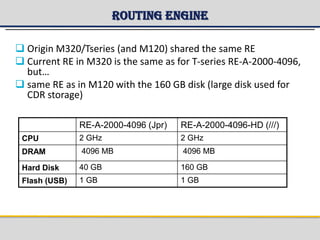
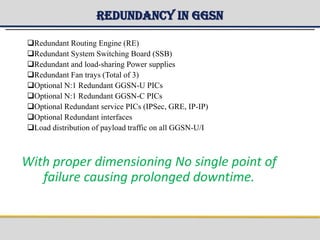
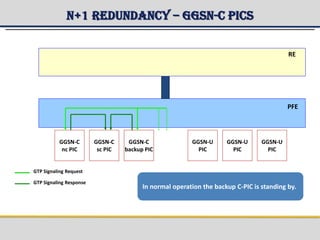
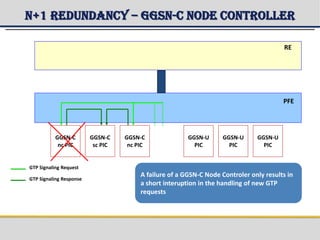
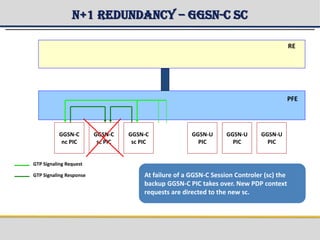
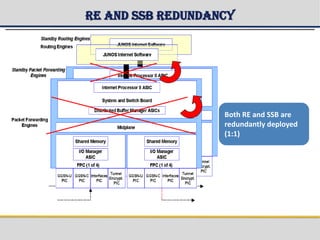
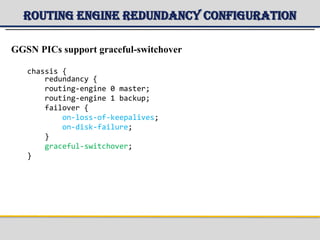
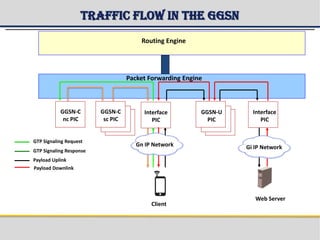
The document provides a detailed overview of the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) architecture, functionalities, and hardware configurations. It covers the GGSN's role as an interface for external networks, its routing capabilities, and various service management features, including session control and node management. Additionally, it outlines redundancy measures for hardware components, ensuring ongoing service stability and performance.


![GGSN/EPG Hardware Overview [EPG-M]
M20
M120
M320
Three different platforms with Juniper HW for EPG-M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class-03-gatewaygprssupportnode-to-be-presented-170726070325/85/GGSN-Gateway-GPRS-Support-Node-4-320.jpg)




![Sample Hardware Distribution
srayan@an1ggsn01-re0> show chassis hardware
Hardware inventory:
Item Version Part number Serial number Description
Chassis JN117A3FAAEA M120 [GGSN/EPG serial number for licensing]
Midplane REV 05 710-018041 RC8637 M120 Midplane
FPM Board REV 06 710-011407 YJ0593 M120 FPM Board
FPM Display REV 02 710-011405 YZ5056 M120 FPM Display
FPM CIP REV 05 710-011410 YY9162 M120 FPM CIP
PEM 0 Rev 10 740-011935 XB10310 DC Power Entry Module
PEM 1 Rev 10 740-011935 WL56066 DC Power Entry Module
Routing Engine 0 REV 04 740-017976 9009069636 RE-A-2000
Routing Engine 1 REV 04 740-017976 9009063056 RE-A-2000
CB 0 REV 11 710-011403 ZG0824 M120 Control Board
CB 1 REV 11 710-011403 ZD6746 M120 Control Board
FPC 2 REV 05 710-015837 YR7501 M120 FPC Type 2
PIC 0 REV 07 750-010616 YM6580 2x G/E SFP, 1000 BASE
Xcvr 0 REV 02 740-013111 B071687 SFP-T
Xcvr 1 REV 02 740-013111 B166055 SFP-T
PIC 1 REV 02 750-018000 ZA6800 GGSN Stargate Type2
PIC 3 REV 02 750-018000 ZB8185 GGSN Stargate Type2
Board B REV 05 710-015838 YR6619 M120 FPC Mezz Board
FPC 3 REV 05 710-015837 YY1420 M120 FPC Type 2
PIC 0 REV 07 750-010616 YM5177 2x G/E SFP, 1000 BASE
Xcvr 0 REV 02 740-013111 B071180 SFP-T
Xcvr 1 REV 02 740-013111 B071681 SFP-T
PIC 1 REV 02 750-018000 ZD0550 GGSN Stargate Type2
PIC 2 REV 03 750-018000 CACC7320 GGSN Stargate Type2
PIC 3 REV 02 750-018000 ZA6747 GGSN Stargate Type2
Board B REV 05 710-015838 YZ4666 M120 FPC Mezz Board
FEB 2 REV 01 710-025843 YZ1903 M120 FEB
FEB 3 REV 01 710-025843 ZC0308 M120 FEB
Fan Tray 0 Front Top Fan Tray
Fan Tray 1 Front Bottom Fan Tray
Fan Tray 2 Rear Top Fan Tray
Fan Tray 3 Rear Bottom Fan Tray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class-03-gatewaygprssupportnode-to-be-presented-170726070325/85/GGSN-Gateway-GPRS-Support-Node-18-320.jpg)

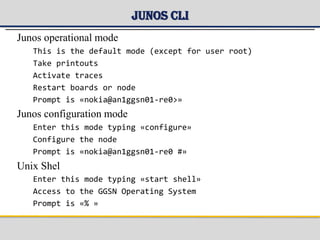
![Junos CLI
? – list available commands and short help
?
Show ?
Show system ?
<tab> or <space> - completes the command
show ver [press space or tab] => show version](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class-03-gatewaygprssupportnode-to-be-presented-170726070325/85/GGSN-Gateway-GPRS-Support-Node-28-320.jpg)

![Physical Interface Configuration
ge-2/0/0 {
description "an1ss01 6:12";
vlan-tagging;
unit 150 {
description Gn-R01;
vlan-id 150;
family inet {
address 10.77.96.6/28; [Physical interface address]
}
}
ge-3/0/0 {
unit 250 {
description Gn-R02;
vlan-id 250;
family inet {
address 10.77.96.22/28; [Physical interface address]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class-03-gatewaygprssupportnode-to-be-presented-170726070325/85/GGSN-Gateway-GPRS-Support-Node-30-320.jpg)


![Charging
cdr-attribute {
no-reduced-partial;
msisdn-always;
traffic-volumes {
qos-always;
}
charging-format 7;
charging-data-file {
user emmuser;
maximum-size 30720; [CDR log file maximum size]
maximum-age 15; [CDR log file maximum duration]
}
characteristics {
default profile8;
profile8 {
volume-limit 2000; [subscriber partial CDR wrap up limit
volume]
time-limit 15; [subscriber partial CDR wrap up limit time]
change-limit 5; [subscriber partial CDR wrap up event limit]
transfer-type ftp-pull; [no GTP prime/push]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class-03-gatewaygprssupportnode-to-be-presented-170726070325/85/GGSN-Gateway-GPRS-Support-Node-33-320.jpg)



