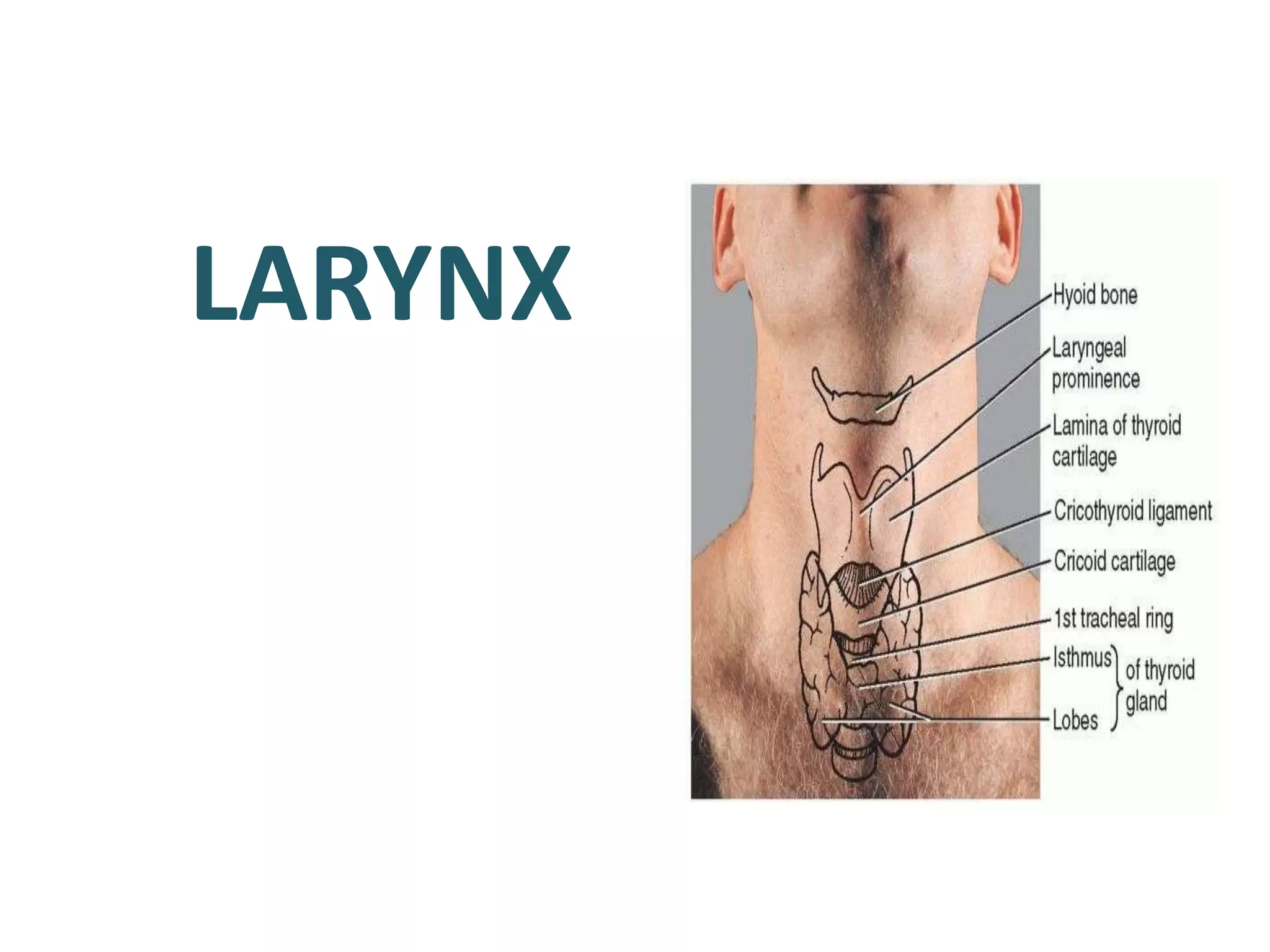
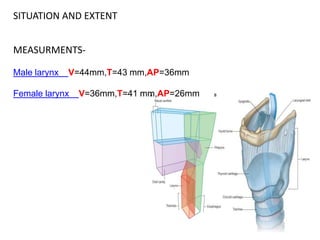
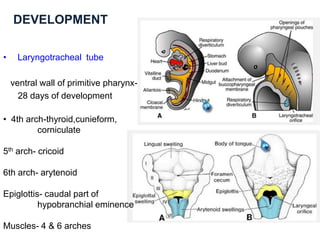
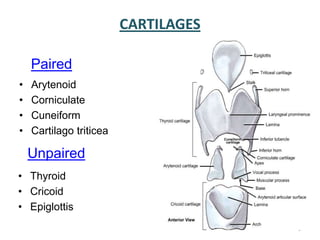
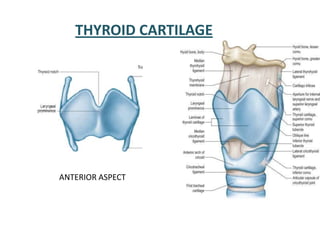
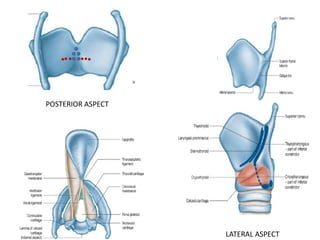
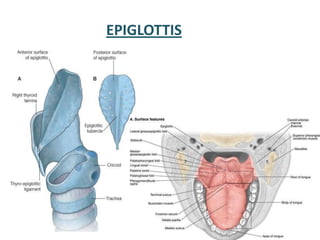
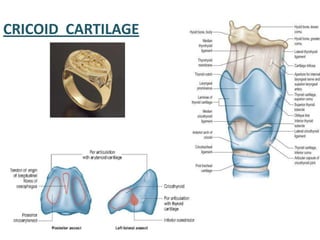
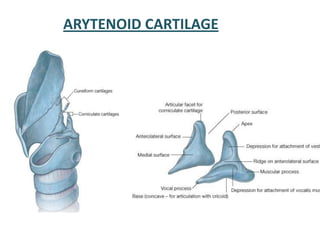
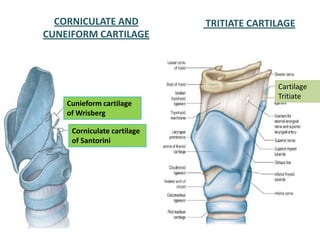
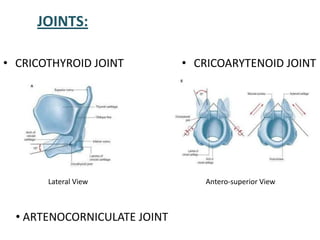
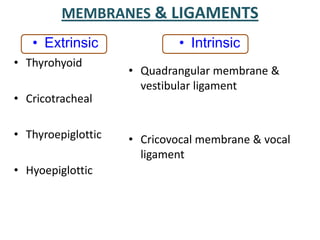
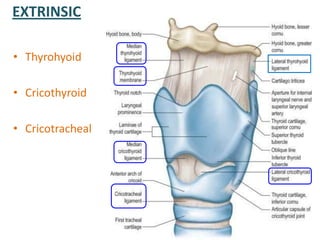
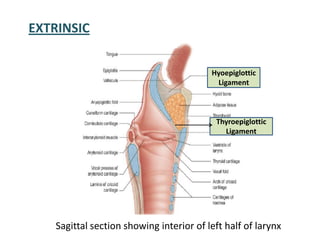
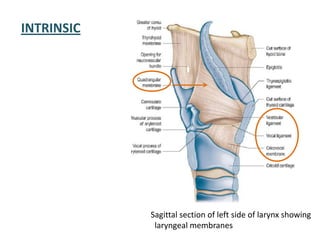
