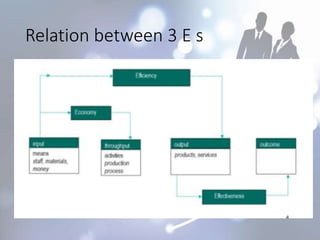
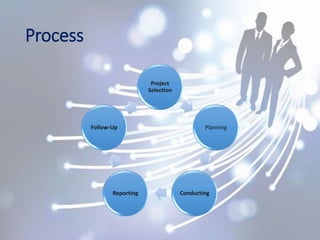
A performance audit examines the effectiveness, economy, and efficiency of a government program or agency. It assesses if resources are being managed properly and accountability requirements are met. A performance audit reviews employee performance against goals, measures efficiency, effectiveness, and economy, and identifies what is and is not working. The process involves project selection, planning, conducting the audit, reporting findings, and follow up to ensure recommendations are implemented.