Theory of cost
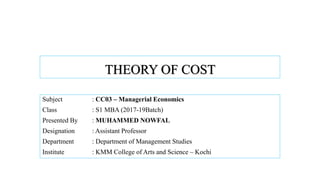
- 1. THEORY OF COST Subject : CC03 – Managerial Economics Class : S1 MBA (2017-19Batch) Presented By : MUHAMMED NOWFAL Designation : Assistant Professor Department : Department of Management Studies Institute : KMM College of Arts and Science – Kochi
- 2. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After this chapter you learn: • The various cost concepts • Cost function and application of cost analysis • Short run cost behaviour with change in one input • Long run cost behaviour with change in two inputs • Meaning and sources of economies of scale and diseconomies of scale 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 2
- 3. COST CONCEPTS 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 3 ACCOUNTING COST CONCEPTS ANALYTICAL COST CONCEPTS 1. Opportunity cost and actual cost 2. Business cost and full cost 3. Explicit cost and implicit cost 4. Out of pocket cost and book cost 1. Fixed and Variable cost 2. Total, Average and marginal cost 3. Short run and long run cost 4. Incremental cost and sunk cost 5. Historical and Replacement cost 6. Private and Social cost
- 4. COST CONCEPTS :- ACCOUNTING COST CONCEPTS Opportunity cost and actual cost Opportunity Cost is the expected return from the second best use of the resources ( alternative use) were forgone due to the scarcity of resources - Opportunity cost refers to the value forgone in order to make one particular investment instead of another. Actual costs are those which are actually incurred by the firm in payment for the labour, material, plant, building machinery etc. - Total money expenses recorded in the books of accounts are for all practical purposes is actual cost 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 4
- 5. COST CONCEPTS :- ACCOUNTING COST CONCEPTS Business cost and full cost Business cost includes all the expenses included to carry out a business – Includes all the payments and contractual obligations made by the firm together with the book cost of depreciation on plant and equipment Full cost includes business cost, Opportunity cost and Normal profit – Normal profit is necessary minimum earning in addition to the opportunity cost, that the firm may receive to remain its present occupation 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 5
- 6. COST CONCEPTS :- ACCOUNTING COST CONCEPTS Explicit and Implicit cost (Economic Cost) Costs that falls under actual and business cost entered in the books are called explicit cost – For example: Wages, salaries, materials, insurance premium – these cost involves cash payments and are recorded There are certain cost which do not take the form of cash outlays, nor do appear in the accounting system is called implicit cost – For example; Opportunity cost (Implicit rent, Implicit wage) 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 6
- 7. COST CONCEPTS :- ACCOUNTING COST CONCEPTS Out of Pocket and Book Cost The items of expenditure which involves cash payments including both recurring and non recurring expenses are called out of pocket costs There are some actual cost which do not involve cash payements, but a provision is made in the books of accounts are known as book cost – example payment made by the firm to itself 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 7
- 8. COST CONCEPTS – ANALYTICAL COST CONCEPTS Fixed and Variable costs Fixed costs are those which remain fixed in volume over a certain level of output – it do not vary with variation of output for certain level of output – Example; cost of managerial and administrative staff Variable cost are those which vary with the variation in output – cost of raw material, running cost of fixed capital i.e. Fuel, Power 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 8
- 9. COST CONCEPTS – ANALYTICAL COST CONCEPTS Total, Average and Marginal cost Total cost is the total expenditure incurred on the production of goods and services – it includes both total fixed cost and total variable cost TC = TFC + TVC Average cost is of statistical nature – it is not an actual cost – it is obtained by dividing the total cost by the total output AC = TC / Q Marginal cost is the addition to the total cost on producing one additional unit of product MC = TCn – TCn-1 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 9
- 10. COST CONCEPTS – ANALYTICAL COST CONCEPTS Short run and Long run costs Short run costs are those which has short run implications in the production process and vary with variation in output – Variable cost Long run costs are the cost which incurred on the fixed assets – Fixed costs Short run costs are those associated with variables in the utilization of fixed plant and other facilities and long run cost are associated with the changes in the size and kind of plant 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 10
- 11. COST CONCEPTS – ANALYTICAL COST CONCEPTS Incremental cost and sunk costs Incremental cost is the total additional cost associated with the decision to expand the output or to add a new variety of product Sunk costs are those which are incurred once for all – such cost cannot be altered, increased or decreased by varying the rate of output 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 11
- 12. COST CONCEPTS – ANALYTICAL COST CONCEPTS Historical and Replacement cost • Historical cost is the cost of the assent acquired in the past where as replacement cost is the expenditure made for replacing and old asset 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 12