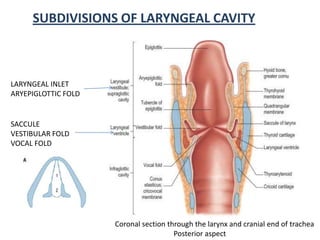
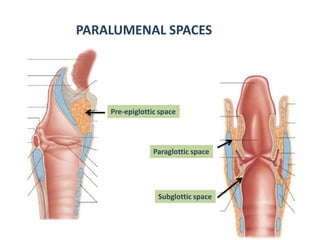
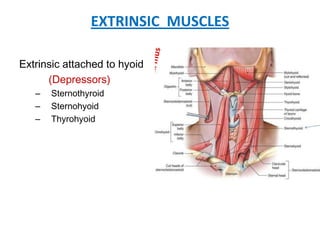
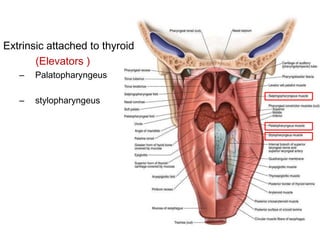
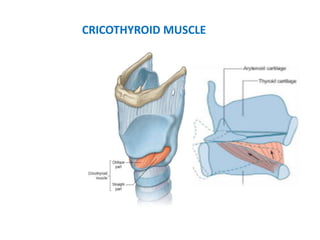
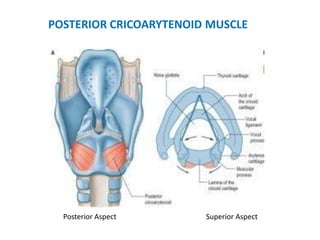
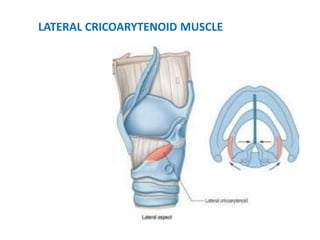
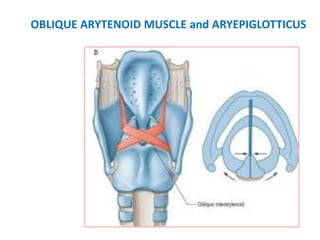
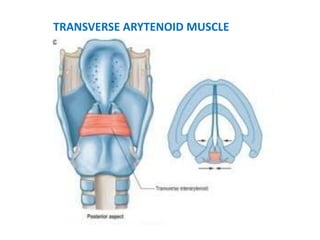
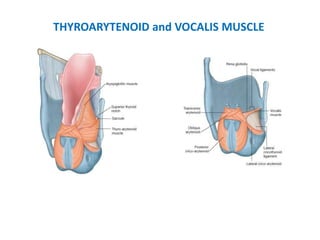
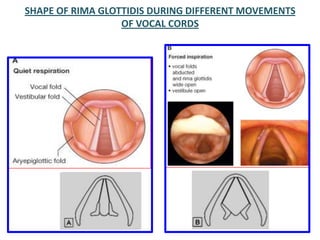
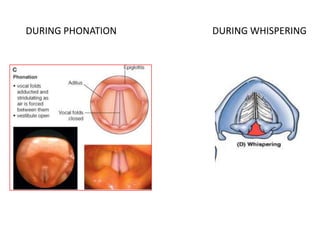
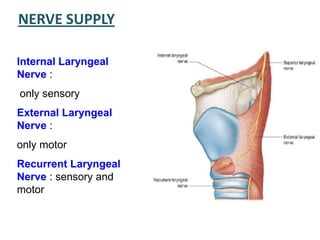
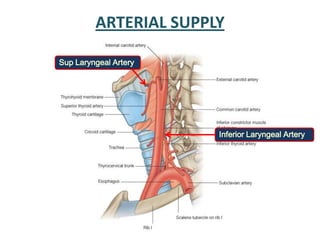
