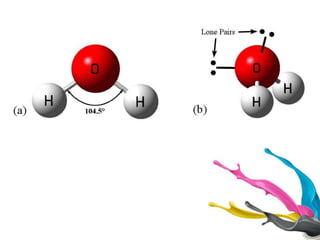
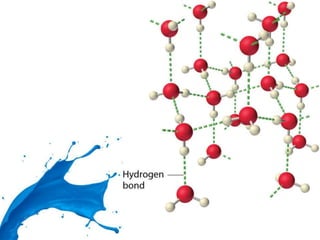
Dihydrogen forms three categories of binary compounds called hydrides with other elements: ionic/saline hydrides, covalent/molecular hydrides, and metallic/non-stoichiometric hydrides. Ionic hydrides are crystalline, non-volatile, and non-conducting solids but conduct electricity when molten. Dihydrogen forms molecular compounds with p-block elements like CH4, NH3, H2O, and HF that are classified as electron-deficient, electron-precise, or electron-rich based on their Lewis structures. Transition metals form non-stoichiometric metallic hydrides that conduct heat and electricity.