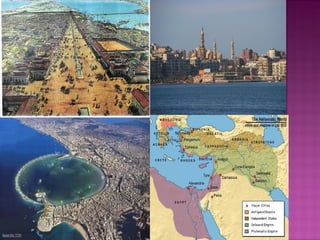
The document discusses the Hellenistic period following the conquests of Alexander the Great. It describes how Alexander linked Egypt and regions of Asia to Greek civilization, marking a new era. For around 300 years, Greek culture and language spread across these areas. Eventually Rome conquered the Hellenistic kingdoms and Roman culture became dominant from Spain to Asia, marking the beginning of the Roman period. Key features of Hellenism included the blending of cultures and religions as well as new philosophical movements seeking salvation and serenity.