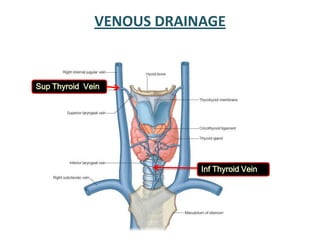
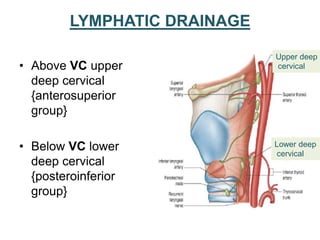
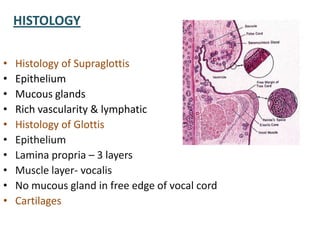
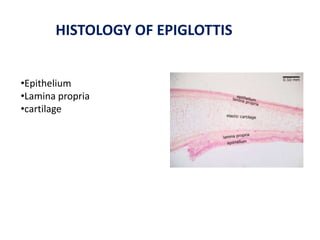
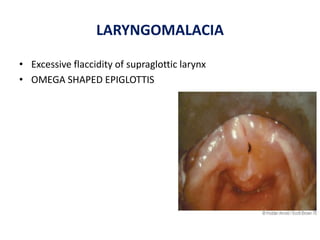
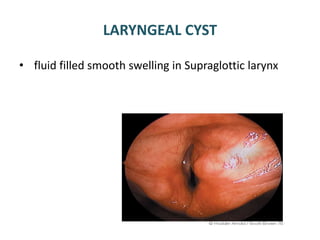
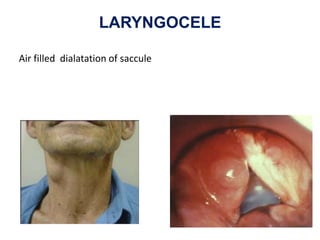
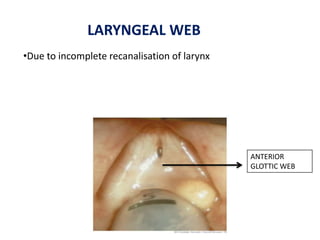
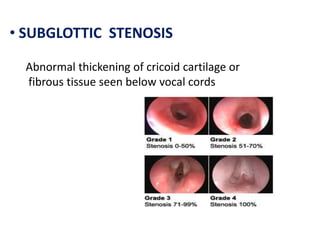
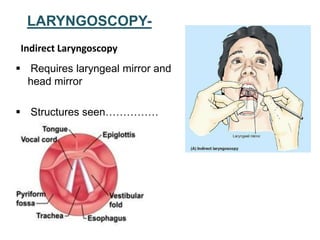
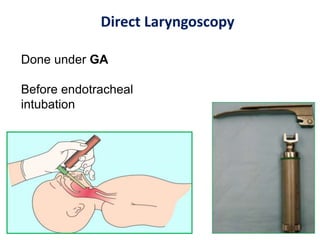
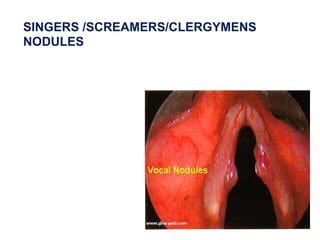
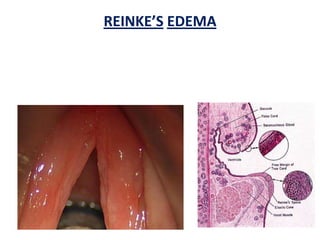
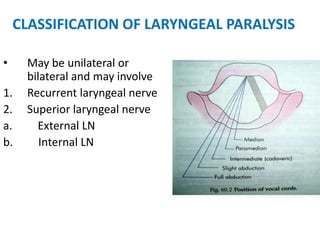
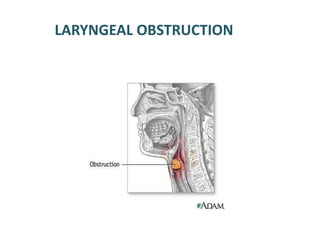
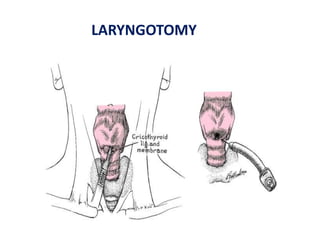
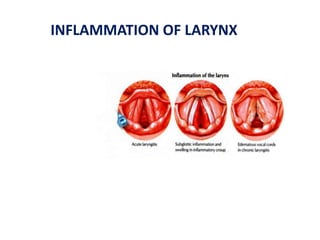
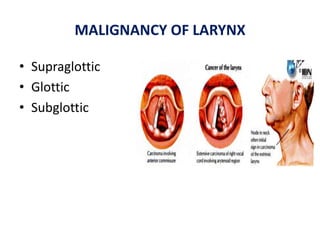
The document describes the anatomy of the larynx. It covers the development, skeletal framework including cartilages, subdivisions, muscles, histology, blood supply, nerve supply, lymphatic drainage and applied anatomy of the larynx. Key points include the cartilages that make up the skeletal framework, the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles that control movement and phonation, the nerve and blood supply, and common congenital anomalies and pathologies of the larynx.