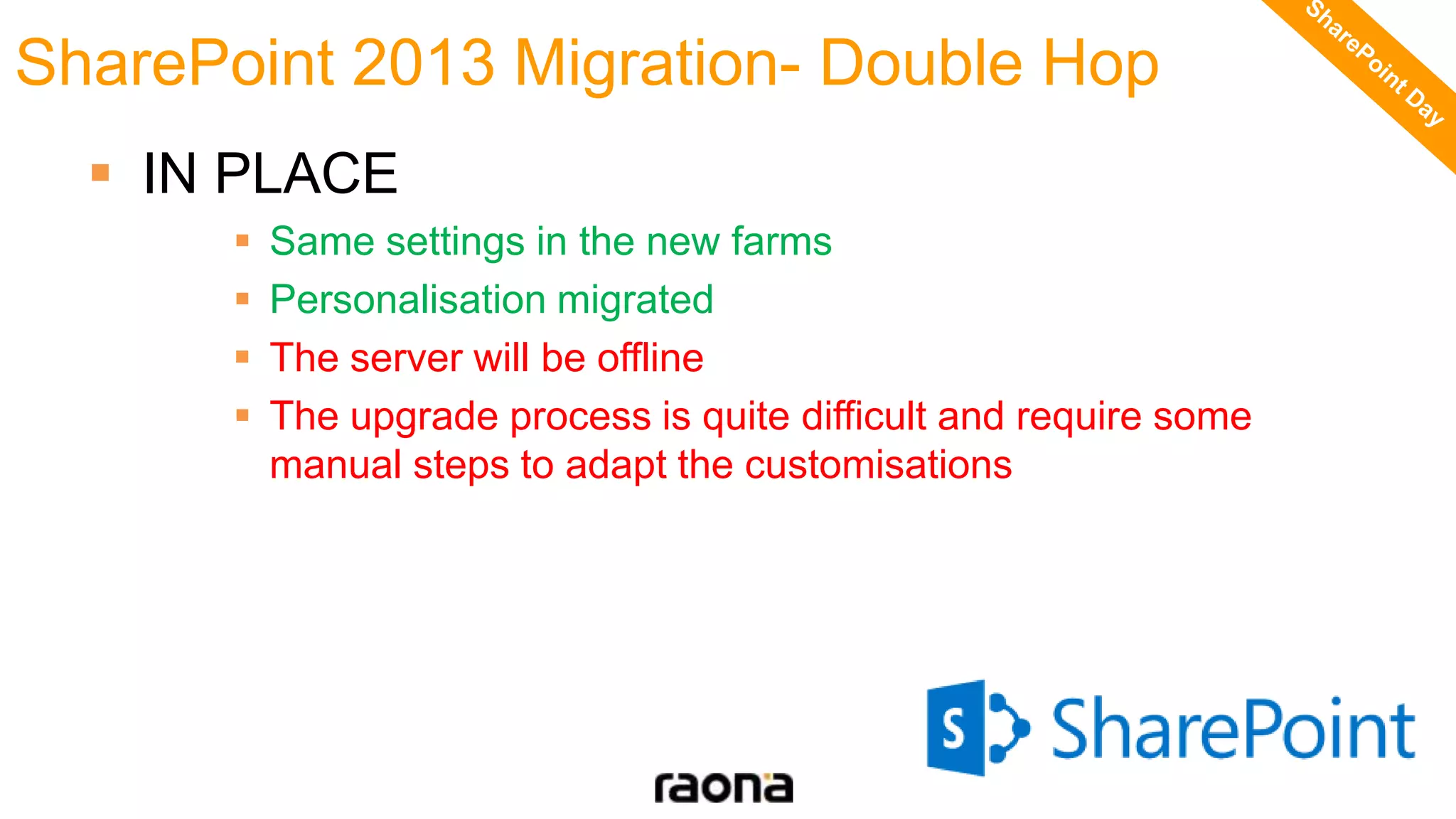
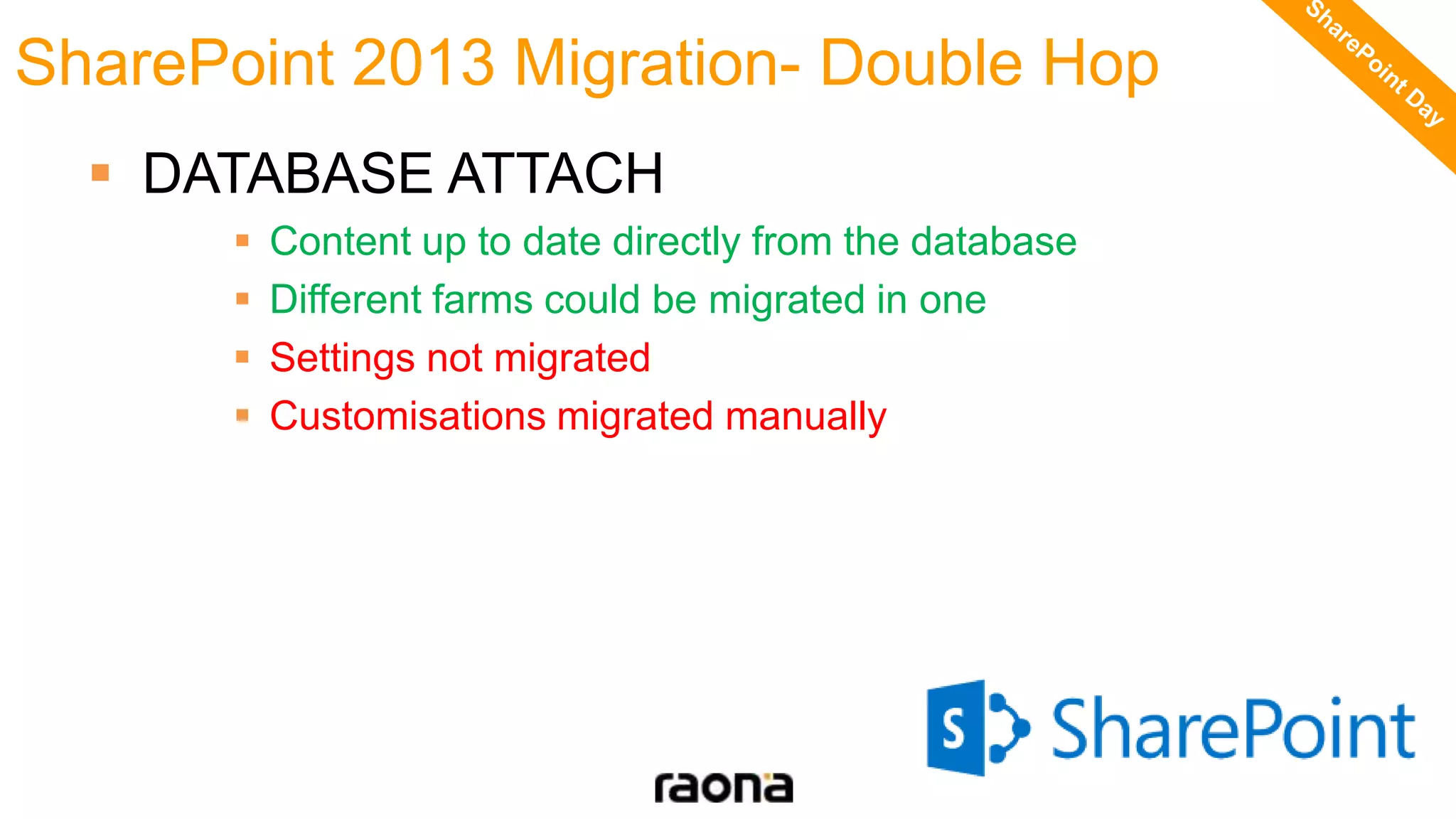
This document discusses key aspects to consider for a successful SharePoint 2013 migration. It outlines steps to learn about new capabilities, prepare by documenting the environment and customizations, test using real data, implement with minimal downtime while monitoring progress, and validate by troubleshooting issues. Migration options like database attach and in-place upgrades are described. Risks include refactoring for .NET 4.0, changes to search, authentication, design elements, and Outlook Web Access.