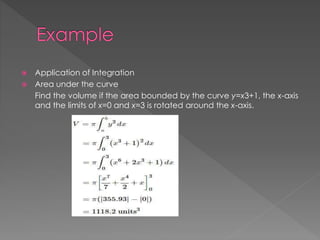
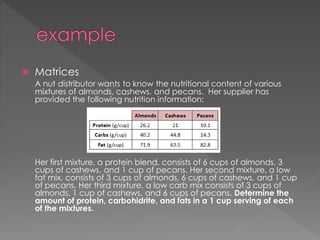
This document discusses different teaching approaches including cooperative learning, contextual learning, mastery learning, self-access learning, future studies, and constructivism. It provides definitions and examples of how each approach is implemented in the classroom with a focus on student and teacher roles. The approaches are categorized based on the level of teacher direction and student participation, ranging from direct instruction to exploratory learning.