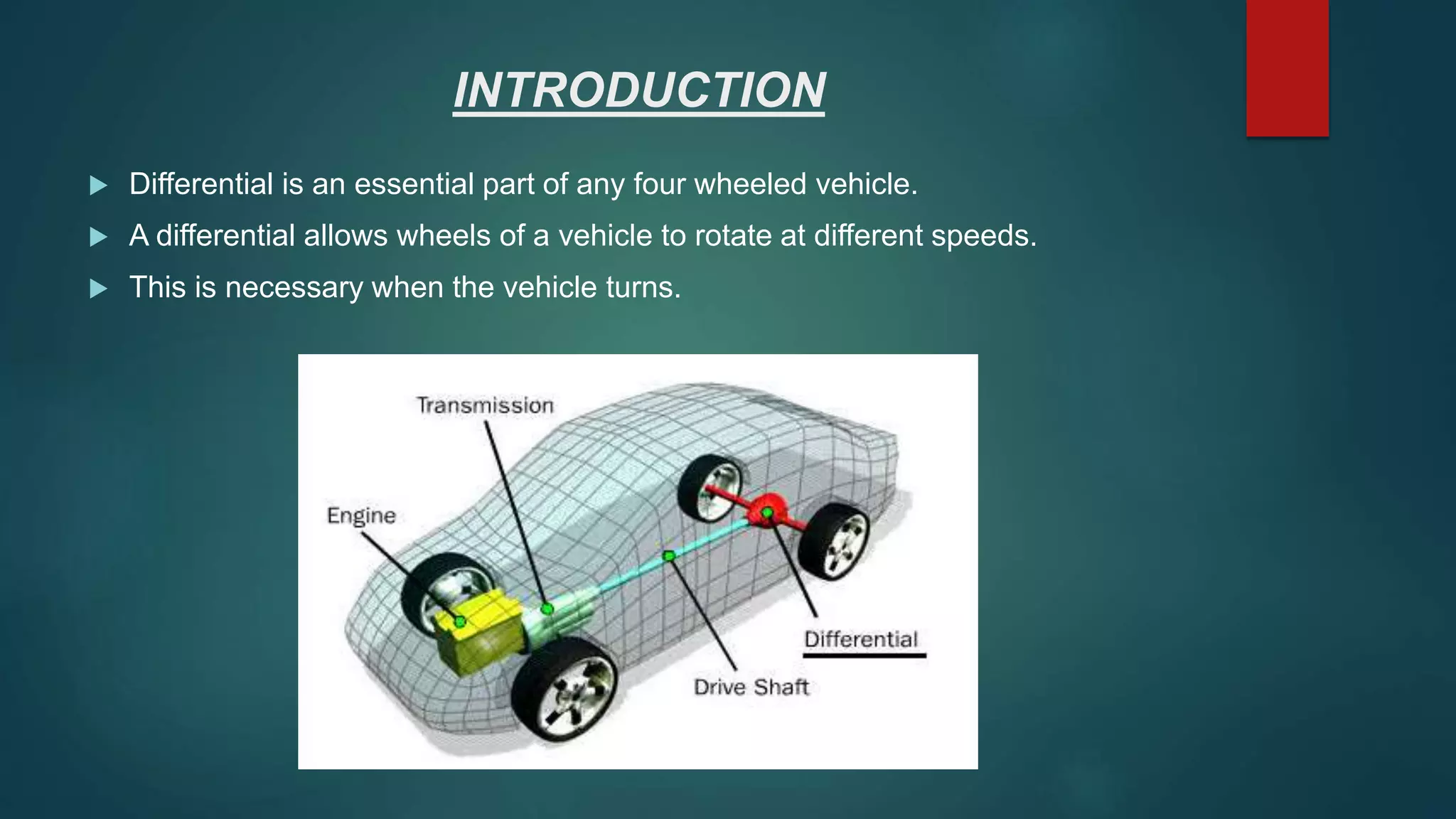
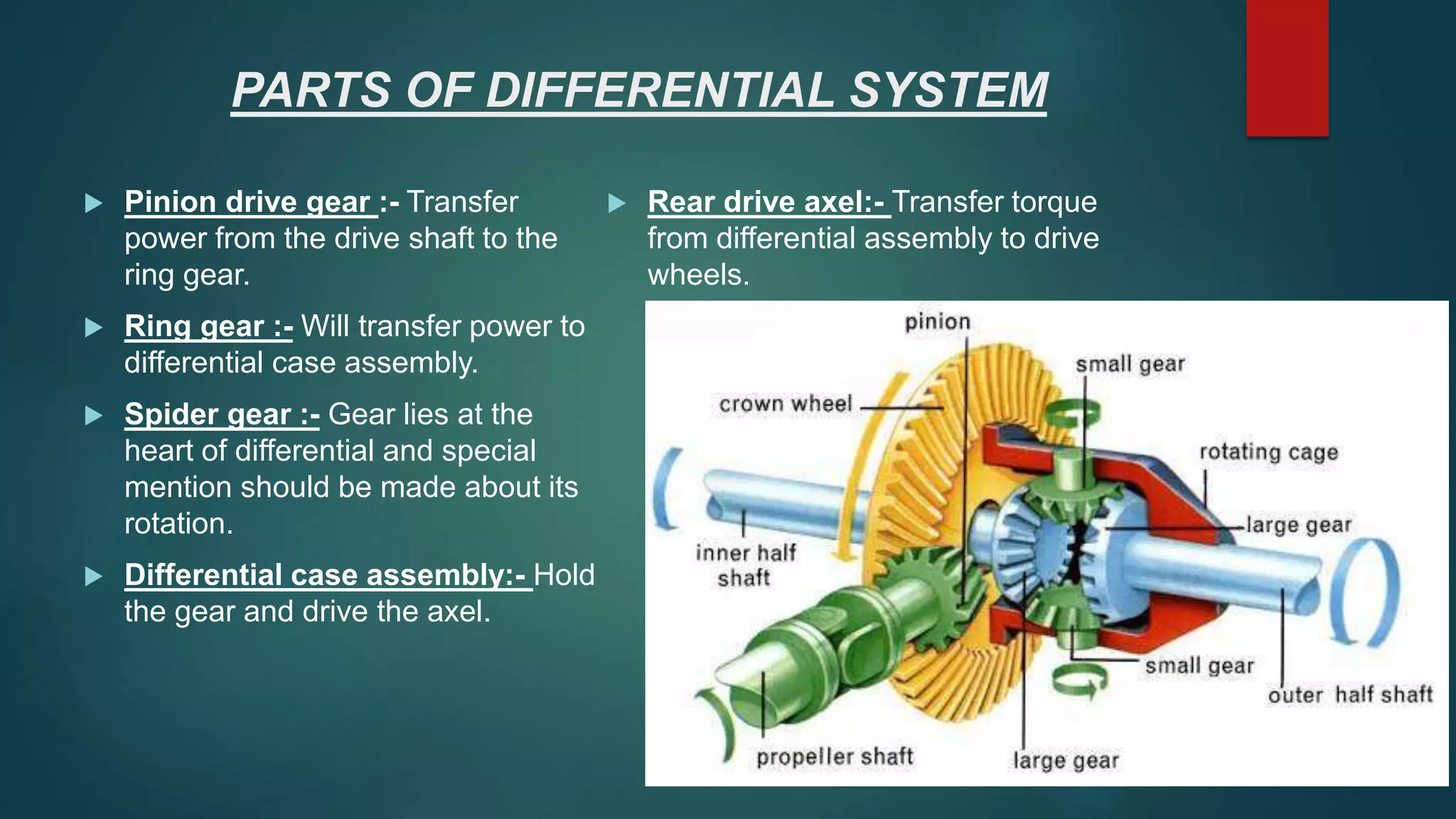
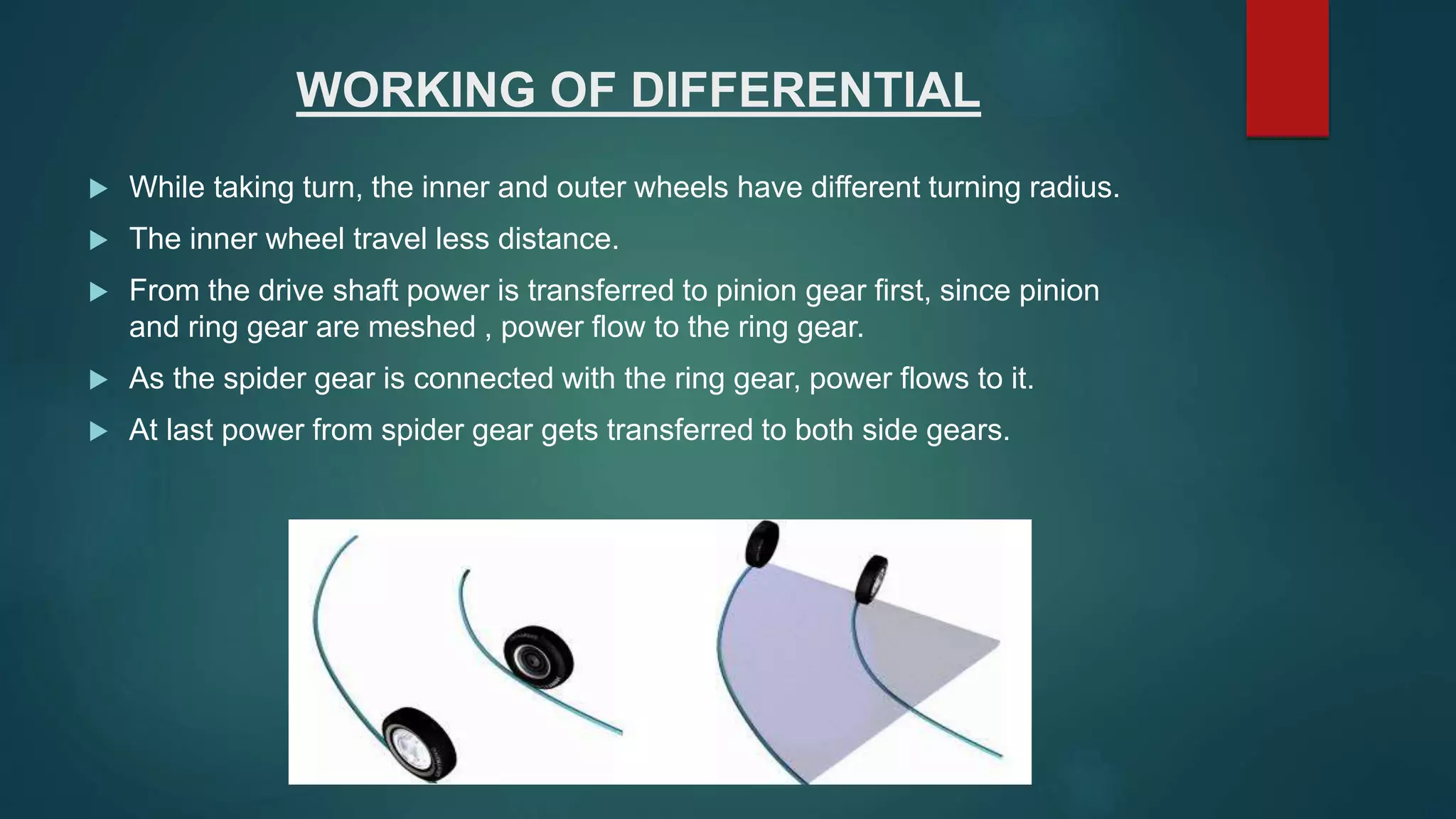
This document summarizes a student project to design and analyze a differential gear box. It includes sections that describe the objective of analyzing the working of a vehicle differential and designing the system. It explains the key parts of a differential system including the pinion gear, ring gear, spider gear, and differential case. It also describes the working of a differential for straight driving and turning, and discusses issues like one wheel slipping. Design parameters and the forces that allow the spider gear to rotate are analyzed. Finally, it briefly mentions the types of differentials.