- 13. COST CONCEPTS – ANALYTICAL COST CONCEPTS Private cost and social cost • Costs paid out or provided for by the firms (for purchase of good and services from the market) is called private cost • Cost not paid or born by the firms including the use of resources freely available in the process of production is social cost – total cost born by the society due to production of commodity 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 13
- 14. COST FUNCTION • Symbolic statement of the technological relationship between cost and output • Total cost function is expressed as TC = f(Q) • This form tells only that there is a relationship between TC and output – but it does not tell the nature of relationship – Since there is a positive relationship between TC and output, the cost function may be written as TC = f (Q), ∆𝑻𝑪/∆𝑸 > 𝟎 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 14
- 15. SHORT RUN COST FUNCTIONS AND COST CURVES The cost output relationships are determined by the cost function and are exhibited through cost curves The shape of cost curves depends on the nature of the cost function Cost function is derived from the actual cost data of the firms Estimated cost function may take a variety of forms, yielding different kind of cost curves such as Linear cost function Quadratic cost function and Cubic cost function 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 15
- 16. LINEAR COST FUNCTIONS Linear cost function expressed as Where as a = TFC and b= 𝜕𝑇𝐶 𝜕𝑄 Given the cost function AC and MC cab obtained as follows 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 16 𝑨𝑪 = 𝑻𝑪 𝑸 = 𝒂 + 𝒃𝑸 𝑸 = 𝒂 𝑸 + 𝒃 𝑴𝑪 = 𝝏𝑻𝑪 𝝏𝑸 = 𝑏 𝑻𝑪 = 𝒂 + 𝒃𝑸
- 17. LINEAR COST FUNCTIONS • Assuming the cost function TC= a+bQ 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 17 Behavior of AC and MC MC is constant in this case AC continuous to decline with the increase in output
- 18. QUADRATIC COST FUNCTION • A quadratic cost function is of the form Where as a and b are constant • Given the cost function AC and MC can be obtained as 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 18 𝑻𝑪 = 𝒂 + 𝒃𝑸 + 𝑸 𝟐 𝑨𝑪 = 𝑻𝑪 𝑸 = 𝒂+𝒃𝑸+𝑸 𝟐 𝑸 = 𝒂 𝑸 + 𝒃 + 𝑸 𝑀𝐶 = 𝜕𝑇𝐶 𝜕𝑄 = 𝑏 + 2𝑄
- 19. QUADRATIC COST FUNCTION Given the cost function TC = a + bQ + Q2 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 19 TFC remains constant TVC increasing at an increasing rate
- 20. QUADRATIC COST FUNCTION • AC MC and AVC Curves 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 20
- 21. CUBIC COST FUNCTION • The cubic cost function is of the form 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 21 𝑻𝑪 = 𝒂 + 𝒃𝑸 − 𝒄𝑸 𝟐 + 𝑸 𝟑 AC = 𝐓𝐂 𝐐 = 𝒂+𝒃𝑸+𝒄𝑸 𝟐+𝑸 𝟑 𝑸 𝑴𝑪 = 𝝏𝑻𝑪 𝝏𝑸 = 𝒃 − 𝟐𝒄𝑸 + 𝟑𝑸 𝟐
- 22. CUBIC COST FUNCTION 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 22
- 23. TFC, TVC And TC 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 23
- 24. 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 24
- 25. AC, AFC, AVC and MC Curves 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 25
- 26. • ATC keeps going down with output. • AVC goes down and then beyond a point starts rising. • AFC keeps going down, and becomes very small as output increases. • MC goes down but beyond a point starts to rise. 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 26
- 27. SOME IMPORTANT RELATIONSHIPS • Over a range of output both AVC and AFC fall, AC also falls because AC =AFC + AVC • When AFC falls but AVC increases, change in AC depends on the change in AFC and AVC • If decrease in AFC > increase in AVC, then AC falls • If decrease in AFC = increase in AVC, then AC remains constant • If decrease in AFC < increase in AVC, then AC increases • When MC falls, AC follows over a certain level of output. When MC falling, the rate of fall in MC in greater than that of AC i.e. AC decreases at a rate lower than MC 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 27
- 28. LONG RUN COST CURVES Long run Total Cost Curve : • Long run Total Cost (LTC) refers to the minimum cost at which given level of output can be produced. • LTC represents the least cost of different quantities of output. LTC is always less than or equal to short run total cost, but it is never more than short run cost. 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 28
- 29. LONG RUN COST CURVES Long run Average Cost Curve • Long run Average Cost (LAC) is equal to long run total costs divided by the level of output. • The derivation of long run average costs is done from the short run average cost curves. 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 29
- 30. LONG RUN COST CURVES Long run Marginal Cost Curve Long run Marginal Cost (LMC) is defined as added cost of producing an additional unit of a commodity when all inputs are variable. This cost is derived from short run marginal cost. On the graph, the LMC is derived from the points of tangency between LAC and SAC. 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 30
- 31. ASSIGNMENT Topic : Economics of Scale and Diseconomies of Scale 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 31
- 32. REFERENCES • D N Dwiledhi, Essentials of business economics, Vikas publishing house Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2009 • D.M. Mithani,Managerial Economics, 5/e, Himalaya Publishing House,Mumbai,2011 • Yogesh, Maheswari, Management Economics,PHI Learnings, New PHIlearning,NewDelhi,2012 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 32
- 33. THANK YOU MUHAMMED NOWFAL.S Assistant Professor, Department of Management studies KMM College of Arts and Science, Thrikkara, Kochi Email ID :- muhammednowfal@kcmtcochin.com 10/13/2017 Theory of Cost 33
