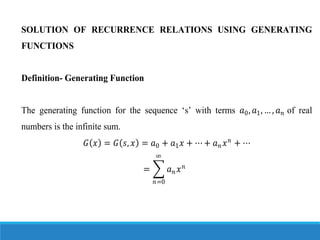
1. Generating functions can be used to represent sequences as power series and solve recurrence relations.
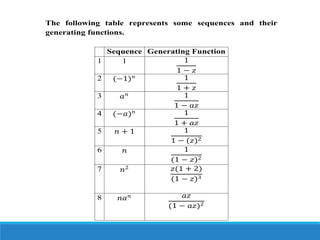
2. Common examples of generating functions are presented for various sequences like the constant sequence {1,1,...}, the sequence of powers of 2, and binomial coefficients.
3. The process of using generating functions to solve recurrence relations involves rewriting the relation, multiplying by x^n and summing, identifying the generating function, and extracting the nth term.









![⟹ 𝑎 𝑛 𝑥 𝑛−3𝑥
∞
𝑛=1 𝑎 𝑛−1 𝑥 𝑛−1
∞
𝑛=1 =0
⟹ (G(x)-𝑎0)-3x G(x) =0
⟹ G(x) (1-3x) = 𝑎0
G(x) (1-3x) =2 [∴ Given 𝑎0=2]
G(x) ⟹
2
1−3𝑥
= 21 − 3𝑥−1
⟹2(1+3x+(3𝑥)2
+........)
G(x) ⟹2 3 𝑛∞
𝑛=0 𝑥 𝑛
Consequently, 𝑎 𝑛 = 2. 𝑐𝑜𝑒𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑥 𝑛
in G(x)
𝑎 𝑛 = 2. 3 𝑛](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/generatingfunction-181029124920/85/Generating-function-12-320.jpg)


